Compositions and methods of use for treatment or improvement of the condition and appearance of skin
a technology applied in the field of compositions and methods of use for appearance of skin, can solve the problems of subject discomfort, scarring of the skin, etc., and achieve the effect of treating or improving the condition or aesthetic appearance of the skin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
QHREDGS (SEQ ID NO: 1) Prevents Changes Associated with Scarring Using Dermis-on-a-Chip Model
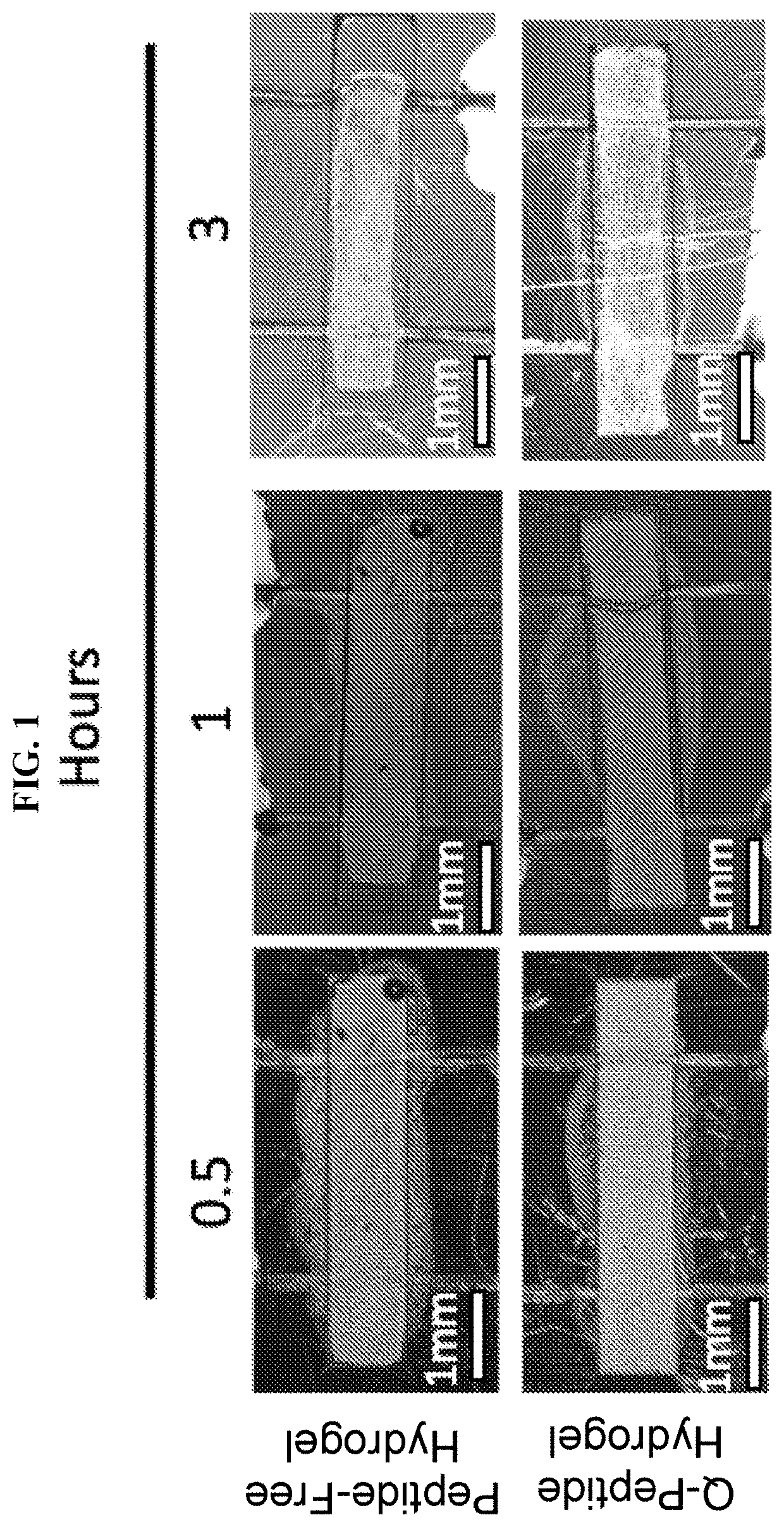
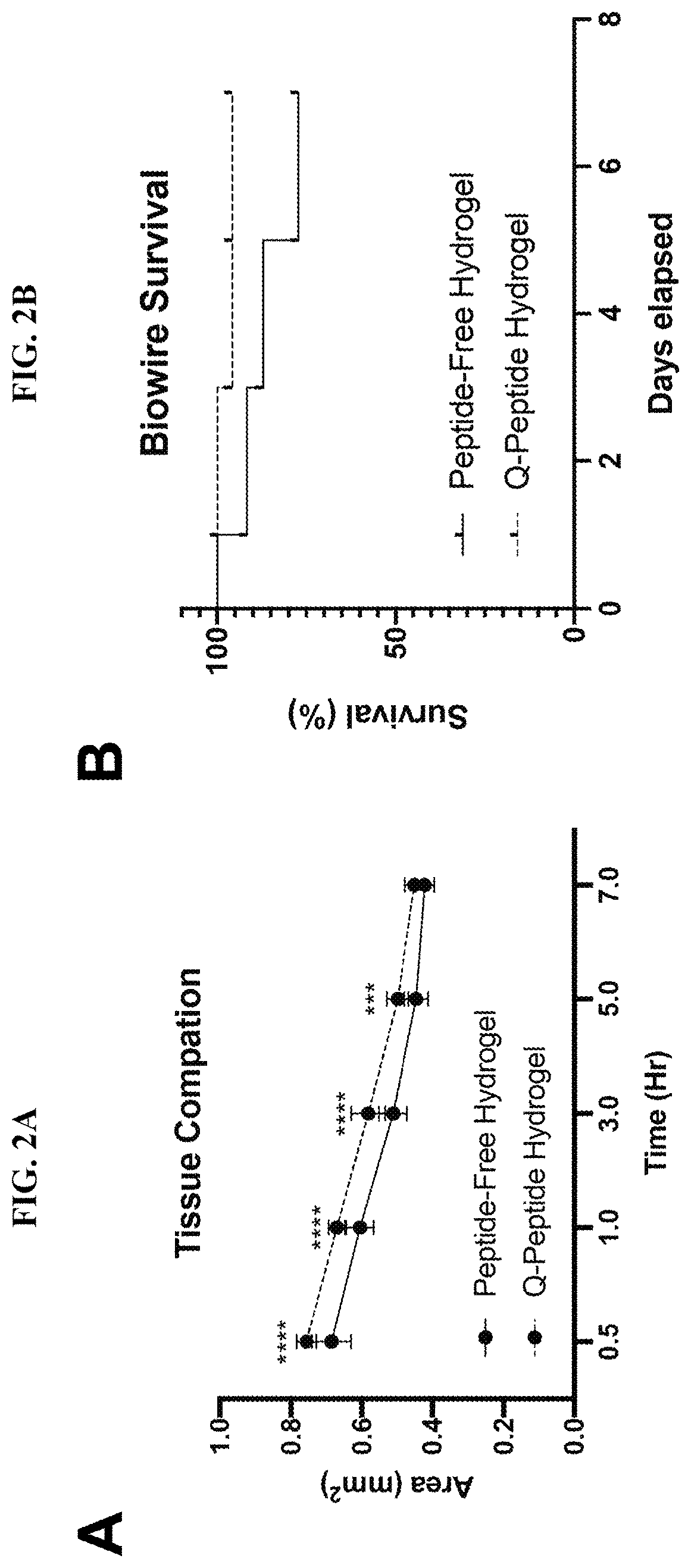
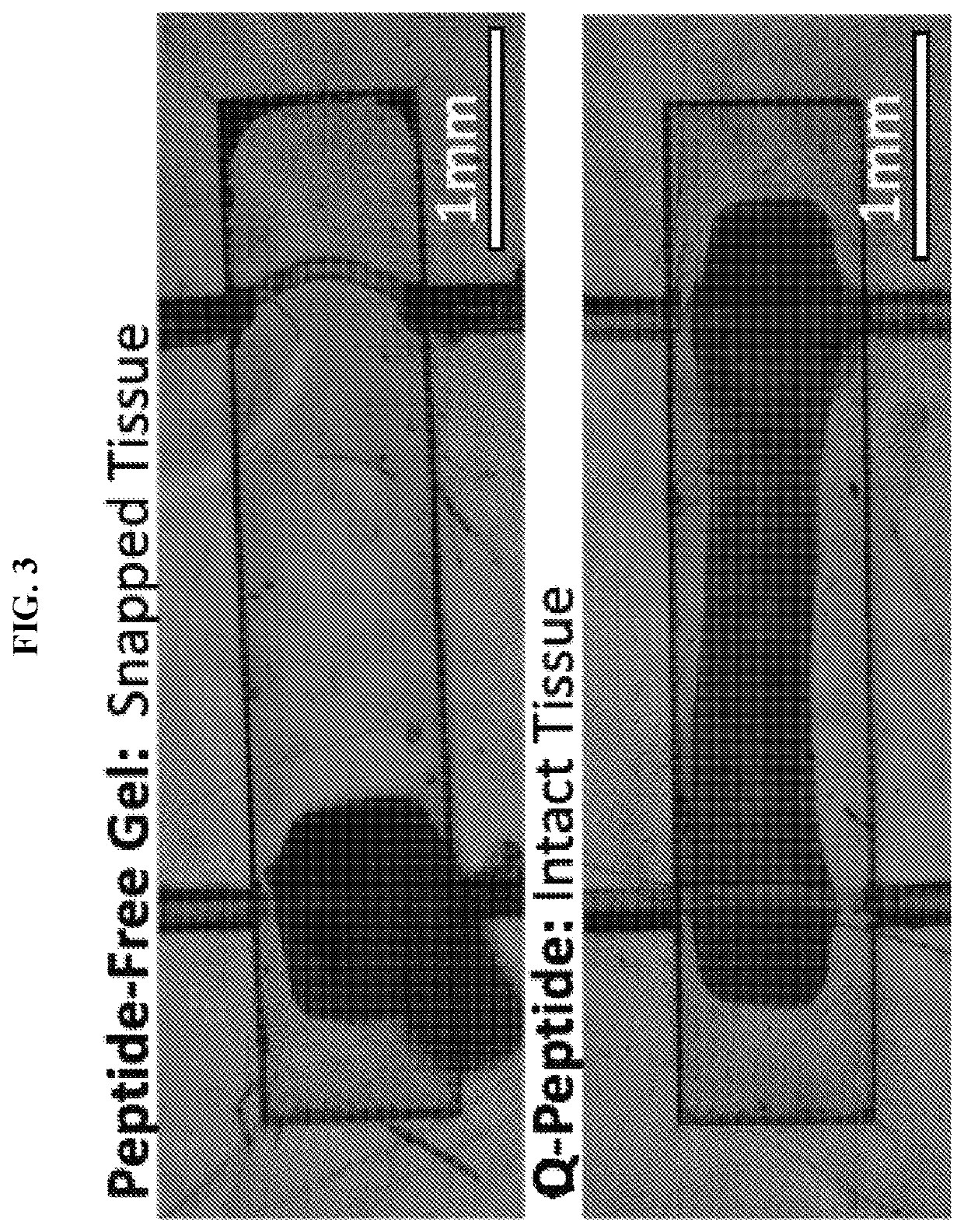
[0221]Disclosed herein is a new dermis-on-a-chip model to assess the effects of the QHREDGS (SEQ ID NO: 1) peptide on mechanisms involved in scarring. The dermis-on-a-chip model consists of adult dermal fibroblasts encapsulated into collagen-chitosan hydrogel seeded into a microwell fitted with 2 parallel elastomeric wires. During the tissue remodelling process, the fibroblasts exert tractional forces that compact the gel into a cylindrical tissue. In some cases, myofibroblast over-activation leads to tissue breakage due to the excessive pulling on the hydrogel matrix. A combination of