Combination of Chinese traditional medicine for treating viral myocarditis and preparation method
A technology for viral myocarditis and composition, applied in the directions of drug delivery, antiviral agents, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problems of no disease research, no development of new traditional Chinese medicines with unique curative effects, no drugs with very precise curative effects, etc., to achieve protection Cardiomyocyte function, increase myocardial nutrient blood flow, and improve microcirculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Embodiment 1, medicine preparation
[0048] 1. Materials:
[0049] (1) Source and dosage of raw materials:
[0050] 1. Astragalus This product is the dried root of the leguminous plant Astragalus mongolica or Astragalus membranaceus. Excavated in spring and autumn, remove fibrous roots and roots, and dry in the sun. Main production: Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Gansu, Heilongjiang.
[0051] 2. Rhodiola This product is the dry root and rhizome of Rhodiola grandiflora or Rhodiola grandiflora of Crassulaceae. Excavated in autumn, removed the rough bark, and sun-dried. Main production: Tibet, Gansu, Xinjiang, Jilin and other places.
[0052] 3. Sophora flavescens This product is the dried root of the leguminous plant Sophora flavescens. Excavated in spring and autumn, removed root heads and small branches, washed, dried, or sliced while fresh, dried. Main production: Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Gansu, Heilongjiang. Produced in most parts of the country.
[0053] The consu...
Embodiment 2
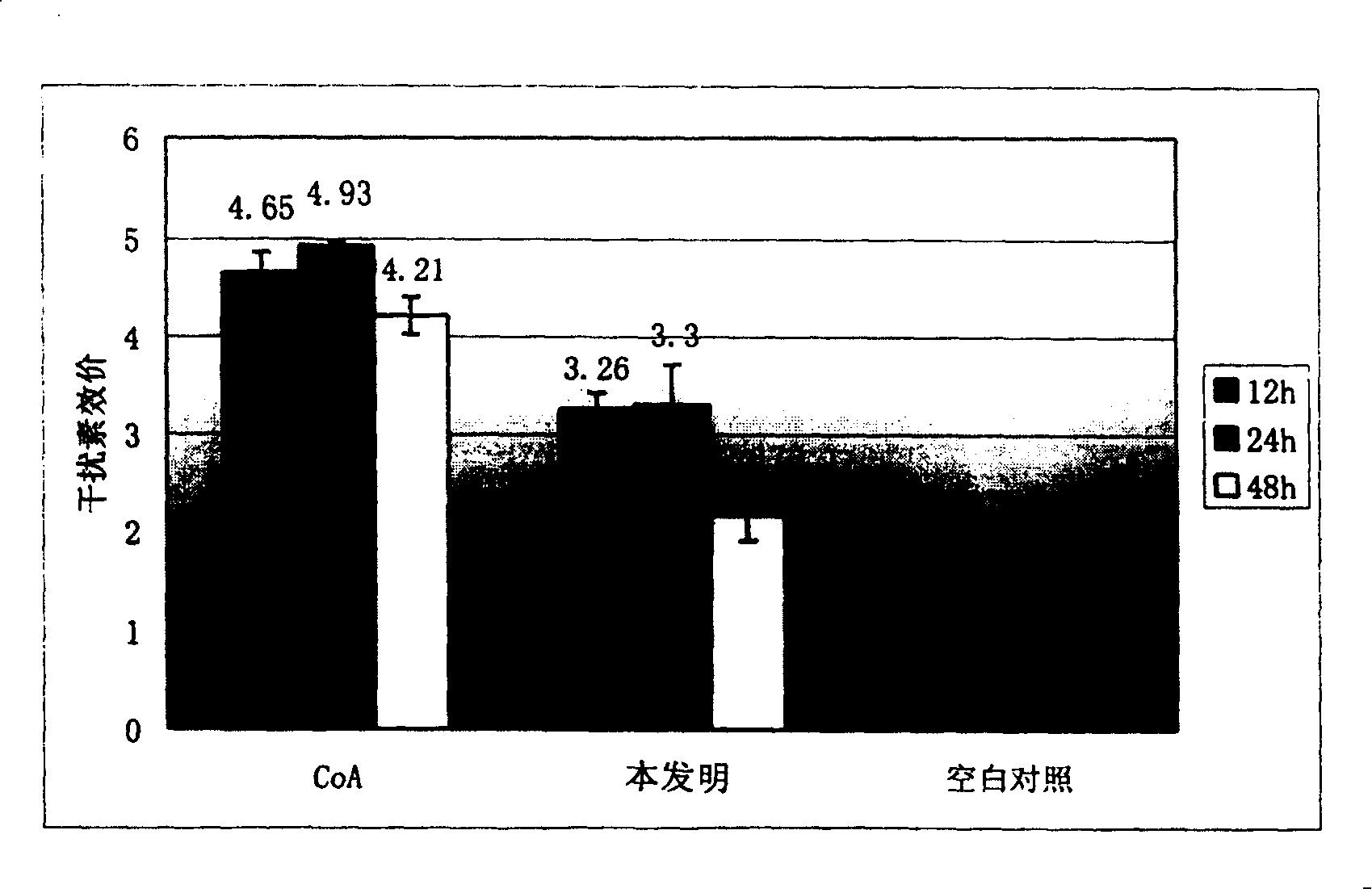
[0089] Embodiment 2, in vitro pharmacodynamics test 1——CPE inhibition experiment at the cardiomyocyte level
[0090] 1. Test materials:
[0091] 1. Test drug: the traditional Chinese medicine composition described in Example 1 of the present invention, the production batch number is: 030904;
[0092] 2. Experimental animals: SD suckling mice, which are second-class animals (certificate number SXK-11-00-0006), were purchased from the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences;
[0093] 3. Coxsackie virus CVB 3 : The strain number is Nancy strain, provided by the virus room of Wuhan Union Medical College Hospital.
