Half-covered self-organizing dynamic multicast routing method
A coverage multicast and semi-coverage technology, applied in digital transmission systems, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of optimizing the data distribution process, difficulty in summarizing member nodes, and failure of the forwarding tree, and reduce duplicate packets on the link. , Support process simplification, expand the effect of node types
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0220] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with drawings and embodiments.
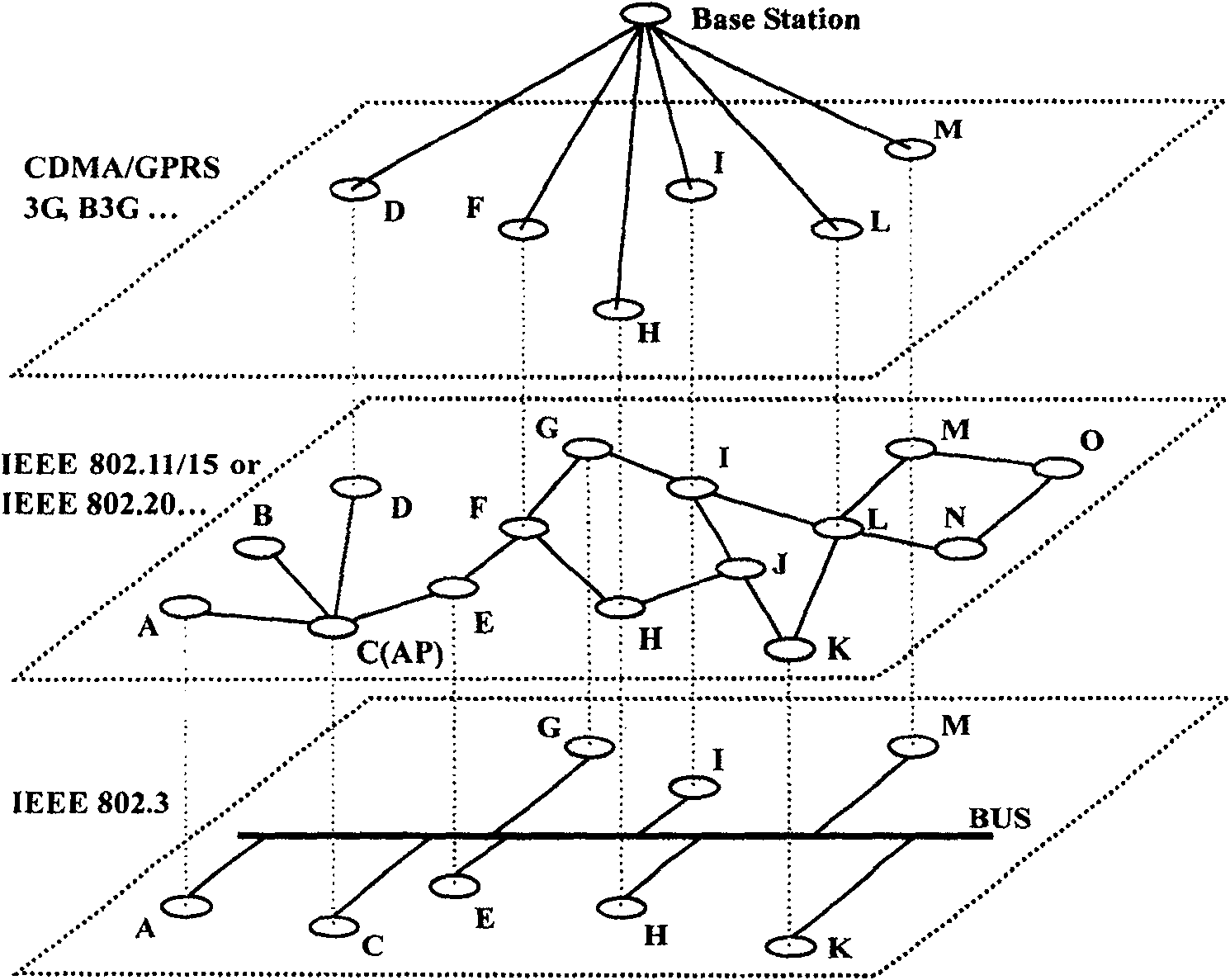
[0221] Figure 10 It shows a typical half-coverage topology stable state and the multicast packet forwarding process in this state. There are 35 nodes in total, and these nodes may be routers, switches, personal computers or handheld digital terminals; some nodes have multiple homogeneous or heterogeneous network interfaces, and some have only one network interface; The connection may be a wired subnet or a wireless network, and the position of the nodes may be fixed or constantly changing; some nodes in the middle have deployed multicast routing modules. Although there are differences in performance and internal structure, they all support the IP protocol, and unicast reachability between any two nodes is the most basic condition for ensuring network connectivity.
[0222] In the current stable state, other 32 nodes except those numbered from 19 to 21 have joined the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com