Process for lyophilized pharmaceutical formulation of a therapeutic protein
a technology of lyophilized pharmaceutical formulation and therapeutic protein, which is applied in the field of biopharmaceuticals, can solve the problems of special problems of products, chemical instability, physical instability,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working examples
[0105]All publications, patents, and patent applications discussed and cited herein are hereby incorporated by reference m their entireties. It is understood that the disclosed invention is not limited to the particular methodology, protocols and materials described as these can vary. It is also understood that the terminology used herein is for the purposes of describing particular embodiments only and is not intended to limit the scope of the appended claims.
[0106]Those skilled in the art will recognize, or be able to ascertain using no more than routine experimentation, many equivalents to the specific embodiments of the invention described herein. Such equivalents are intended to be encompassed by the claims that follow.
example 1
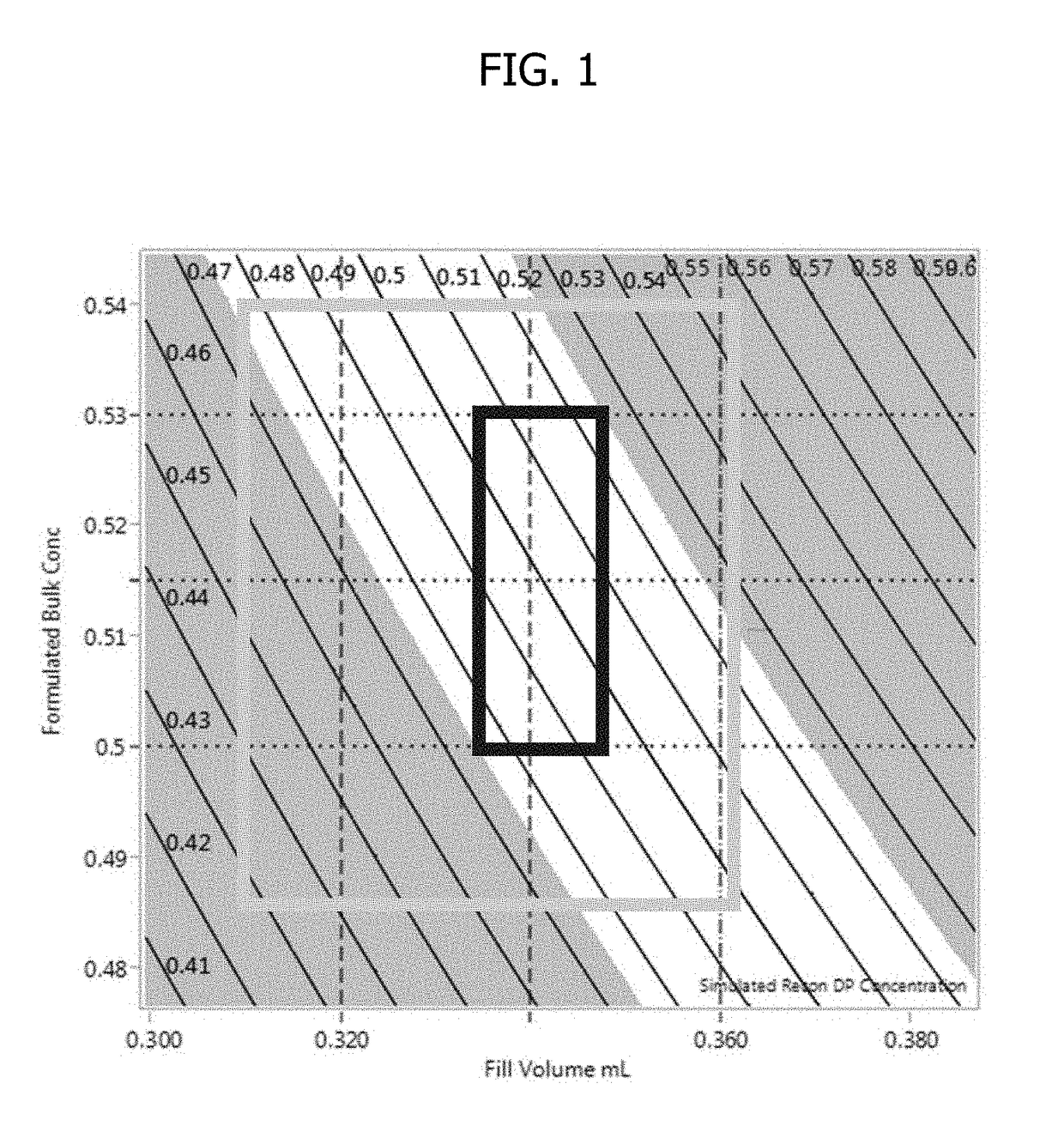
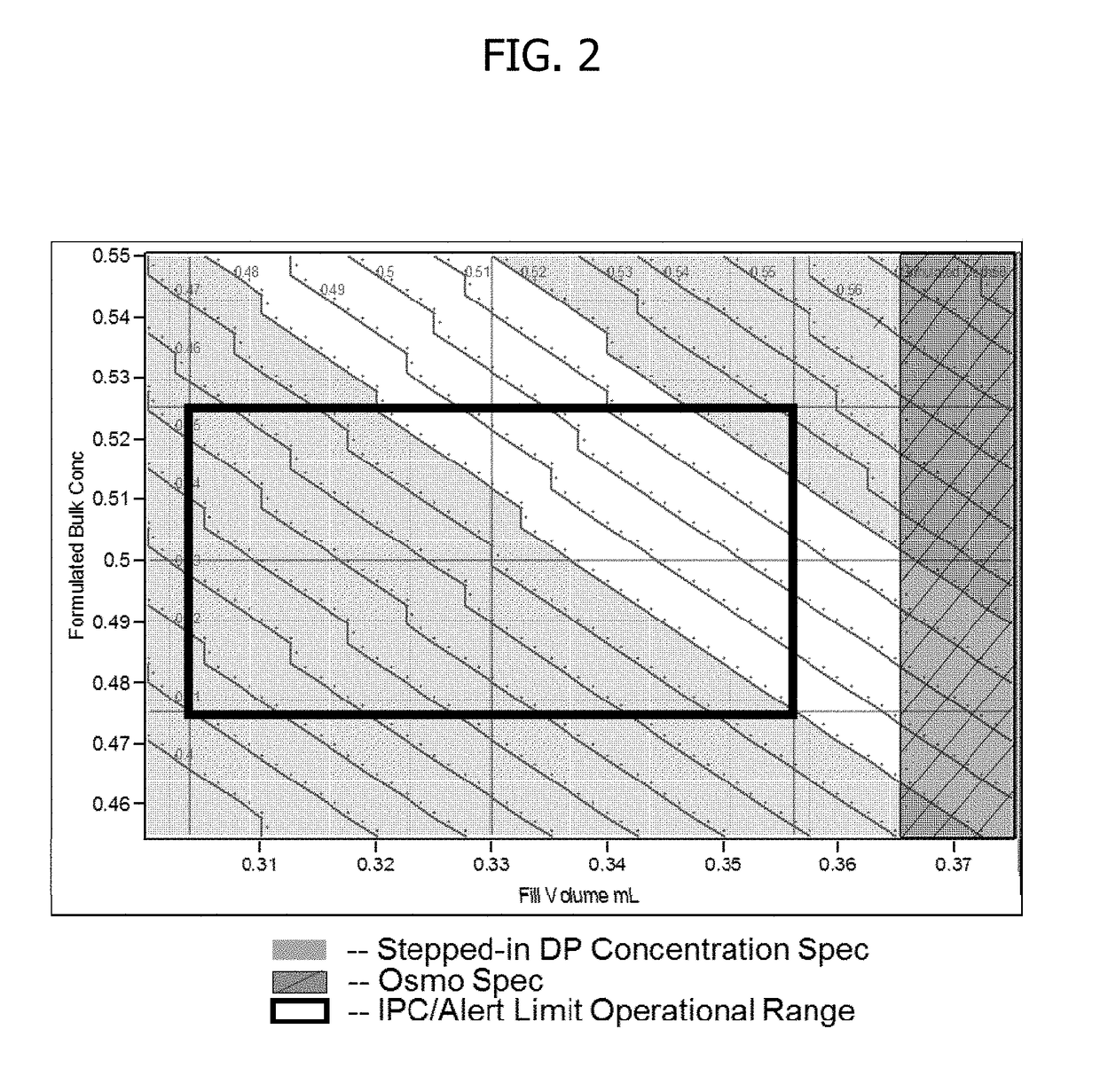
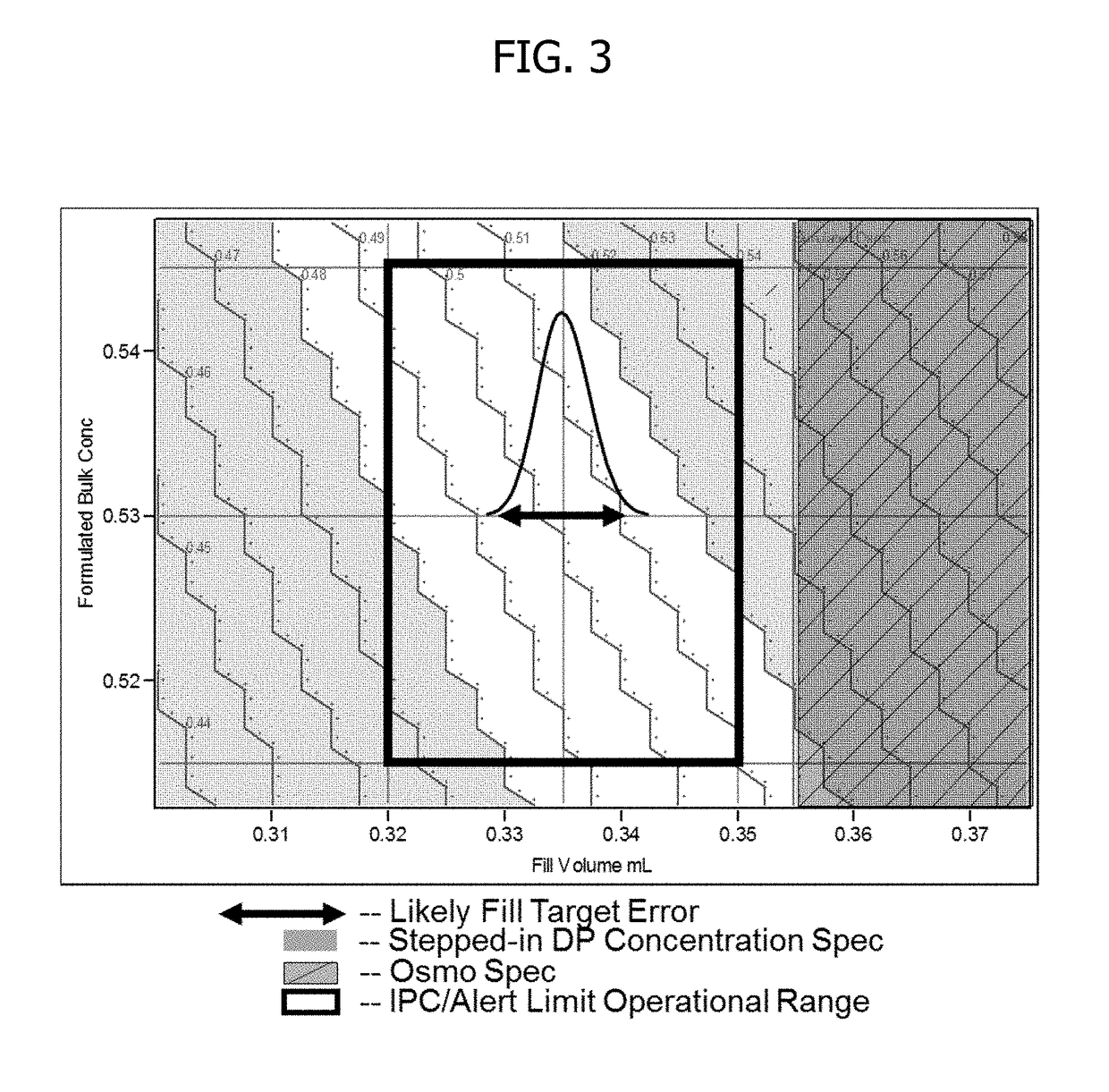
[0107]This experiment demonstrates that by adjusting fill weight targets, protein concentration can be precisely targeted for the respective reconstituted drug product.
Materials
[0108]Buffer containing: Mannitol, Sucrose, L-Histidine, Polysorbate 20 at pH 5[0109]Container Vial, 3 cc, Blowback, Type I Glass, Non-treated, 13 mm Finish with Stopper, 13 mm, 4432 / 50 V-50,[0110]romiplostim Filtered Purified Bulk
Method
[0111]1. Dilute drug to target product formulation (0.5 mg / mL) utilizing required amount of the dilution buffer.[0112]2. Filter formulated solution using a 0.22 μm Polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) filter.[0113]3. Ensure vials and stopper: 3 cc vials have been washed and depyrogenated.[0114]4. Fill sufficient quantity of vials to respective fill weight targets: 0.307, 0.322, 0.342, 0.357, 0.373 g.[0115]5. Partially stopper vials and place in lyophilizer.[0116]6. Run required lyophilization cycle with adequate freezing, vacuum, with primary and secondary drying, followed by stop...
example 2
[0128]The protein blinatumomab has 55 μg / mL, formulated to 200 mM L-lysine-HCl, 25 mM citric acid, 15% (w / v) trehalose dihydrate, 0.1% (w / v) polysorbate 80, pH 7.0. The formulated protein allowable range is measured at the filtered bulk stage. Bulk concentrations ranging from 48.0 μg / mL to 65.0 μg / mL are used. Target fill weights are calculated based upon the measured protein concentration to target a reconstituted drug product of 12.5 mcg / mL when reconstituted with 3 mL of water.
Creconstitution*Vreconstitution=(CFormulated−Closs)*Vfill
Where
Creconstitution*Vreconstitution=Target protein contentreconstitution
[0129]Then the Target protein content can then be multiplied by the product density and divided by the measured drug concentration (adjusted for loss due to binding if needed) to determine the Target fill weight.
[0130]The target fill weight is calculated according to the following formula, with a corresponding fill weight range of 0.634 to 0.858 gm.
Fillweight(g)=targetdose(38.5...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com