Furanocoumarin removal from grapefruit juice by edible fungal hyphae
a technology of edible fungal hyphae and furanocoumarin, which is applied in the direction of fruit/vegetable preservation using acids, food preparation, and extraction of tea, etc. it can solve the problems of too much drug being absorbed into the body, adversely affecting the grapefruit industry, and no satisfactory means of producing furanocoumarin-free citrus juice. , to achieve the effect of reducing the level of furanocoumarin
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0029]A culture of Aspergillus niger van Tieghem was obtained from the ARS Culture Collection at the national Center for Agricultural utilization Research in Peoria, Ill. (NRRL No. 326). The fungus was grown on potato dextrose agar (BD / Difco, Sparks, Md.) plates for about 5 to 7 days at approximately 25 degrees centrigrade. Spores were removed from the plate surface using sterile water containing about 0.1% Tween 20 and gently rubbing with a sterile disposable transfer needle (Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, Pa.). The resulting liquid was filtered through 3 layers of cheesecloth, and the filtrate was collected as a spore suspension and adjusted for inoculum concentration using a haemocytometer (Hausser Scientific, Horsham, Pa.).
example 2
[0030]Grapefruit juice samples were prepared by squeezing pink grapefruit obtained from a local store, followed by a pH adjustment to 5.0. The grapefruit juice was stored at −20° C. for future use. Fifty or one hundred mL grapefruit juice in 250 mL flasks was placed in a circulating water bath, heated to 90° C. until the internal temperature of grapefruit juice reached 71° C. The grapefruit juice samples were held at this temperature for 15 sec, removed, chilled and brought to ambient temperature (25° C.).
[0031]To culture A. niger in grapefruit juice, a 1 mL of spore suspension (106 spores / mL) was inoculated into a 100 mL grapefruit juice, and incubated for 4 days at 120 rpm, 25° C. After incubation for 4 days, the grapefruit juice samples were filtered through Miracloth, and the resulting filtrate and mycelial tissue on Miracloth were collected and subjected to ethyl acetate extraction.
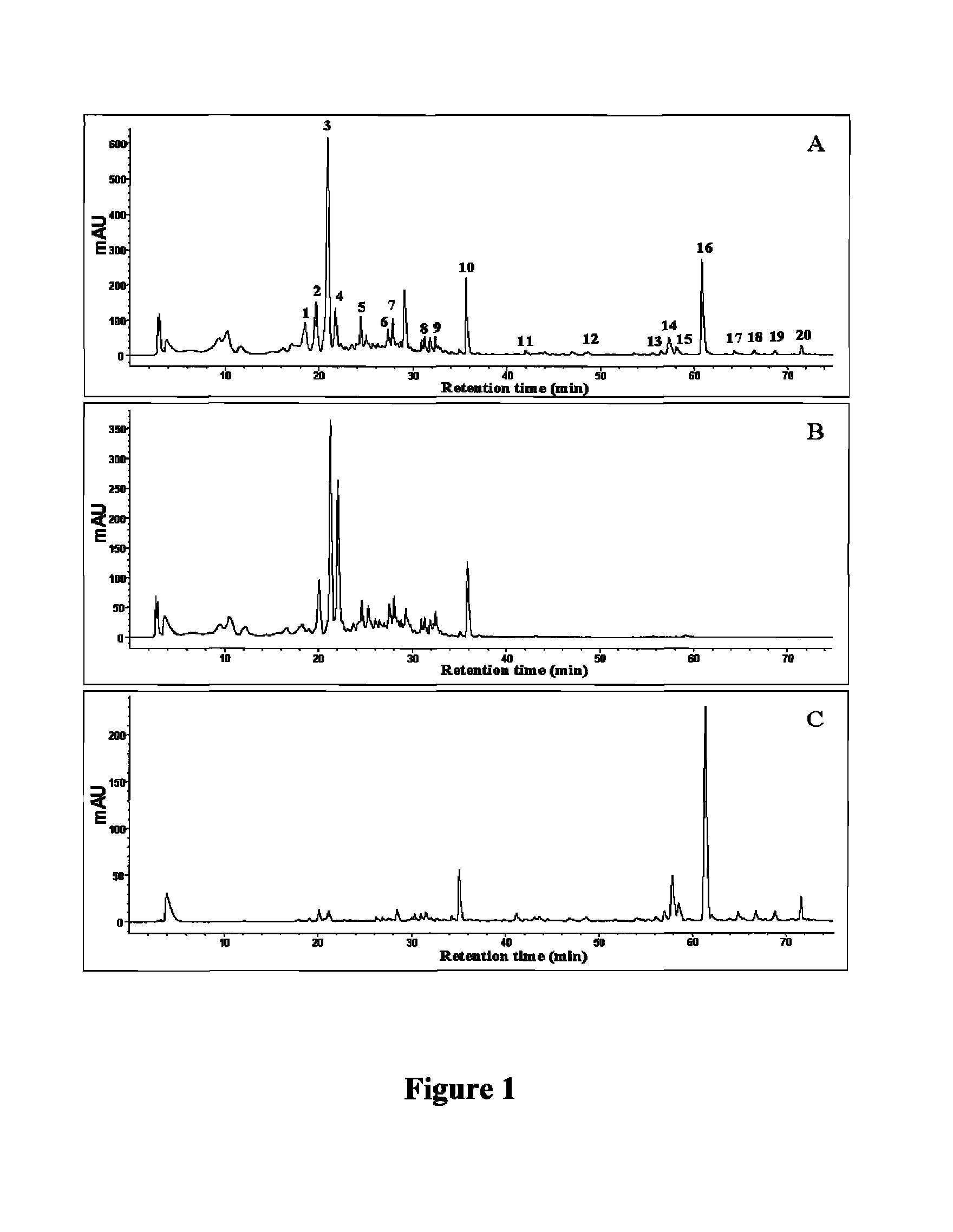
[0032]To determine compounds in grapefruit juice filtrates from grapefruit juice incubated with A...
