Compositions and methods to barcode bacteriophage receptors, and uses thereof
a technology of bacteriophage receptors and barcodes, applied in the field of engineered bacteriophage, can solve the problems of many technological gaps that need urgent attention, need substantial investment of money, time and labor, and no standard way to track these changes, and achieve the effect of easy identification, quantification and/or tracking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Discovery and Engineering of Host-Phage Interaction Determinants for Designed Manipulation of Microbial Communities
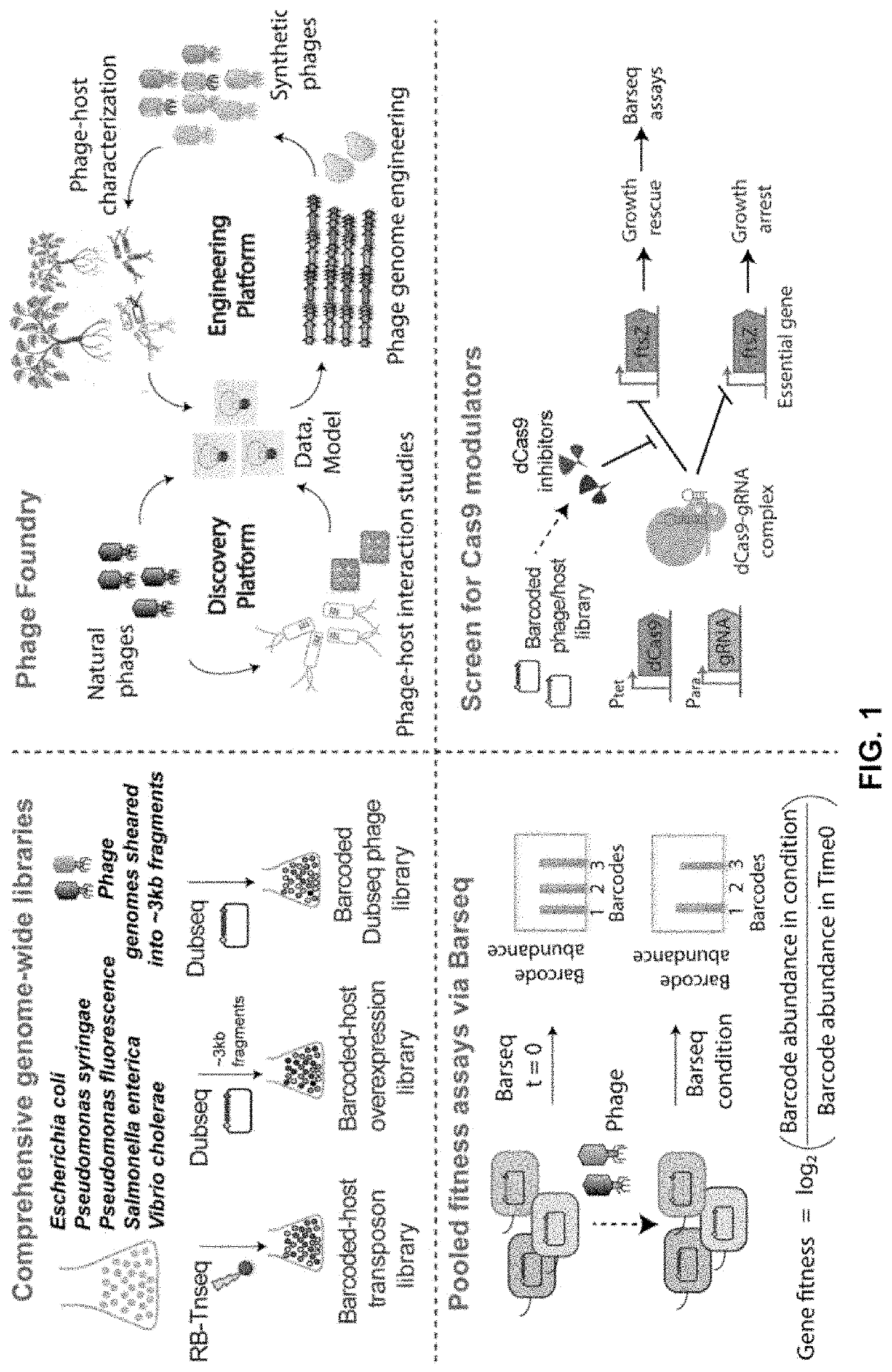
[0162]Microbial communities drive and are driven by significant environmental processes, affect agricultural output, and impact human and animal health1,2. Complex interactions among themselves, their hosts and environments are thought to be important for these effects1-6. Manipulation of these communities can potentially lead to improved health, crop productivity and environmental resilience7-11. The virome—the collection of viruses that parasitize these microbial communities—are a critical feature of microbial community dynamics, activity and adaptation4,12,13.
