Biochemical substance sensing method and biosensor optical sensing structue
A sensing method and technology of biochemical substances, applied in the field of biochemical sensors, can solve problems such as difficult conversion to practical instruments and difficult operation of optical waveguide biosensors, and achieve fast multi-channel simultaneous detection and avoid coupling loss effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
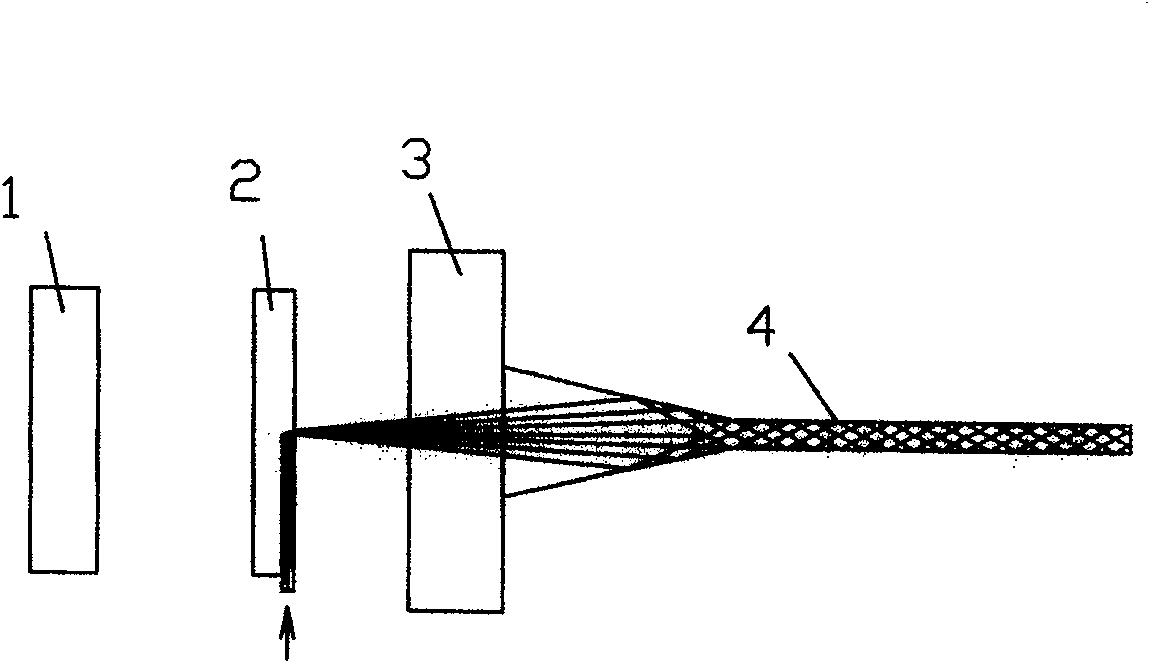
[0037] Example 1, see Figure 1-2 . The thickness of the waveguide 4 in the sensing working area of the present invention is about 30 μm, and the width of the waveguide in the vertical direction is large enough so that each slot can be considered as an anti-resonant planar waveguide. In the middle of the back of the sensor head is a conical microlens light-collecting area, so that the incident light enters the waveguide in the sensing area at an appropriate angle. The third part is an aspheric microlens 1, which is used to collect the fluorescent signal output from the sensing waveguide. Its working principle is as follows: a laser diode is used as a light source, and a self-focusing microlens is used to couple the laser beam into an anti-resonant planar waveguide. The 45° notch is plated with a reflective mirror to form a point light source on the axis of the molded waveguide. This injection of the laser beam at 90° to the axis makes the incident light and the fluorescent ...
