Modification of temperature dependence of pitch viscosity for carbon article manufacture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
ng Characteristic Temperature and Characteristic Viscosity
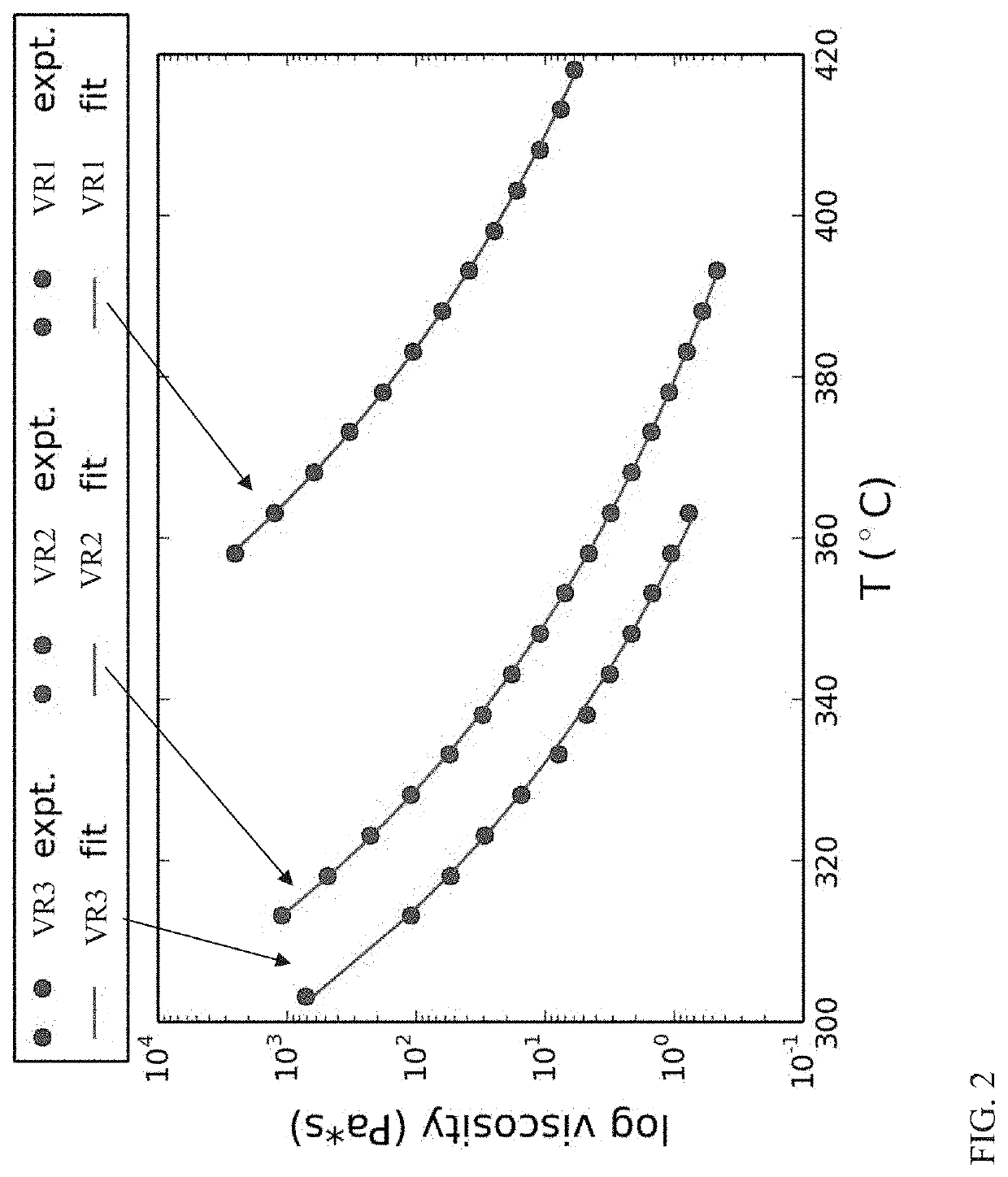
[0059]Characteristic temperature values corresponding to T0 values and characteristic viscosities corresponding to ηinf values were determined for three representative vacuum resid fractions. The dots in FIG. 2 correspond to measured values for viscosity at various temperatures. It is noted that the vertical axis in FIG. 2 corresponds to the log of the viscosity. The lines in FIG. 2 correspond to fits of the measured values to Equation (2), the Arrhenius-style equation for the viscosity-temperature relationship as described above. As explained in association with Equation (2), D was set to 7.5 for purposes of fitting the curve to the data. As shown in FIG. 2, the form of Equation (2) provides a relatively good fit for the shape of the data for each of the vacuum resid fractions. Table 1 shows the resulting T0 and ηinf values determined based on the curve fitting.