[0163]Though viruses / phages represent the most abundant biological entities with an estimated range of 1030-1032-tenfold greater than bacteria14,15, the virome is deeply under-characterized, which limits our ability to understand microbial community dynamics and activity or to utilize this resource for microbial...
example 2
Methods to Barcode Phages to Identify, Track, Quantify and Protect Intellectual Property of Therapeutic Phages
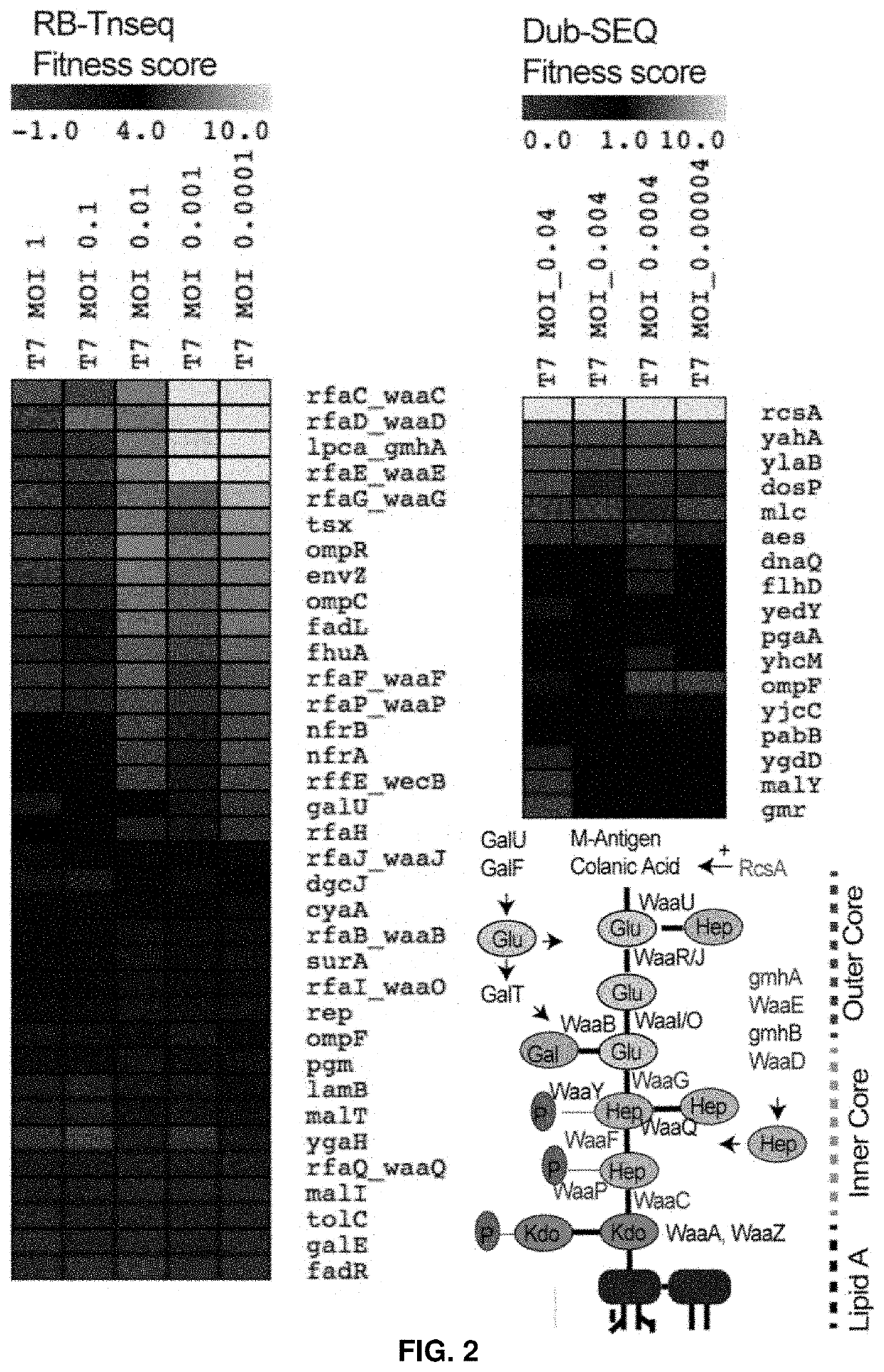
[0198]In this invention, we use non-essential gene location of phage to insert a unique “n-mer DNA barcode” such that it may not impact the infectivity of a phage. These DNA barcodes are composed of n-mer randomized or defend DNA region surrounded by primer binding region that helps in amplifying the ‘barcode’. This barcoding strategy creates a handle for identifying, quantifying, and tracking a barcoded phage.
[0199]Methods
[0200]Plasmid Construction λ
[0201]A region encoding non-essential region in phage P1 genome (Lobocka et al., 2004) was selected for the insertion of DNA barcodes. 50 bp of the non-essential region was selected as the site for homologous recombination (Datsenko & Wanner, 2000, Piya et al., 2017). A DNA fragment consisting of the first 50 bp homology region of DNA, followed by a universal primer binding region (P1), followed by a 10-mer unique DNA barcode, a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com