Power semiconductor device
a technology of power semiconductor and semiconductor device, which is applied in the direction of transistors, basic electric elements, substation/switching arrangement casings, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the overall packaging area, malfunction or breakdown of the power conversion device, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the wiring inductance and packaging area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
ferred embodiment;
[0022]FIG. 8 shows a structure of an element used in a power conversion device 3 according to a third preferred embodiment of the invention;
[0023]FIG. 9 shows a structure of an element used in the power conversion device 3 according to the third preferred embodiment; and
[0024]FIG. 10 is a perspective view showing a connection configuration of the elements in the power conversion device 3 according to the third preferred embodiment.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
[0025]
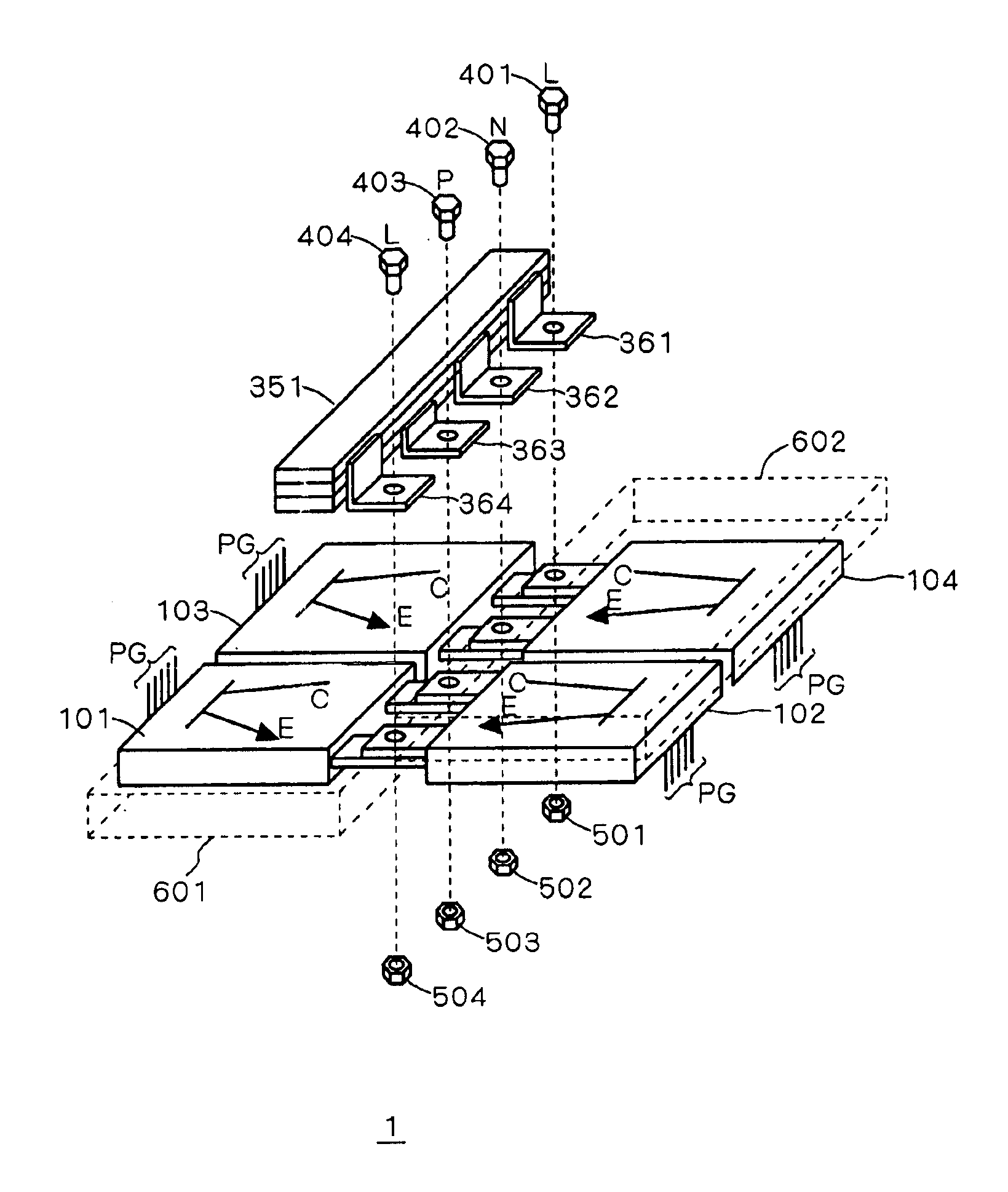
[0026]A power semiconductor device (power conversion device) according to a first preferred embodiment of the present invention features a reduction in length of a bus bar and packaging area, by arranging two power module elements each on both sides of the bus bar rather than arranging four power module elements on one side of the bus bar. Namely, the elements arranged in twos face each other with the bus bar between.