TABLE 1Characteristic Temperature and Viscosity ParametersSample...
example 3
of Extract and Raffinate to Form Modified Mesophase Pitch
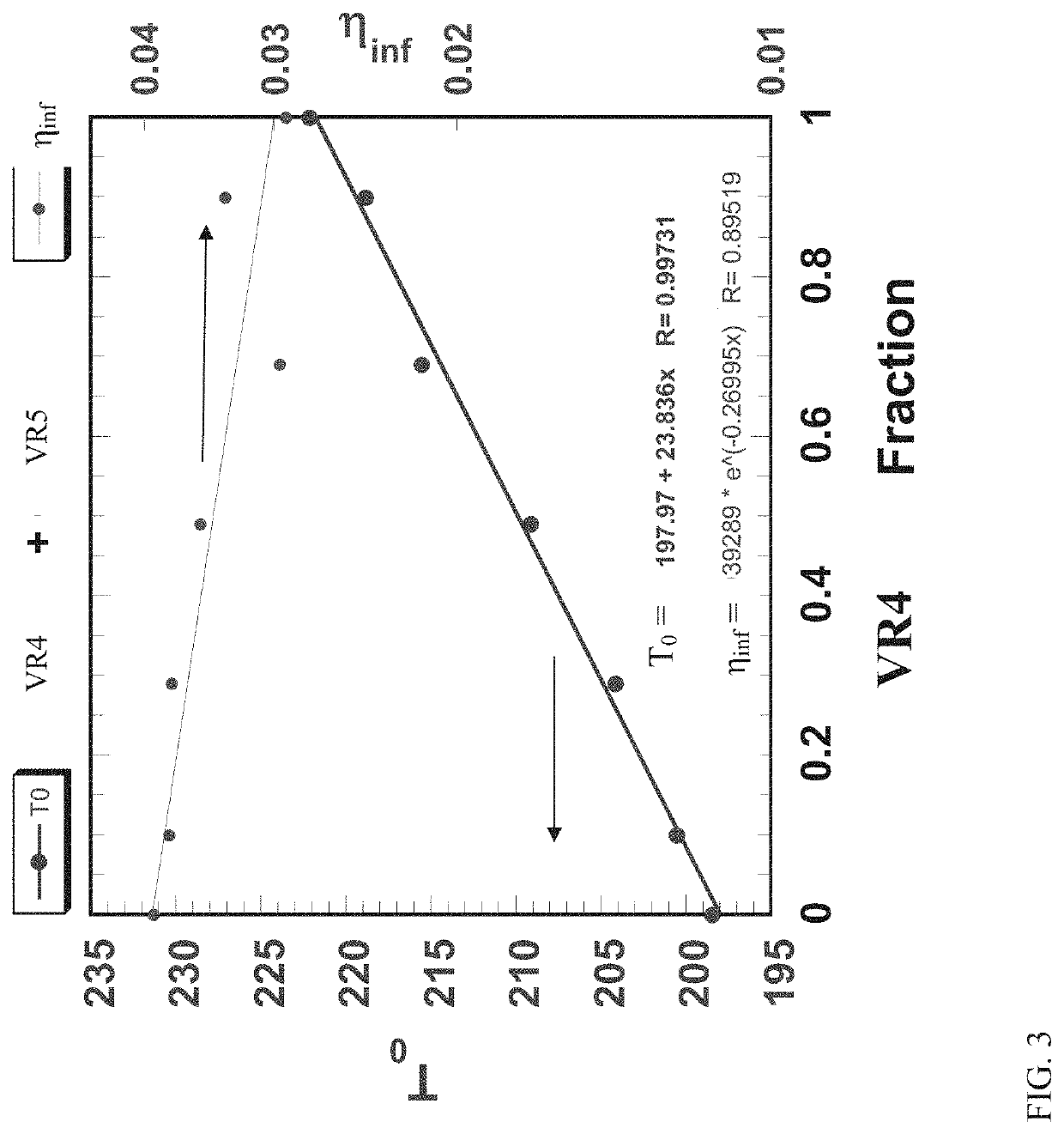
[0063]The following example is a prophetic example. In this example it is assumed that the initial feed has T0=300 K and ηinf=8×10−5 Pa*s. The initial feed is then separated into two streams with different T0 and ηinf. Stream 1 has T0=230 K and ηinf=8×10−5 Pa*s and stream 2 having T0=315 K and ηinf=8×10−5 Pa*s. Stream 1 corresponds to 18 vol % of the initial feed, while Stream 2 corresponds to 82 vol % of the initial feed. The streams were combined in the volumetric fractions ϕ1=0.30 and ϕ2=0.70, producing a modified product with T0=289.5 K and ηinf=8×10−5 Pa*s.
