Narrow shoe journal microfinishing apparatus and method
a microfinishing and shoe journal technology, applied in metal-working apparatus, superfinishing machines, belt grinding machines, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the load carrying capacity and performance of bearings, affecting the service life of the journal, and requiring long service life for owners and operators of such equipment, so as to achieve flexible journal diameter and sufficient compliance of the tooling backing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
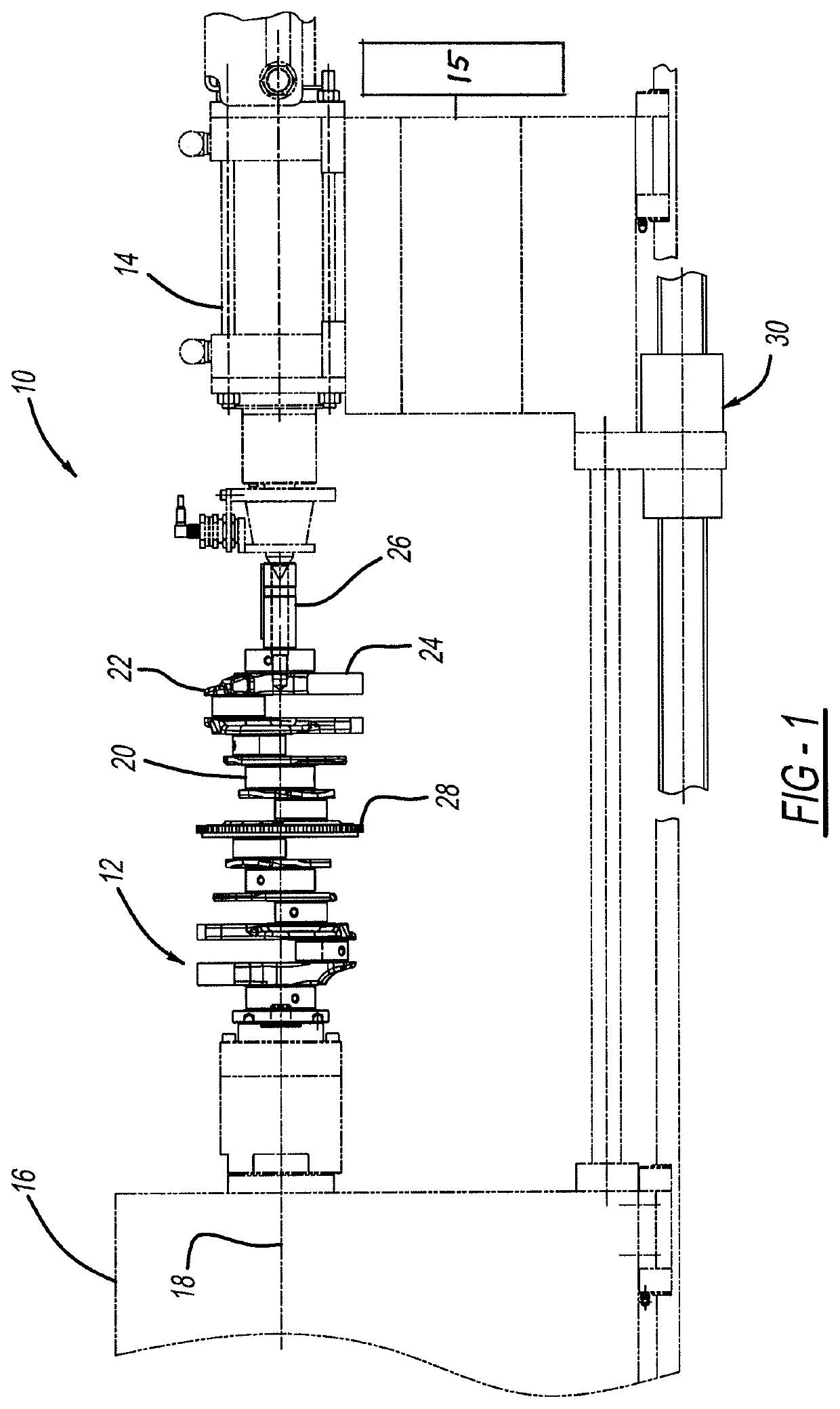
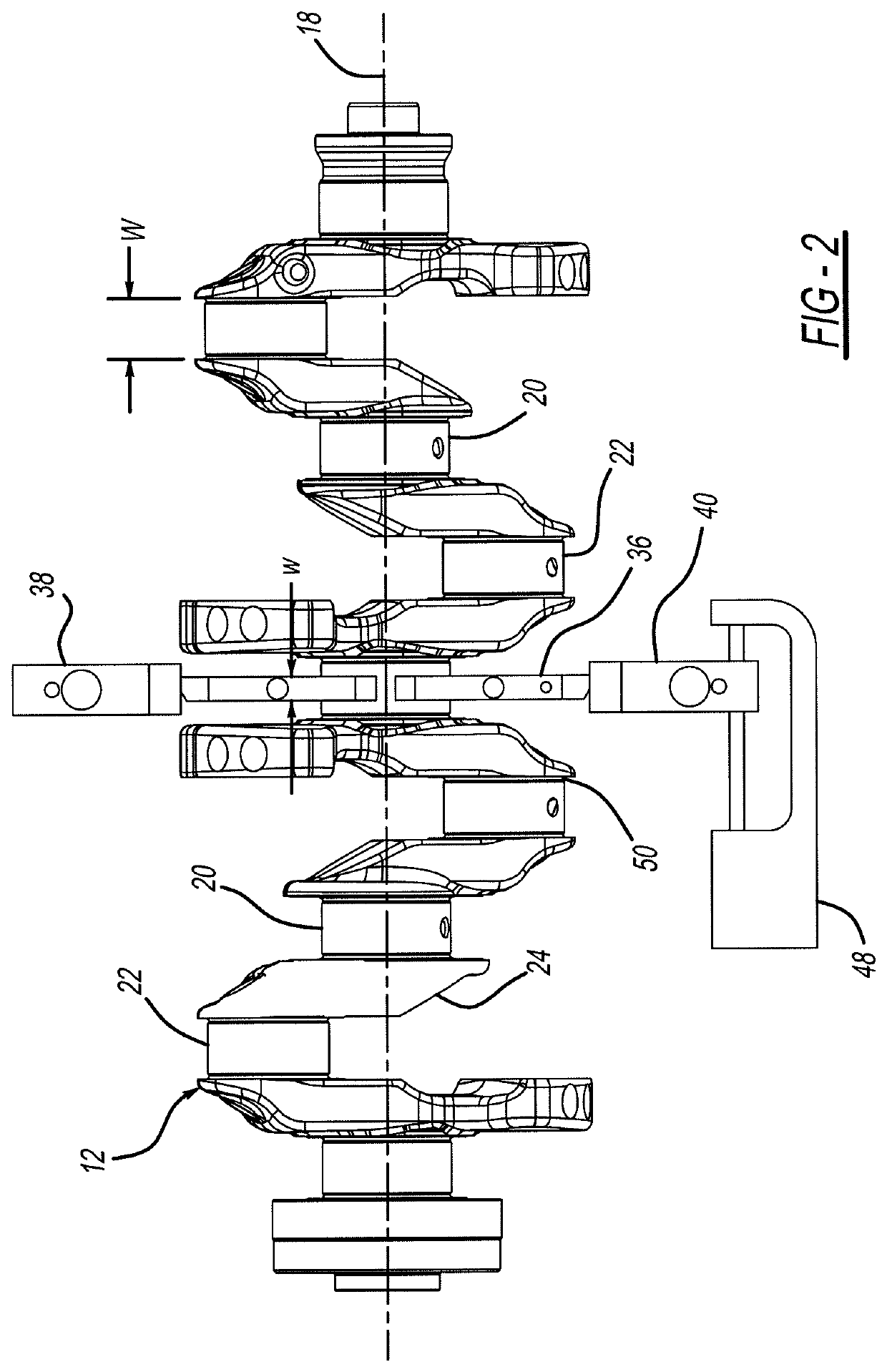
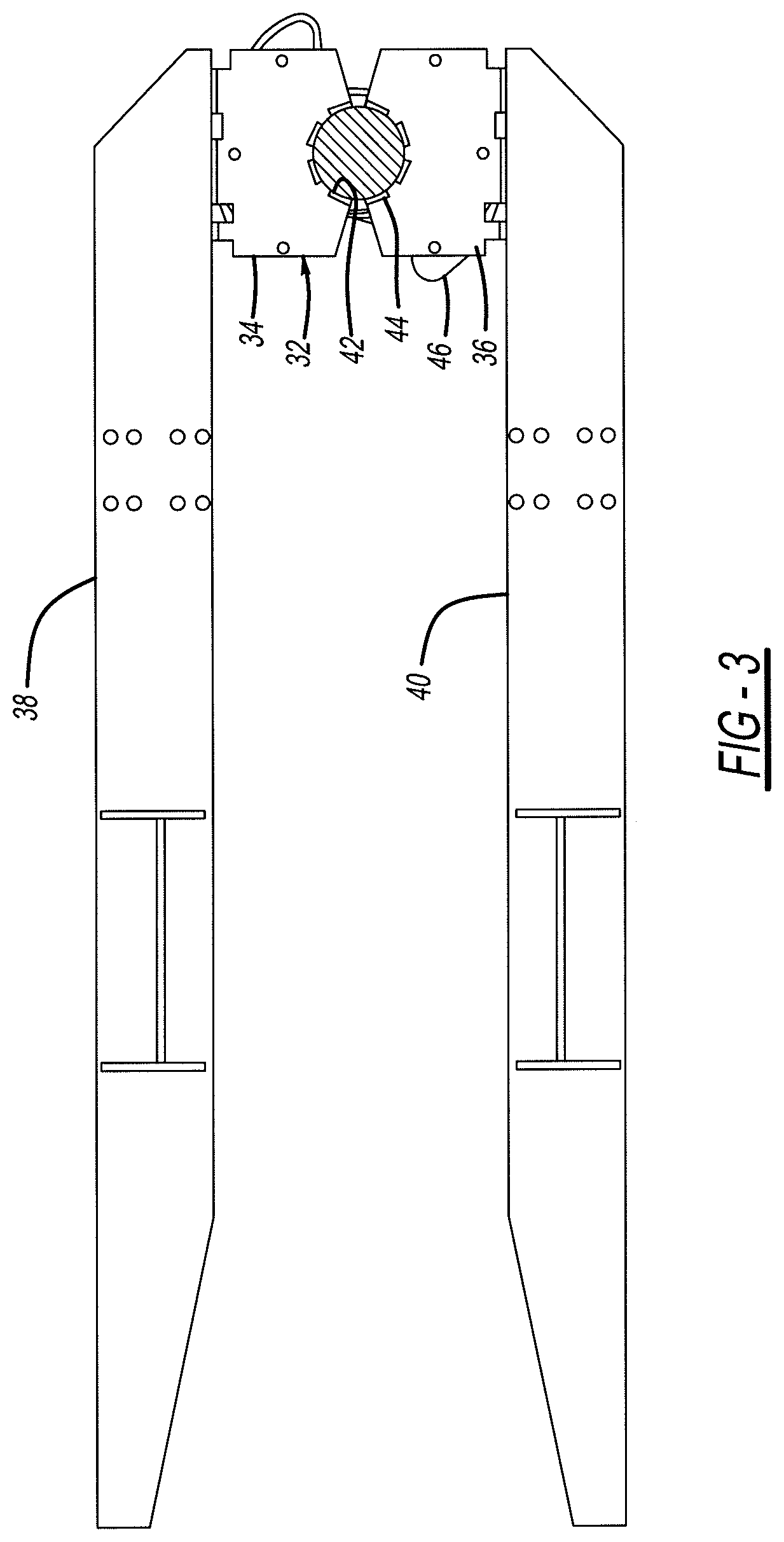
[0018]FIGS. 1, 2 and 3 illustrate a microfinishing machine 10 in accordance with the present invention and which is capable of being operated to practice the methods in accordance with the present invention. As shown by the figures, a representative workpiece shown as internal combustion engine crankshaft 12 is supported at opposing ends by machine headstock 14 and tailstock 15 which together cause crankshaft 12 to be rotated about its longitudinal center axis 18. Crankshaft 12 forms a number of cylindrical journal bearing surfaces to be microfinished, including main bearing journals 20 (four shown in FIG. 1) which are concentric with axis 18, and rod bearing journals 22 (six shown in FIG. 1) which move in rotational and orbital paths upon rotation of crankshaft 12. Since crankshaft 12 is rotated about its longitudinal axis 18 which is coaxial with main journals 20, their centers remain theoretically stationary during rotation of the crankshaft. Crankshaft 12 includes a number of st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com