S-band low-noise amplifier with self-adjusting bias for improved power consumption and dynamic range in a mobile environment
a low-noise amplifier and mobile environment technology, applied in low-noise amplifiers, gain control, transmission, etc., can solve the problems of system consuming as little power as possible, difficult to predict the jamming environment to which the system will be exposed, and long battery life, so as to achieve low noise, high dynamic range, and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
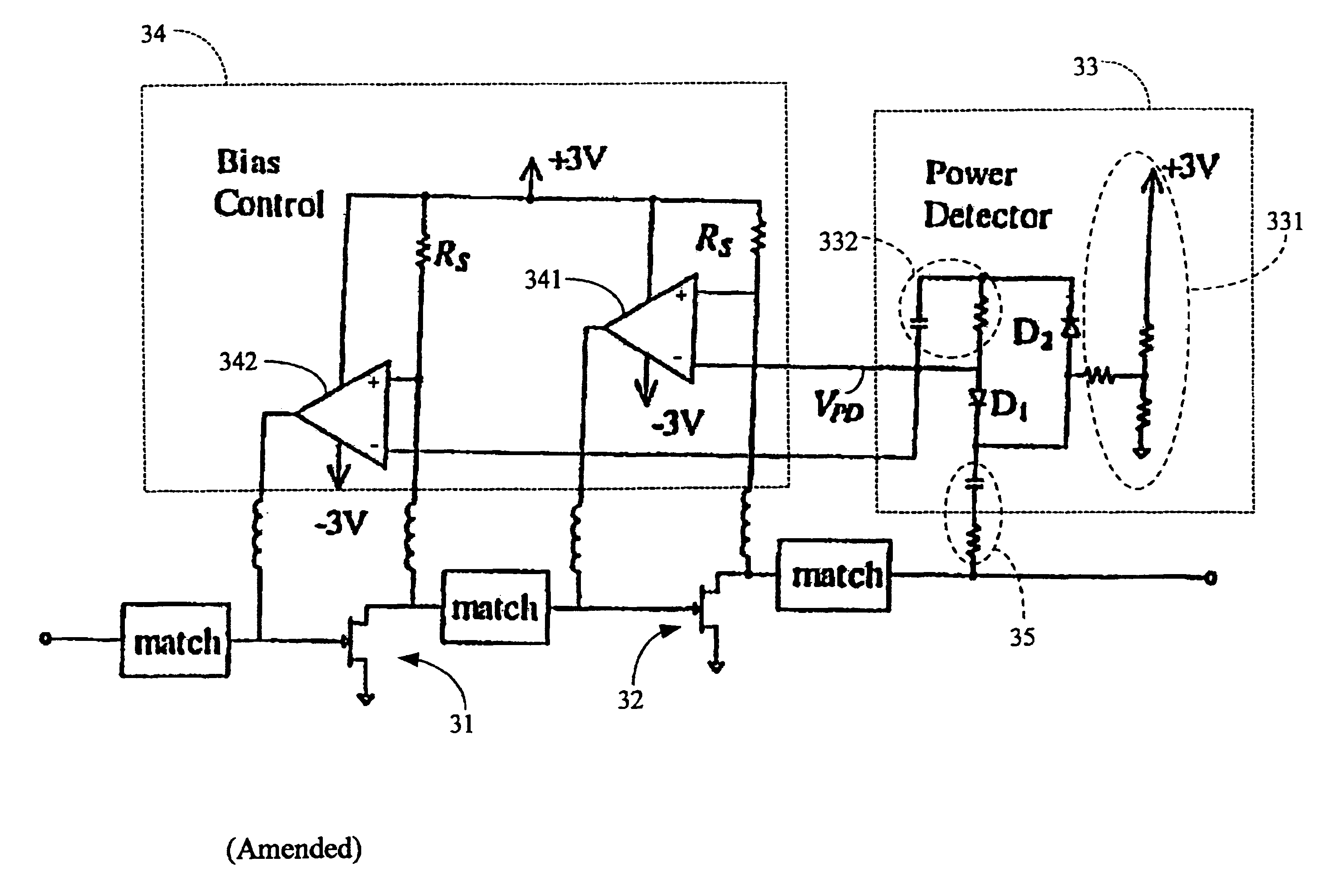
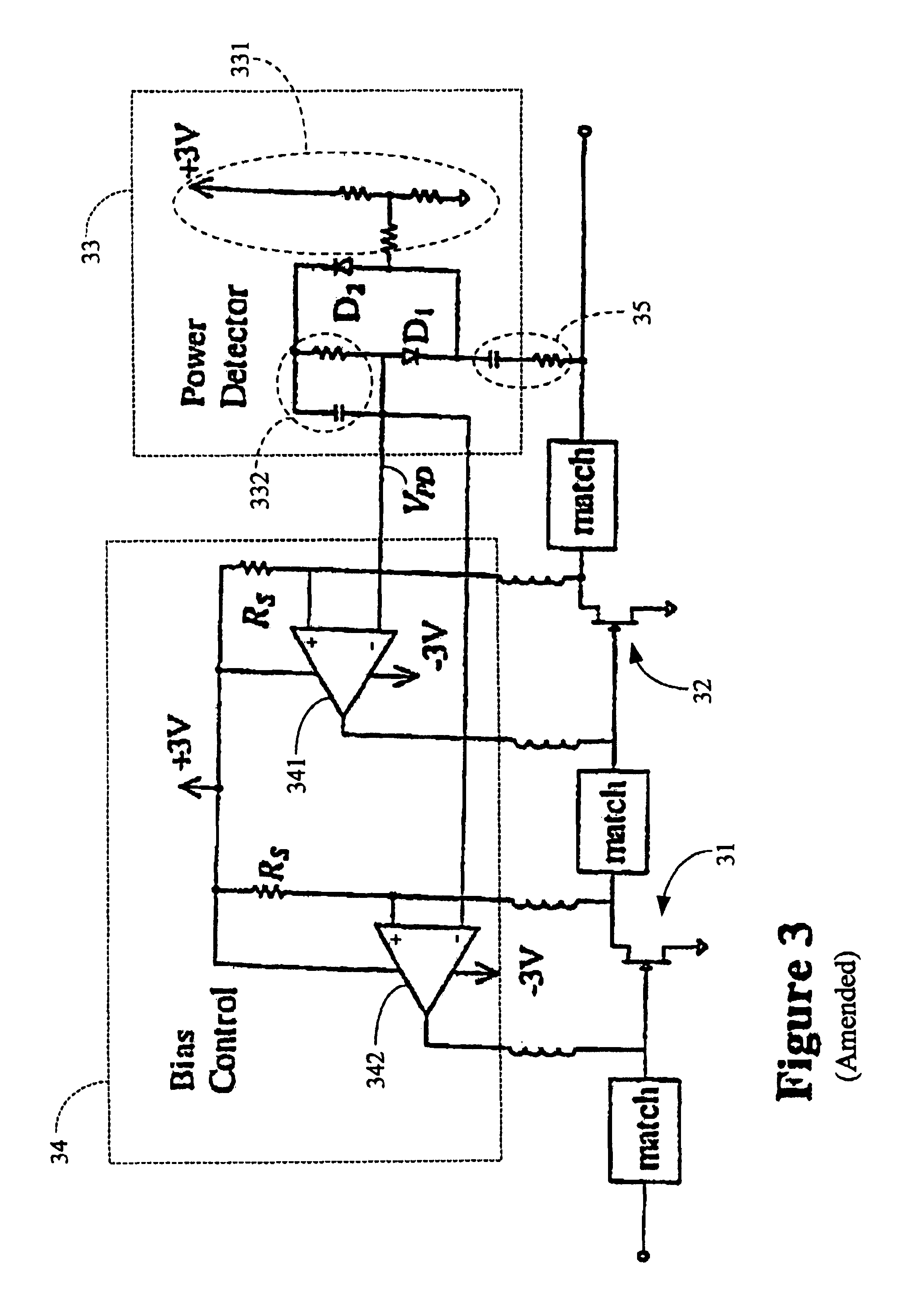
[0053]The present invention is embodied in a Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) circuit of new design. The LNA is particularly useful in a cellular, mobile, wireless radio communications system where jamming is occasionally experienced.