[0094] 2. Test method:
[0095] (1) CVB 3 Virus virulence titration method (TCID 50 , 50% tissue culture infectious dose):
[0096] 1. Experimental steps:
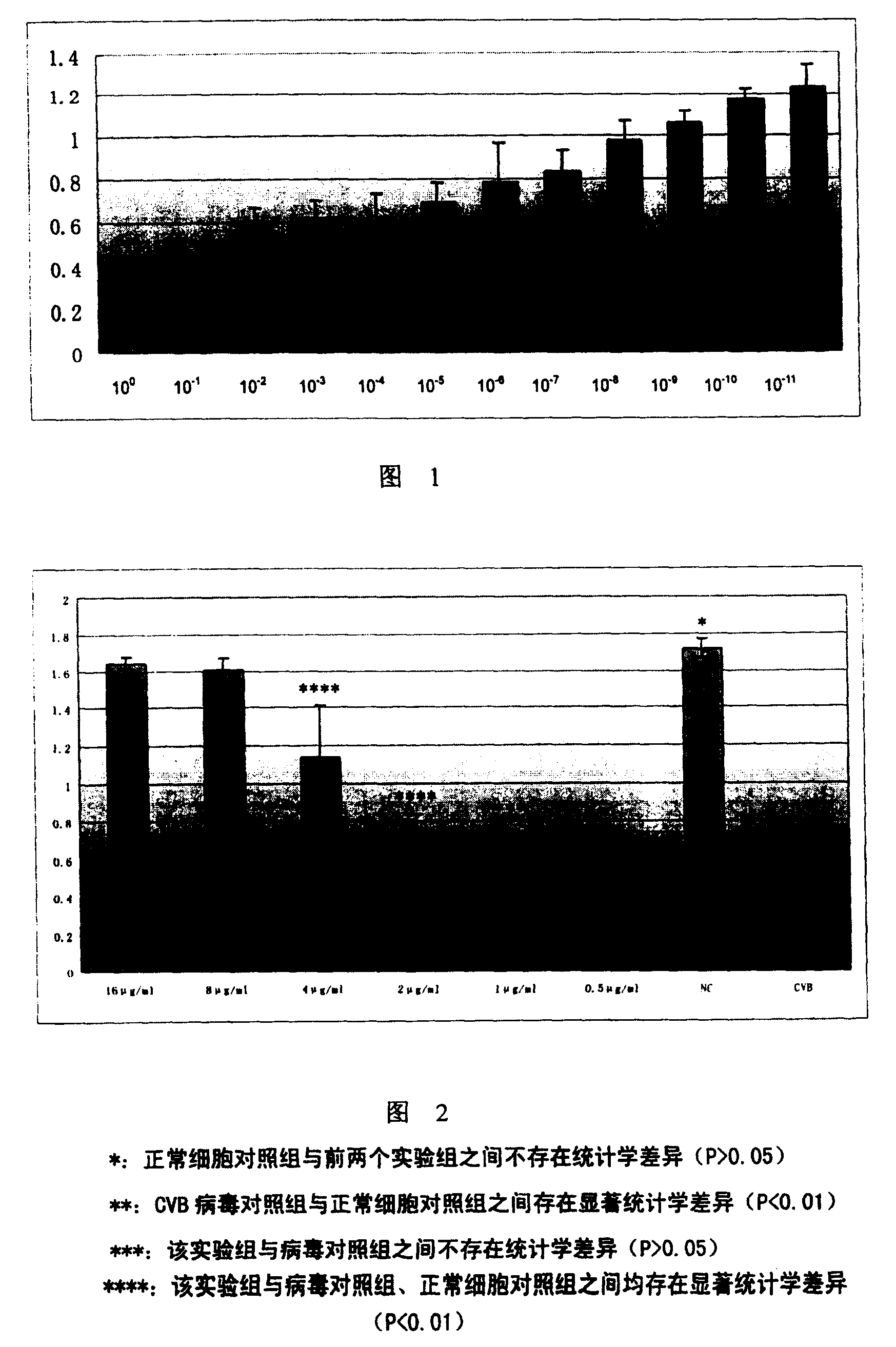
[0097] Culture Vero cells in a 96-well plate; the virus was serially diluted 10-fold with serum-free medium, respectively 10 -1 ~10 -8 Dilution, then seeded in 96-well plate (the wells are...
