Rolling member and producing method thereof
A technology of rotating components and manufacturing methods, applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, coatings, furnace types, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient strength, inability to obtain hardness, insufficient surface hardness, etc., and achieve the effect of excellent bending strength of the tooth root
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0196] [Example 1; Anti-dent strength (preliminary test)]
[0197] In this example, in order to study the rotational fatigue strength accompanied by sliding on the tooth surface of the gear, the Figure 12 A rolling dent test was performed on the test piece shown, and the dent strength of various quenched and tempered carbon steels and carburized and quenched case hardened steels was investigated. Table 1 represents the chemical composition of various carbon steels and surface carburizing hardened steels used in this embodiment, and various steel materials are processed into Figure 12 After the shape of the small roller test piece 17 shown in (a), No. 1, 2, and 4 were heated at 820°C for 30 minutes, then water quenched, and tempered at 160°C for 3 hours for testing. In addition, No. 3 and No. 4, after quenching and tempering the billet, use a 40kHz, 200kW high-frequency power supply to heat the rotating surface to 950°C, then quench and harden, and perform the same tempering...
Embodiment 2
[0208] [Example 2: Confirmation of high-frequency heating conditions]
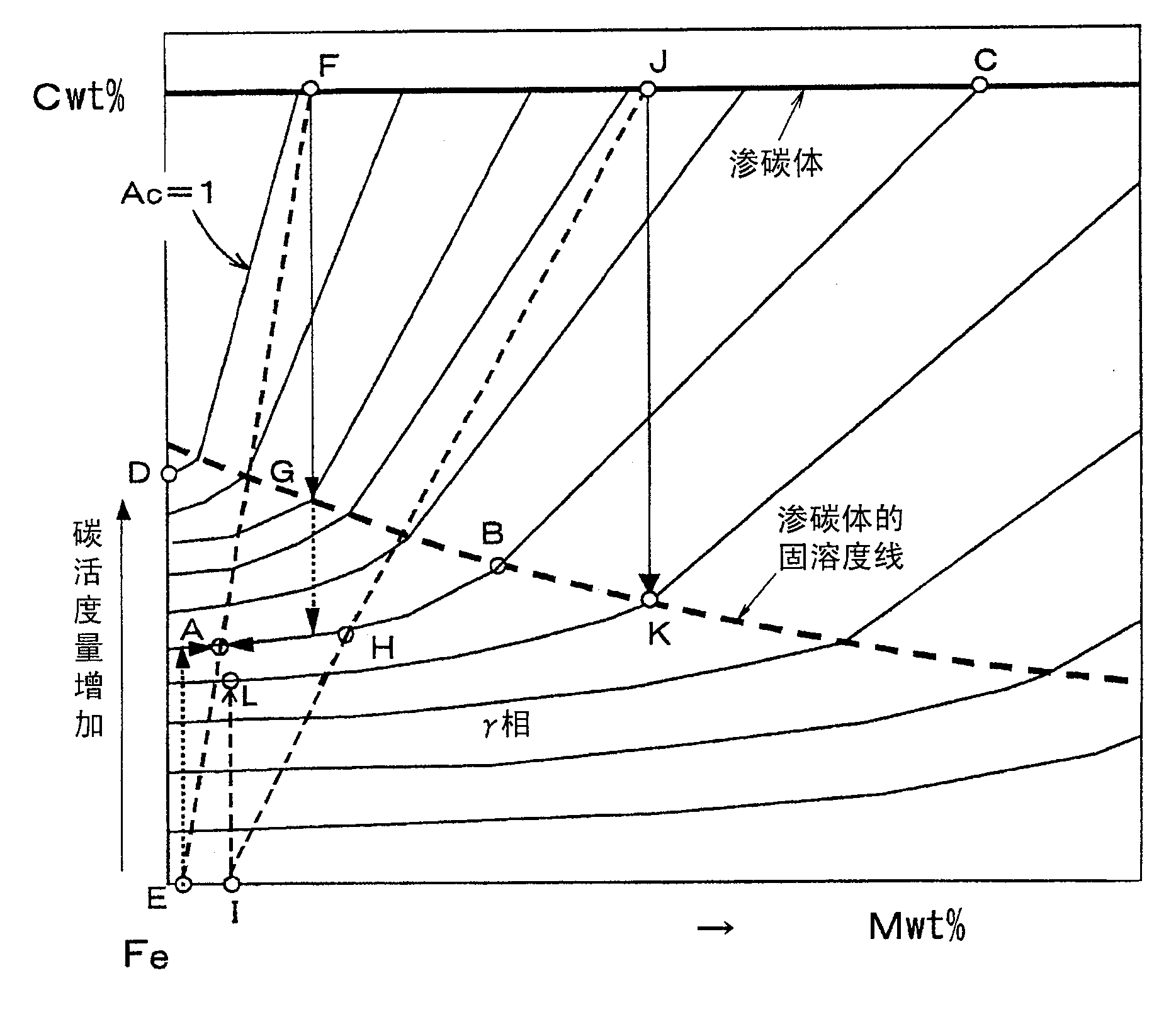
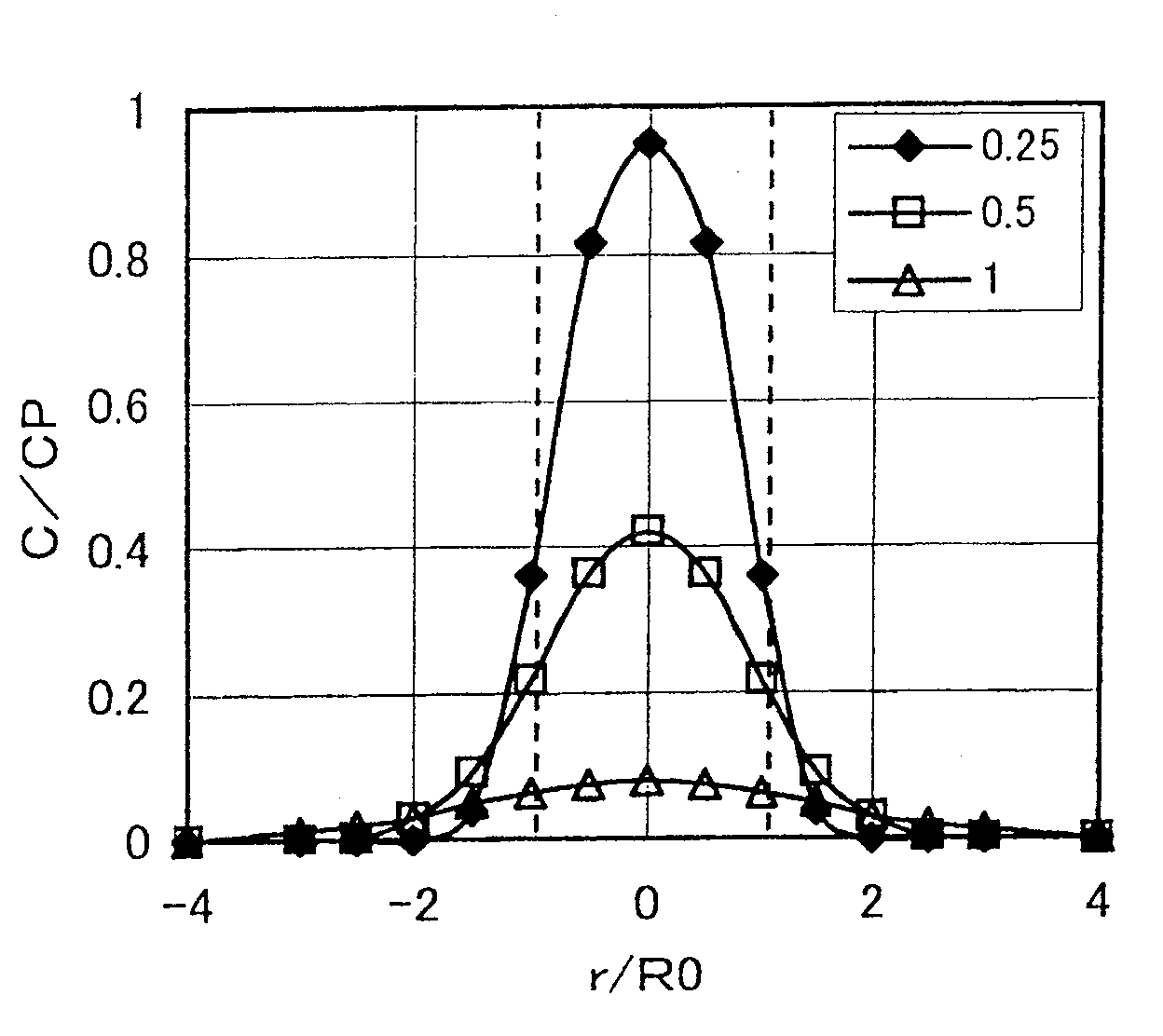
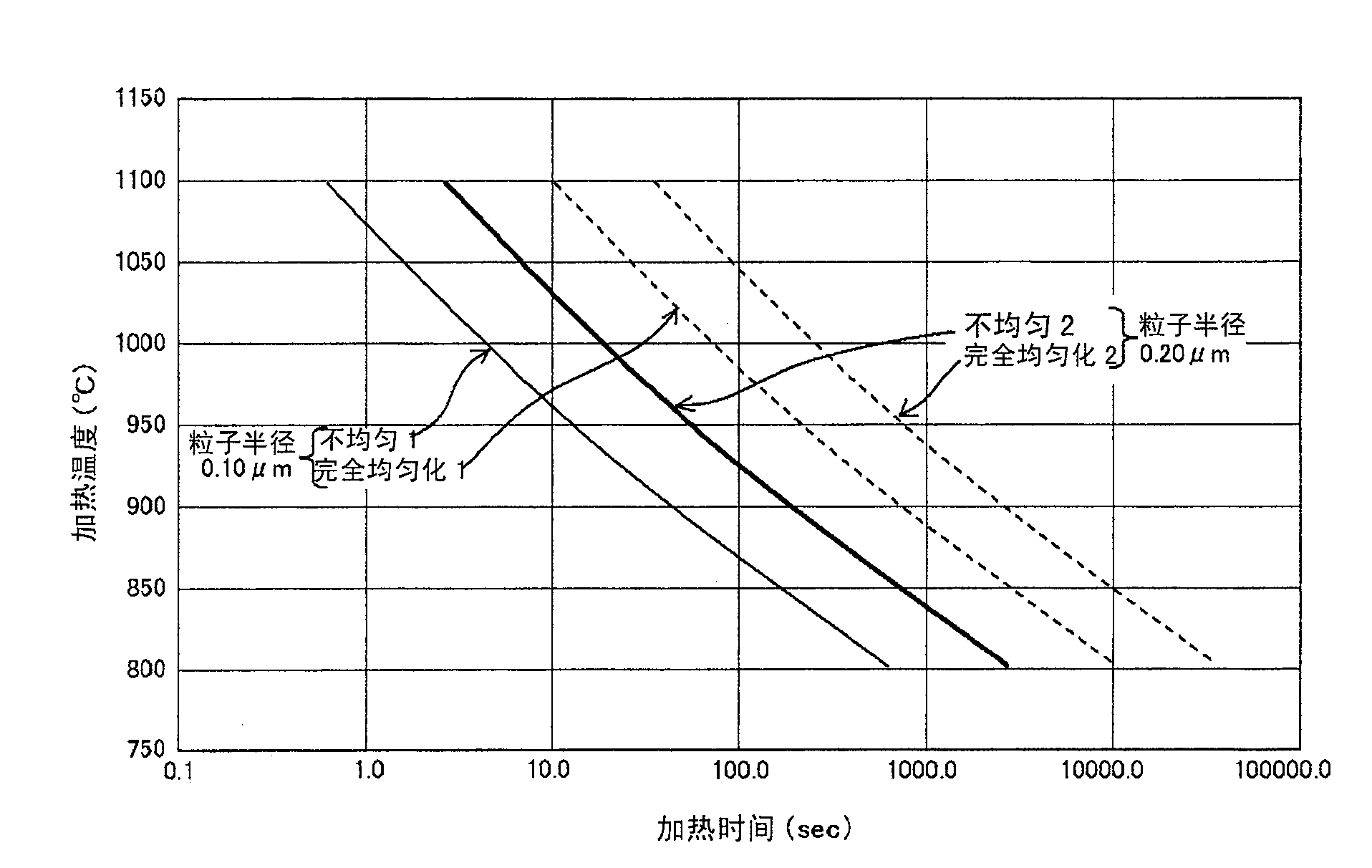
[0209] Example 1 Figure 13 (a), (b), and (c) indicate that the No.1 steel in Table 2 (equivalent to the SUJ2 material of No.4 in Table 1) was heated at 810°C for 2 hours, and gradually cooled to 600°C. After the cementite granulation treatment (slow cooling method) at ℃, it is heated to various temperatures from 800 to 1050 ℃ by high-frequency heating at a heating rate of 6 ℃ / sec, and then water quenching is carried out to study the hardness of the quenched layer and pass through The results of X-ray analysis of the relationship between the carbon concentration in martensite and the amount of undissolved cementite calculated from them. From these figures, it can be seen that in order to obtain martensite with sufficient hardness necessary for the aforementioned rotating members and gear members through the concentration of Cr into the cementite (about 7.8% by weight of Cr), as mentioned above As mention...
Embodiment 3
[0233] [Example 3: Confirmation of temper softening resistance]
[0234] Table 3 shows the composition of the alloys used in this example. After normalizing at 950°C, heat treatment at 810 to 870°C for 30 minutes, water cooling, and tempering at 250, 300, and 350°C for 3 hours were studied. (Rockwell) hardness HRC, and then, analyze the influence of various alloying element additions on these hardnesses.
[0235] [table 3]
[0236] Composition (weight %) of the steel material that is applied to embodiment 3
[0237] TP No.
C
Si
Al
mn
Ni
Cr
Mo
V
B
No.6
0.45
1.45
0.46
1.49
0.52
0.14
0.0018
No.7
0.49
1.45
0.46
1.01
1.03
0.15
0.0019
No.8
0.47
0.31
0.46
2.01
1.03
015
0.0019
No.9
0.49
0.29
0.45
1.5
1.49
0.23
0.0019
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com