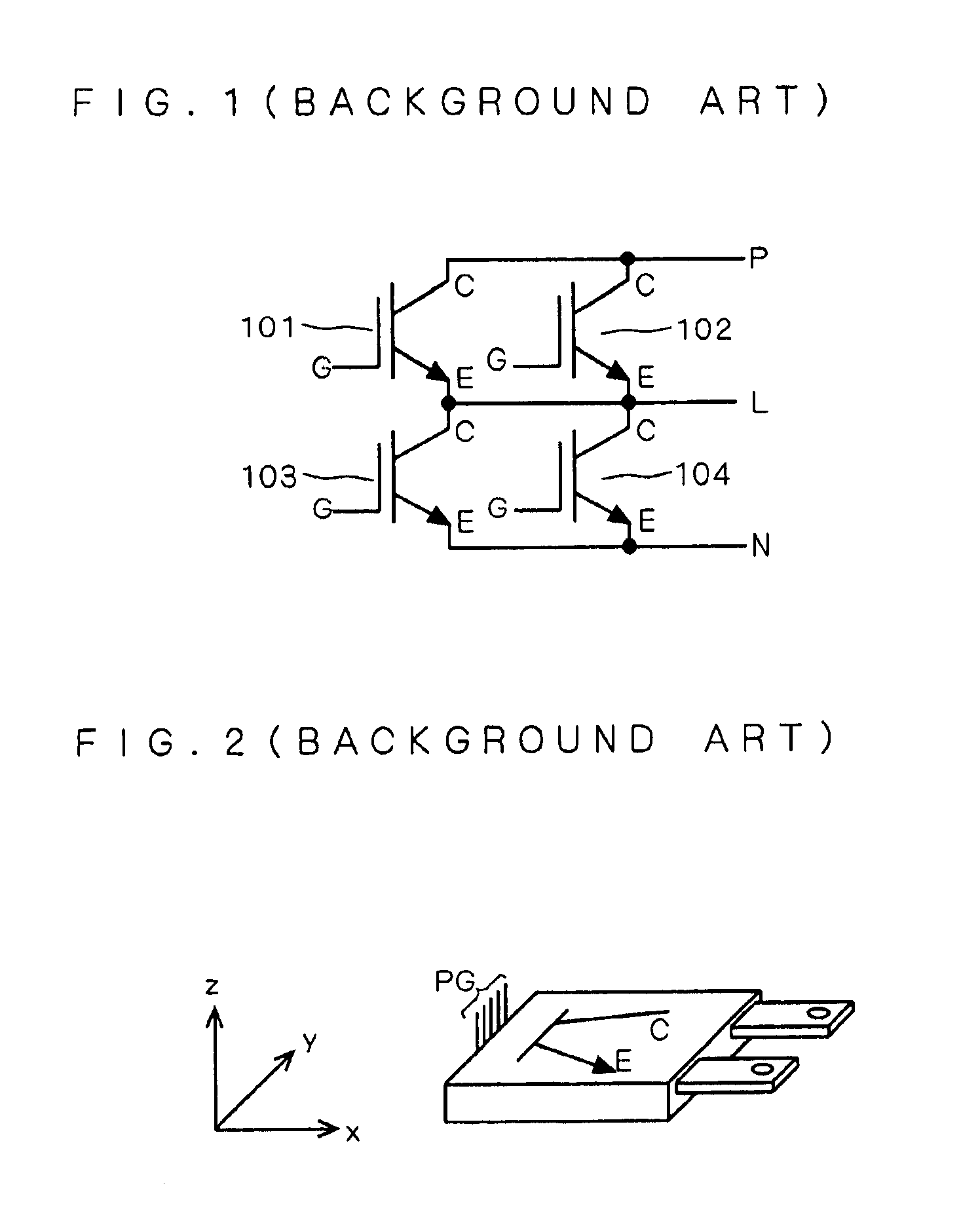
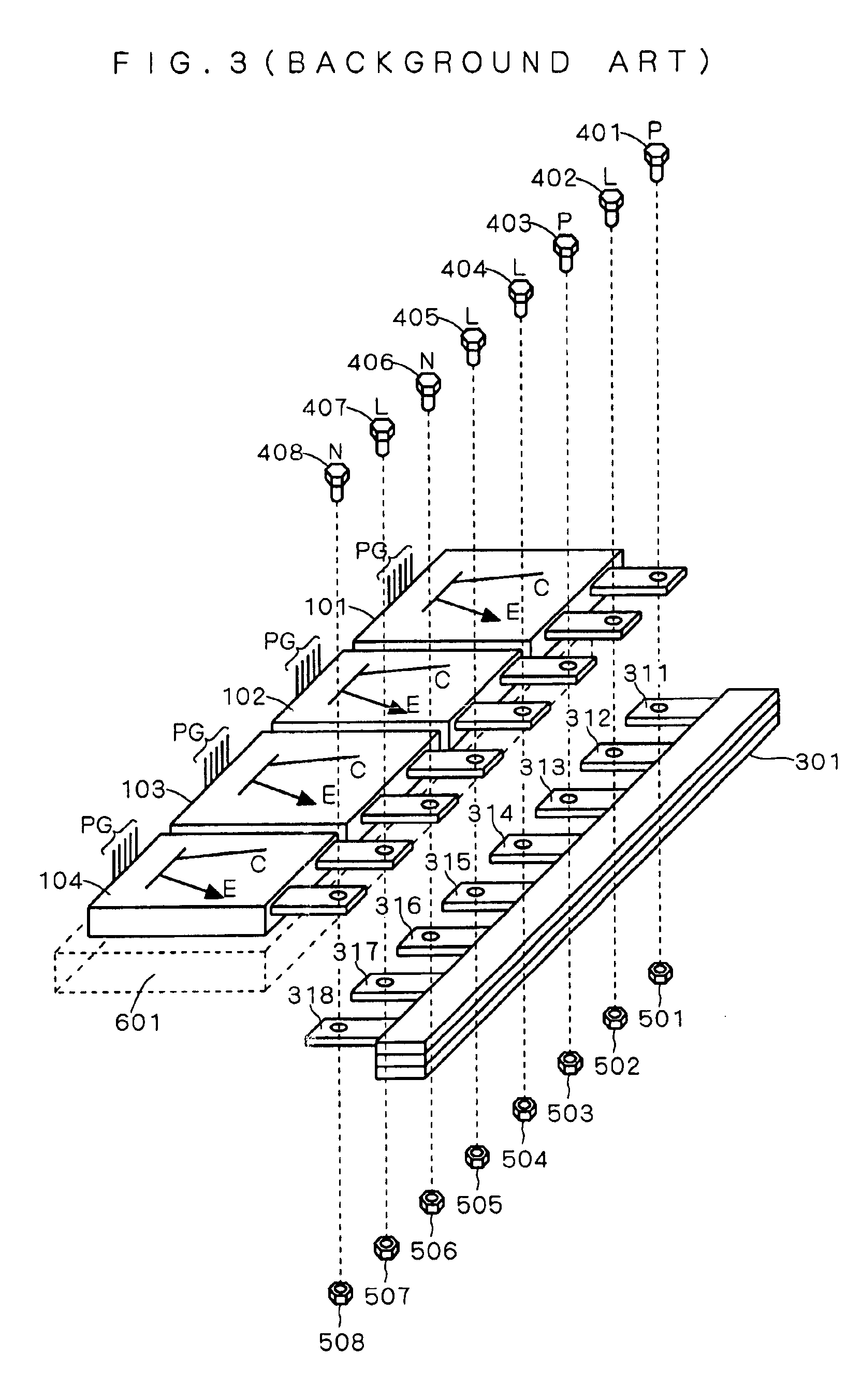
[0027]First, as a background to the present preferred embodiment, a configura...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com