Supervision device for ambulatory infusion
a technology of ambulatory infusion and supervising device, which is applied in the direction of other medical devices, process and machine control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient thermal coupling, difficult to achieve good thermal coupling e.g. with tubing walls, and at least partly insufficient thermal coupling, so as to enhance the thermal coupling between thermoelectric elements and increase the thermal insulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
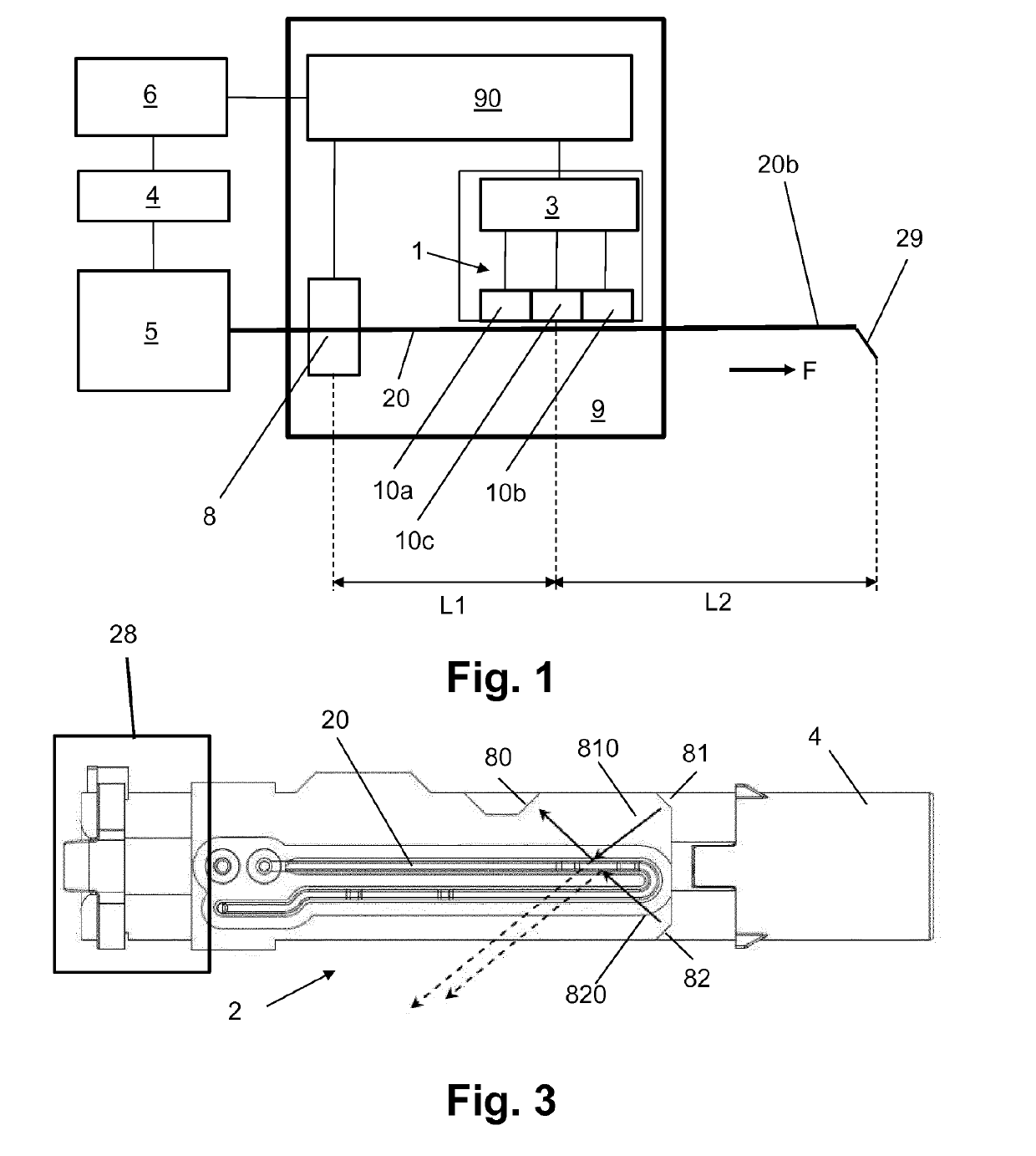
[0111]In the following, reference is first made to FIG. 1, showing an exemplary embodiment of a supervision device 9 in accordance with the present disclosure in a schematic view. The supervision device 9 includes an optical gas detector 8 and a thermal flow detector 1.