Embodiment 3
[0132] Embodiment 3, in vitro pharmacodynamics test 2 - virus reproduction inhibition test
[0133] 1. Test materials:
[0134] Vero cells, Coxsackie virus CVB 3 And test drug: with embodiment 2.
[0135] 2. Test method:
[0136] 1. Inoculate Vero cells on a 24-well plate, and then add drugs and viruses in groups. The experimental design is shown in Table 13:
[0137] Table 13-well plates were inoculated with Vero cells and added drugs and viruses in groups
[0138]
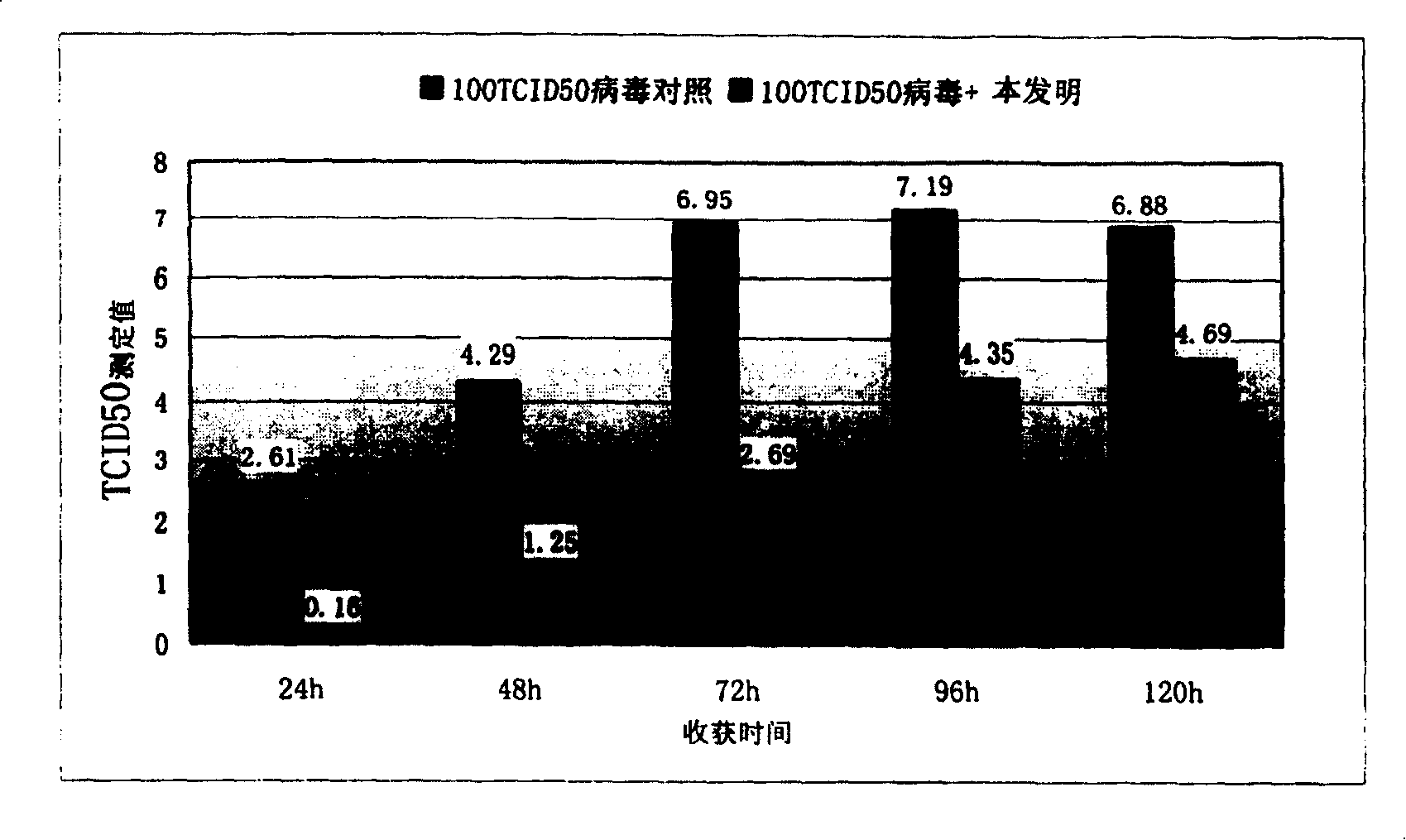
[0139] 2. Harvest grouped cells according to different harvest time, and titrate CVB with virus titration method 3 virulence.
[0140] 3. Test results:
[0141] Harvest grouped cells according to different harvest time, and titrate CVB with virus titration method 3 Virulence, then TCID calculated by the Reed-Muench method 50 , the result is as image 3 shown.
[0142] In the development of antiviral drugs, if the drug can reduce the titer of the virus by more than 1 logarithmic value, it is considered...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com