[0064]FIG. 4 show a comparison of the temperature dependence of the viscosity for the initial feed and the modified product. In FIG. 4, the viscosity is plotted on a log scale. As shown in FIG. 4, the modified product has a reduced temperature dependence for all temperatures, including those temperature near 550 K to 595 K that correspond to a desirable temperature rang...
embodiment 1
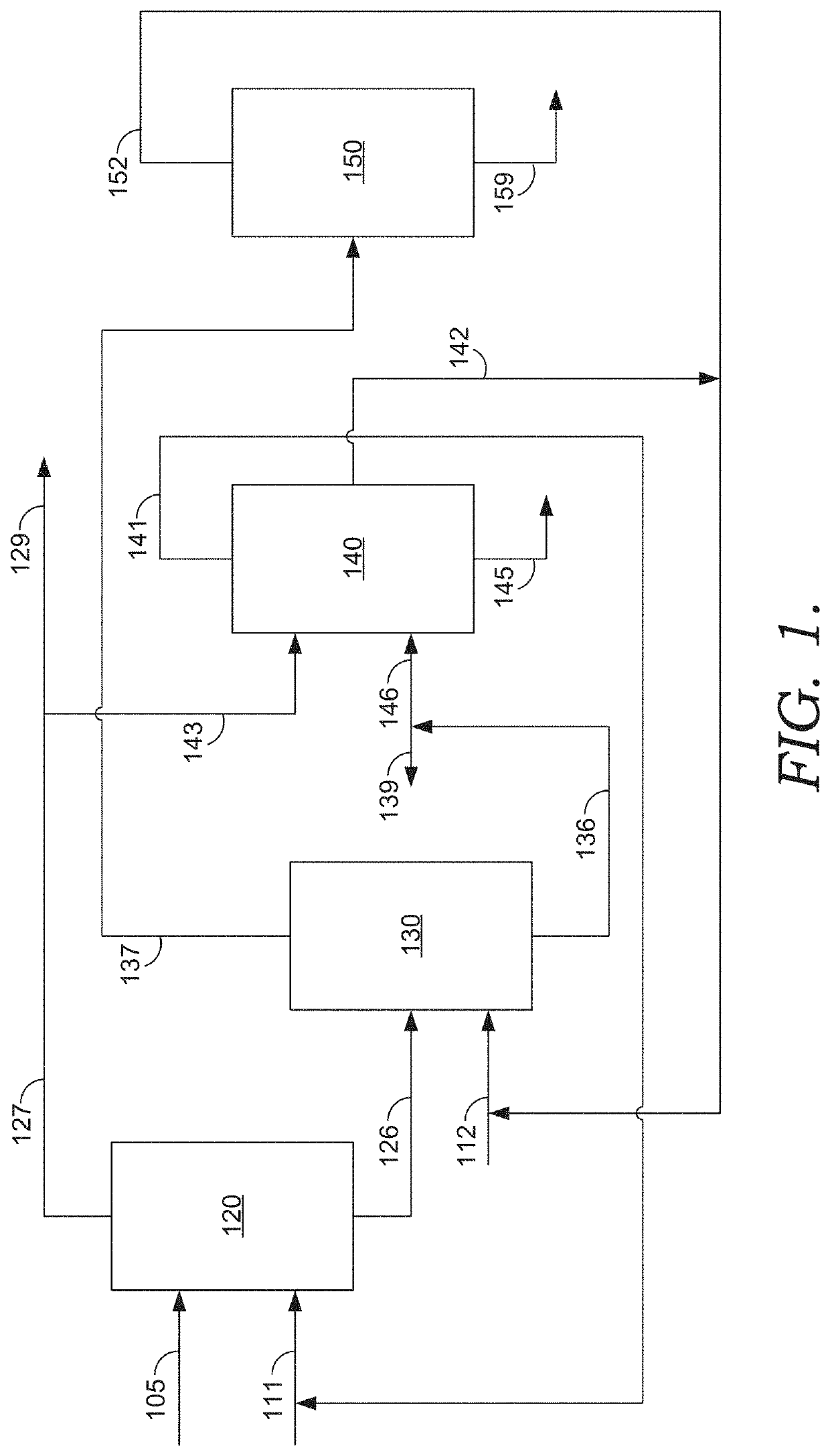
[0067]A method for forming a modified pitch, comprising: performing solvent extraction on a pitch comprising a T0 value to form an extract comprising a first fraction of the pitch and a raffinate comprising a second fraction of the pitch; and blending at least a portion of the first fraction with at least a portion of the second fraction to form a modified pitch having a modified T0 value less than the T0 value of the pitch.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com