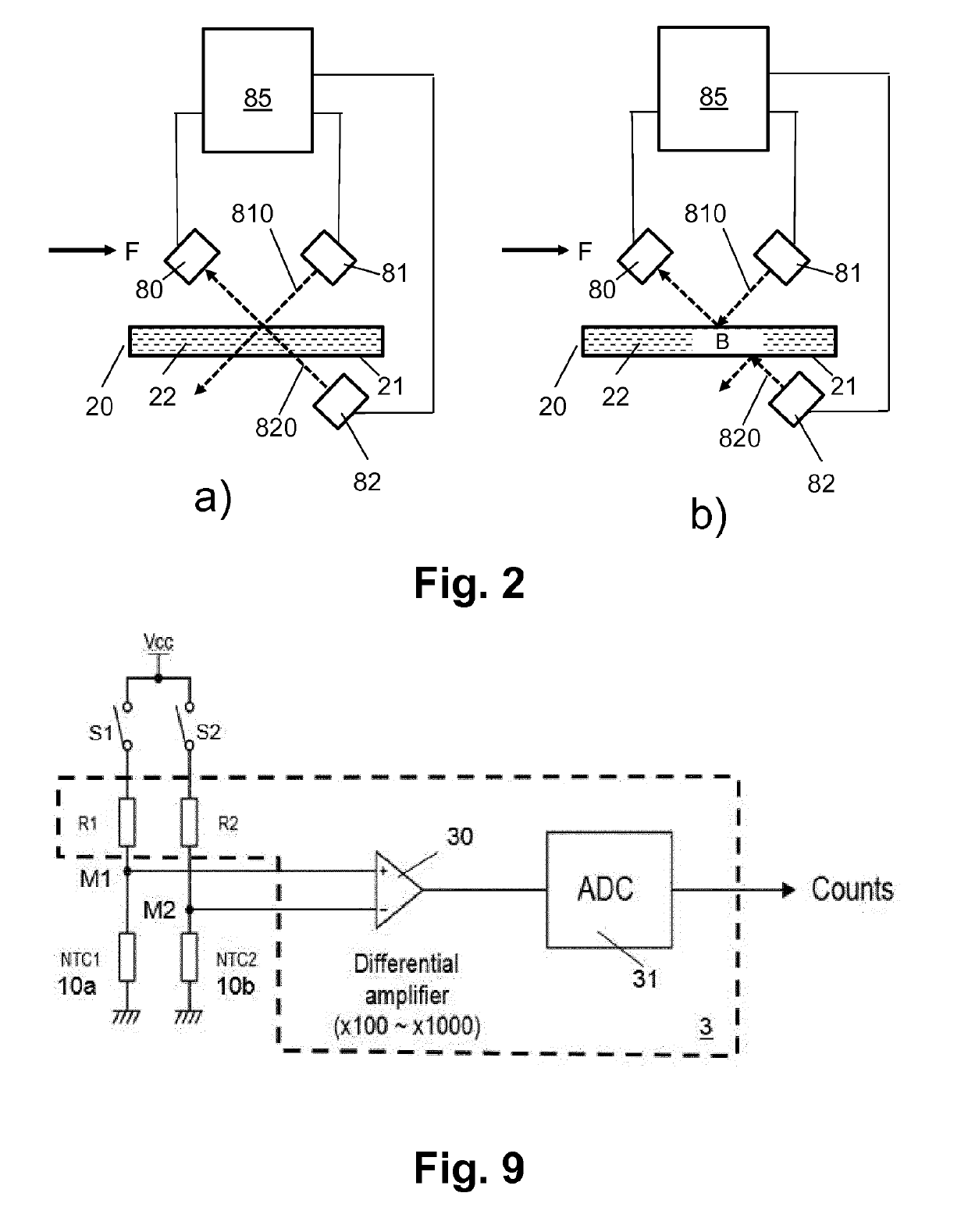
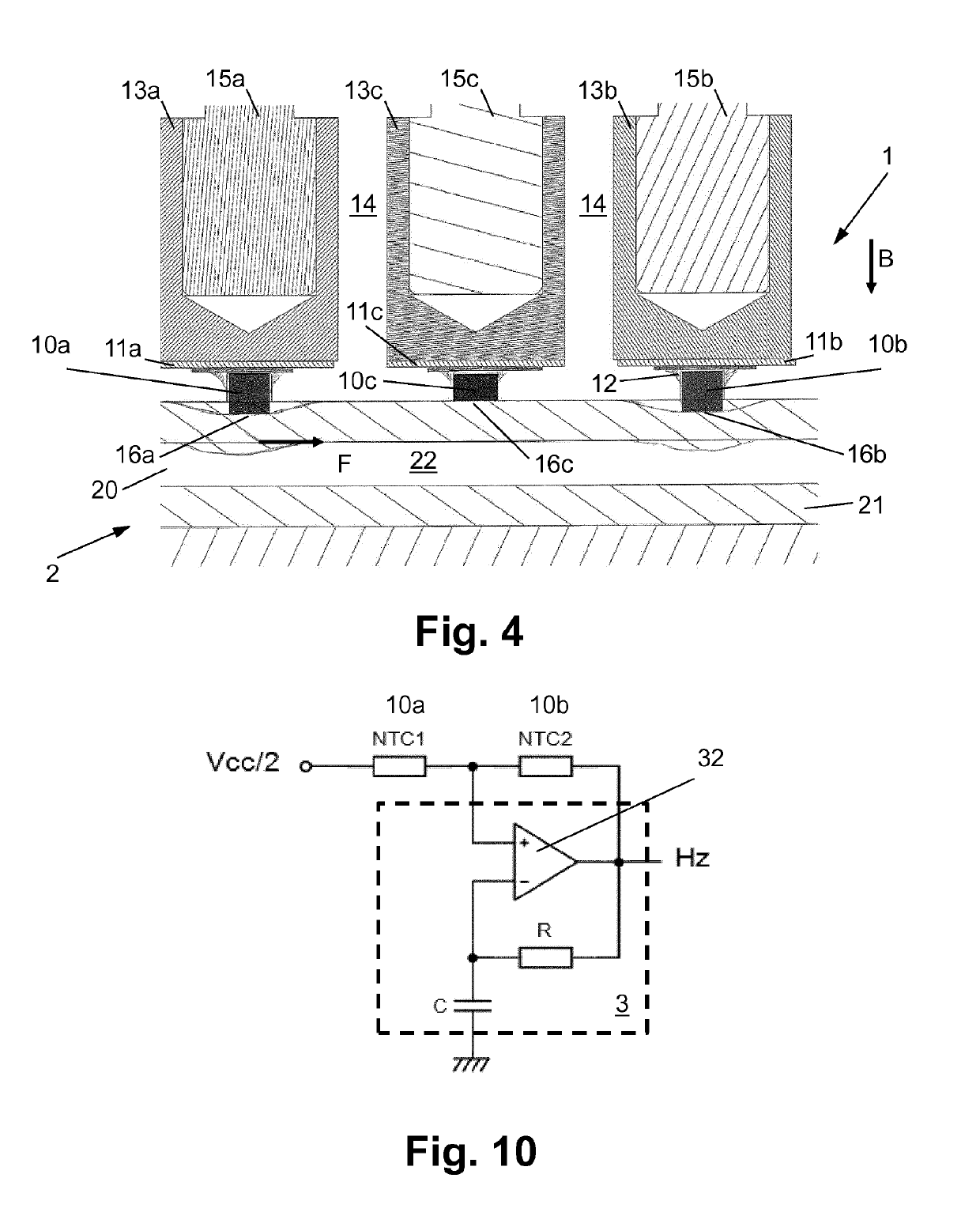
[0112]The thermal flow detector 1 exemplarily includes an upstream thermoelectric element 10a as upstream temperature sensor, a downstream thermoelectric element 10b as downstream temperature sensor, and a middle thermoelectric element 10c that is arranged between the upstream thermoelectric element 10a and the downstream thermoelectric element 10b and serves as heating element. The flow detector 1 further includes a flow detector evaluation unit 3 that generates the flow detector signal from the electric raw signals that are provided by the thermoelectric elements, in particular the upstream thermoelectric element 10a and the downstream thermoelectric element 10b.
[0113]The optical gas detector 8 exemplarily includes...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com