1. The Operational Environment
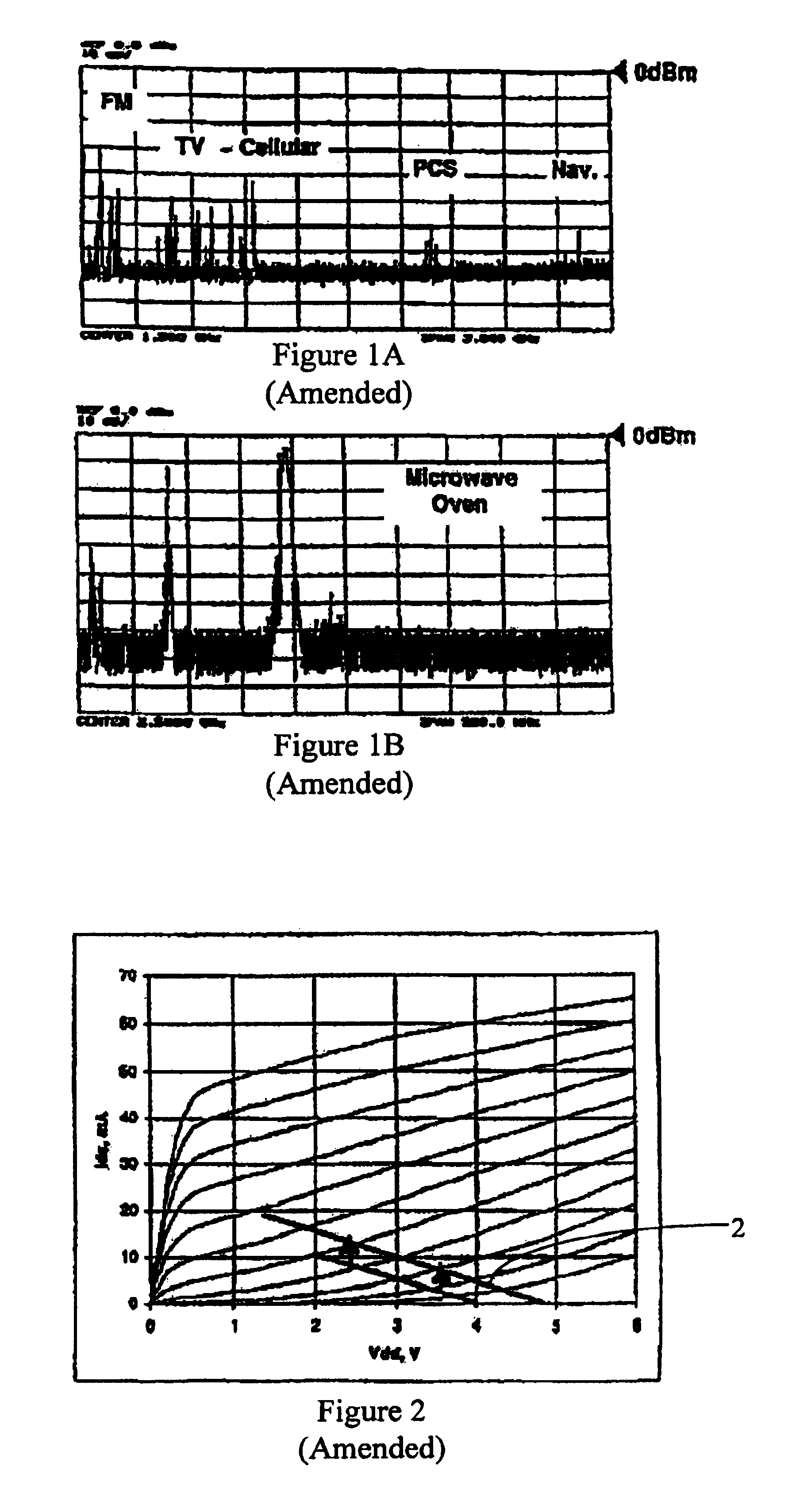
[0054]FIG. 1, consisting of FIGS. 1a and 1bFIGS. 1A and 1B, illustrates some typical jammers as measured by an omni-directional 2.5 GHz antenna. Sources of a microwave oven, a navigational beacon (“nav.”), a personal communication system cellular telephone (“PCS”), an analog cellular telephone (“Cellular”), television (“TV”) and frequency modulation radio (“FM”) are in particular illustrated. To avoid fatal interference from these jamming signals a low-noise amplifier must have a large dynamic range: namely, a low noise figure and low intermodulation distortion. See S. Chen, “Linearity Requirements for Digital Wireless Communication,” IEEE GaAs IC Symp. Dig., At Anaheim, Calif., pp. 29-32, October 1997.
[0055]To meet these demands,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com