example 3
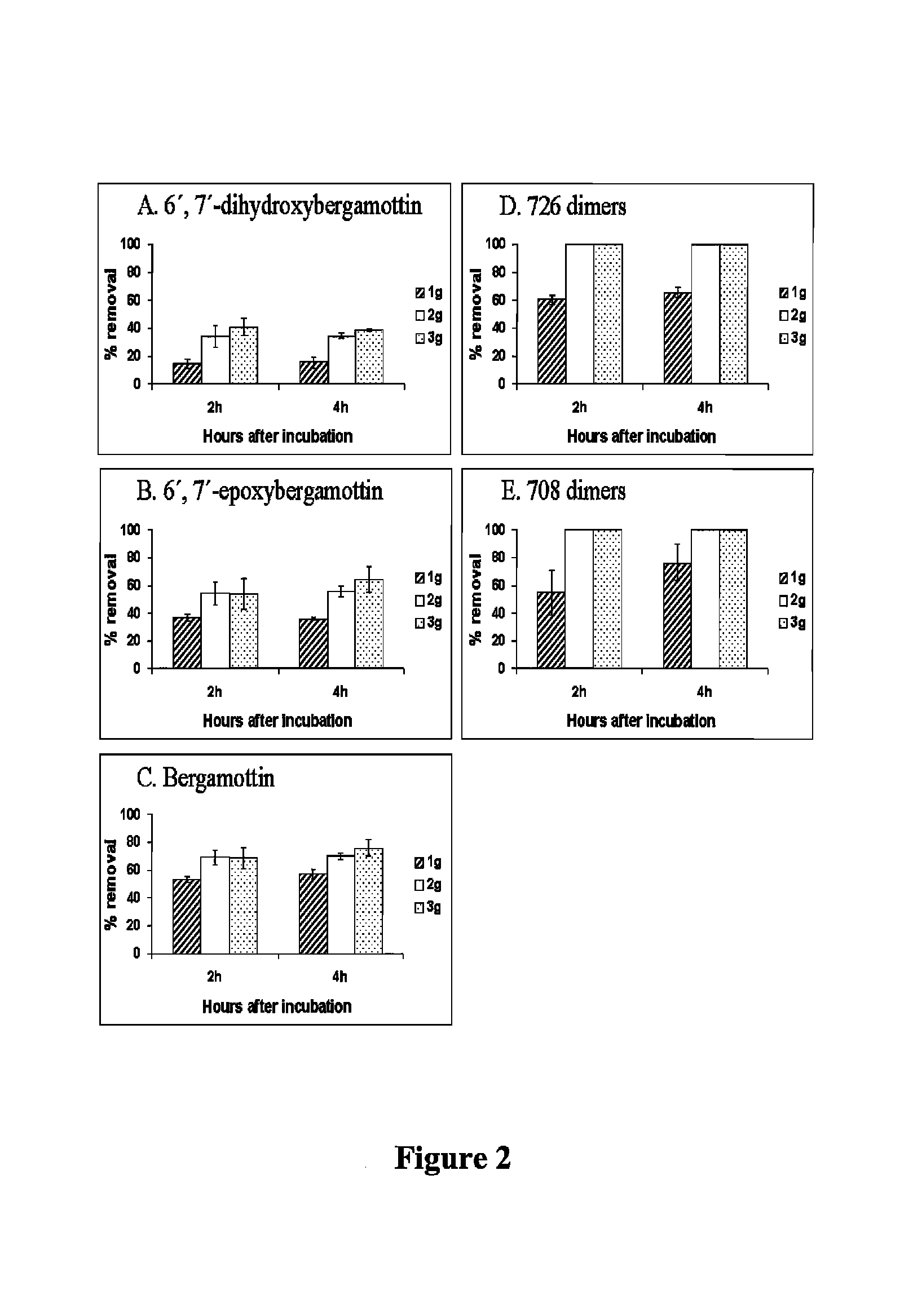
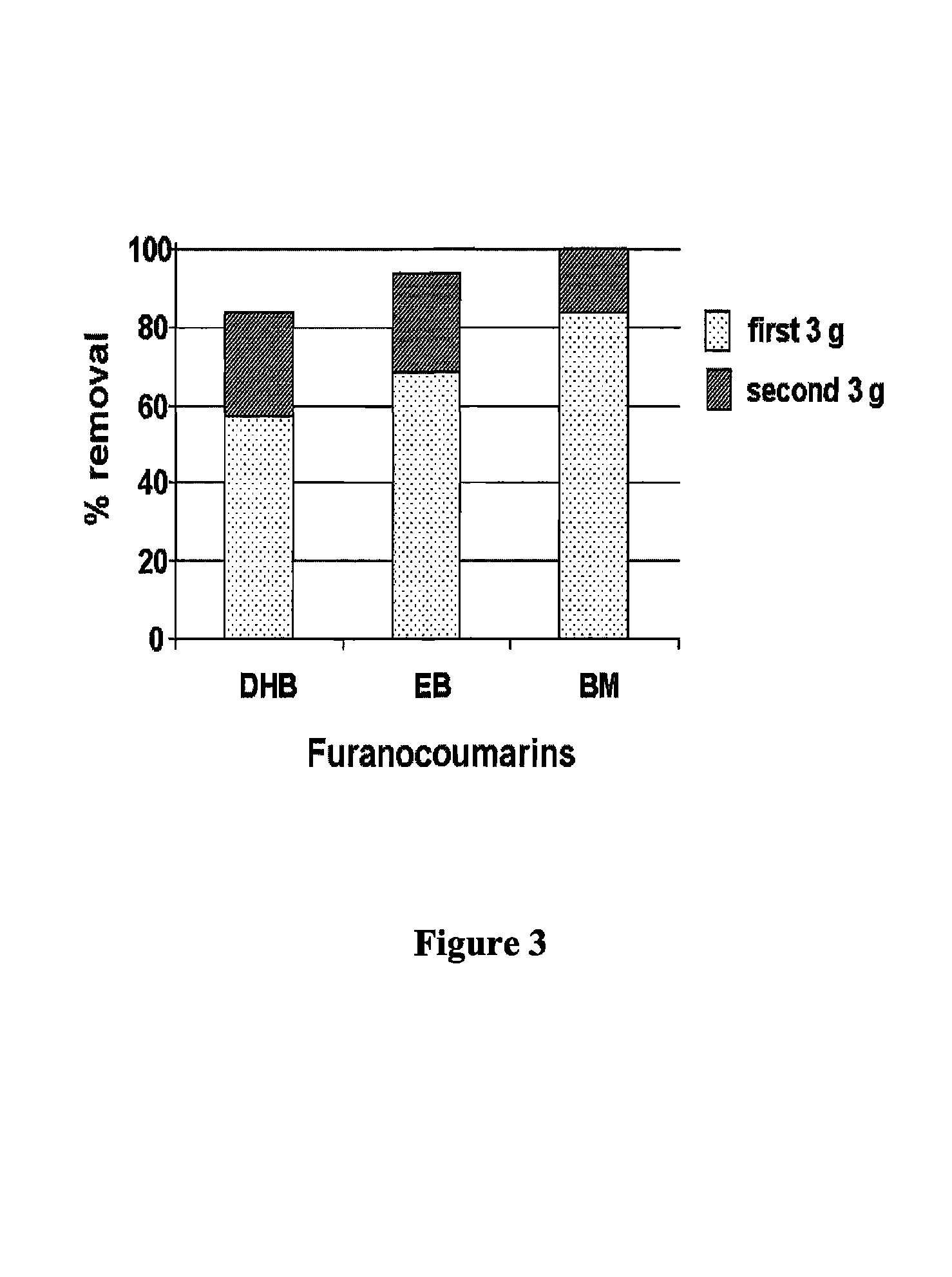
[0035]In experiments using autoclaved A. niger, 5 mL of spore suspension (106 spore / mL) was inoculated in an 2 L flask containing 1 L potato dextrose broth, and shaken on a large capacity orbital shaker at 275 rpm to avoid mycelial cohesion to the sides of the flask at 25° C. After one week, the flasks were autoclaved for 20 min at 121° C. to kill the fungus. The dead fungal material was vacuum-filtered from the broth and used as adsorbent. Approximately, 10 g fresh weight of the dead fungal material was collected from a flask. Grapefruit juices (100 mL) in 250 mL flasks were incubated with or without 2 g (fresh weight) of autoclaved A. niger for 4 days at 25° C.
[0036]Four flavanones were not adsorbed by dead fungus, while 7-geranyloxycoumarin and furanocoumarins, except furanocoumarin-like 1, 2, 3, and 4, were adsorbed by dead fungus (Table 1). Similar results of compound compositional changes in grapefruit juice, except ferulic acid, were achieved from experiments using live and d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com