functional readouts together with immunostaining and second harmonic generation microscopy was used to assess the anti-scarring behaviour of peptide modified gel. Anti-scarring properties were defined by: higher survival of intact tissues, slower gel compaction, and higher native collagen regeneration.
[0222]Fi...
example 2
Materials and Methods for Assessment Wound Healing in a Human to Mouse Xenograft Model
[0226]Human Split Thickness Xenograft—Human skin was harvested and grafted as previously described. Briefly, full thickness adult skin samples were obtained with informed consent from abdominoplasty patients from the Foothills Medical Center in Calgary Alberta. Within 24 hours of procurement, the human skin was grafted onto the backs of mice. Full thickness skin wounds (2 cm2) were created on the backs of adult athymic (Nu / Nu) mice. HSTGs were cut to the exact size and sutured into place. The wounds were bandaged for 10 days with a foam-based silver dressing held securely with and elastic adhesive bandage circumferentially around the abdomen.
[0227]Wound Creation—After 2-3 months of integration, a 4 mm full excisional wound was created on the HSTG, and the wound received one of the following treatments: 1) no treatment, 2) FDA approved wound management material (Primatrix®), 3) Collagen-chitosan gel...
example 3
Effect of Q-Peptide Hydrogel on Healing of Human Epidermis and Wound Contraction
[0232]To examine the effect of the Q-Peptide hydrogel on wound healing in human epidermis, 4 mm wounds were treated with a no-treatment control (E), an FDA approved control (P, Primatrix®), a peptide-free hydrogel (H), and the Q-Peptide hydrogel (QH). Gross morphological images of the treated wounds were taken at the time of sacrifice to allow for gross observation of wound healing (FIG. 8). Wound appearance was evaluated by two blinded observers using a wound closure score where open wounds=0, closed wound with attached eschar (scab)=0.5, and closed wound with no eschar present=1. By day 28, the wound can be clearly seen in the no-treated control and in Primatrix®, with the empty hydrogel reducing the appearance of the wound, and the Q-Peptide hydrogel nearly eliminating the appearance of the wound. Wounds treated with the Q-Peptide hydrogel score significantly higher than all treatment groups, with all...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elasticity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com