Embodiment 2
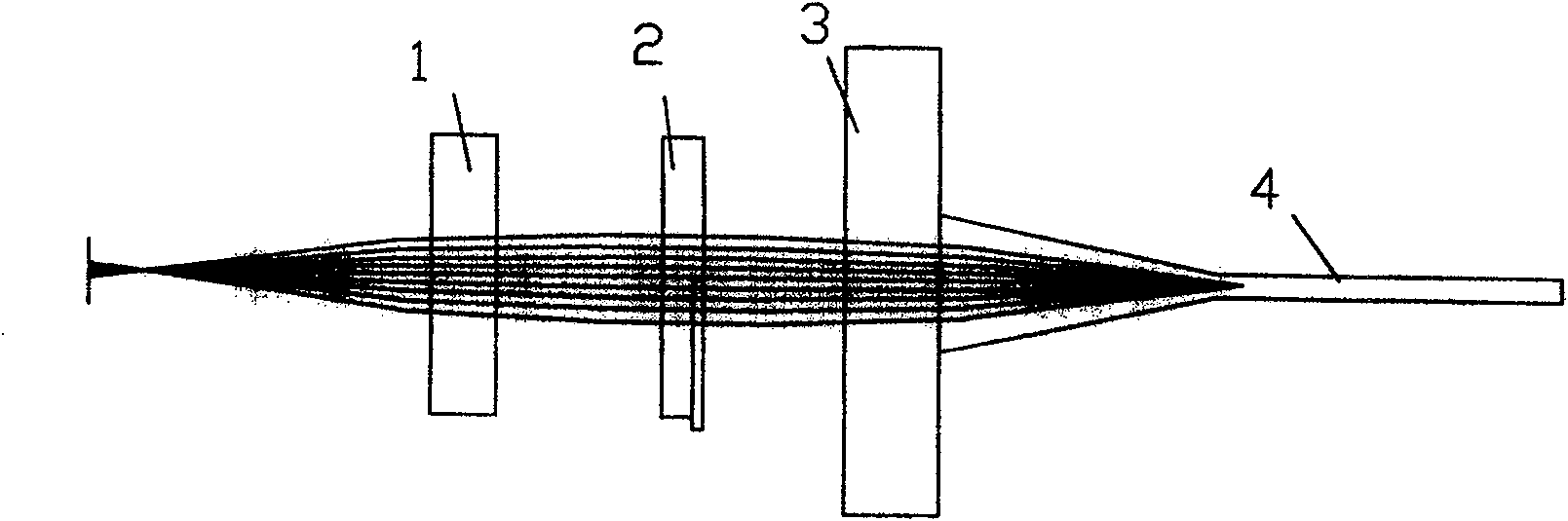
[0040] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the laser is coupled into the waveguide by a bypass, such as image 3 .
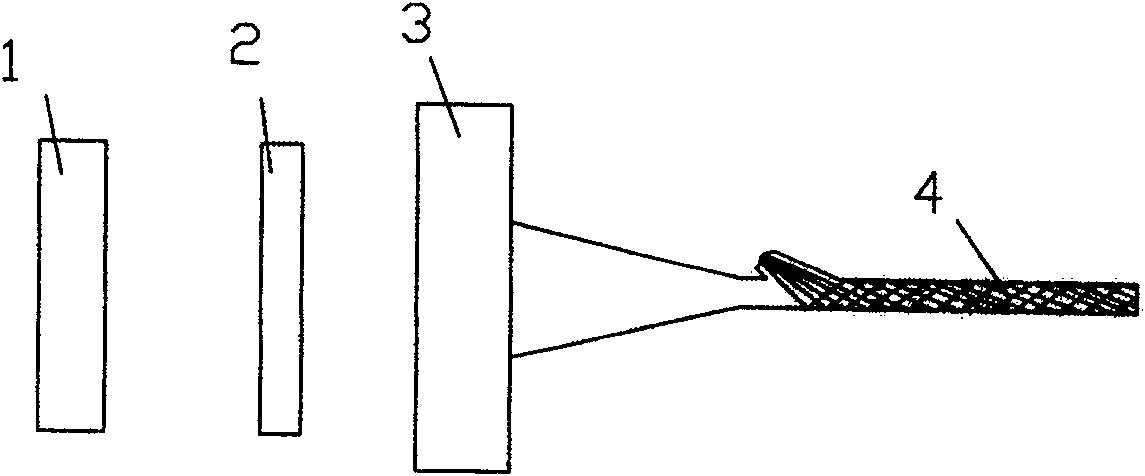
[0041] The substance solution to be tested in the present invention and the high and low optical materials together form the ARROW waveguide, such as Figure 4 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com