Uninterruptible power supply
A technology of power supply and DC power supply, which is applied in the direction of current collectors, electric vehicles, electrical components, etc., and can solve problems such as low utilization rate of inductance, out-of-control fluctuation of bus capacitor voltage, and large filter volume, so as to prevent unbalanced bus voltage and reduce Bus voltage ripple, effect of reducing filter volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
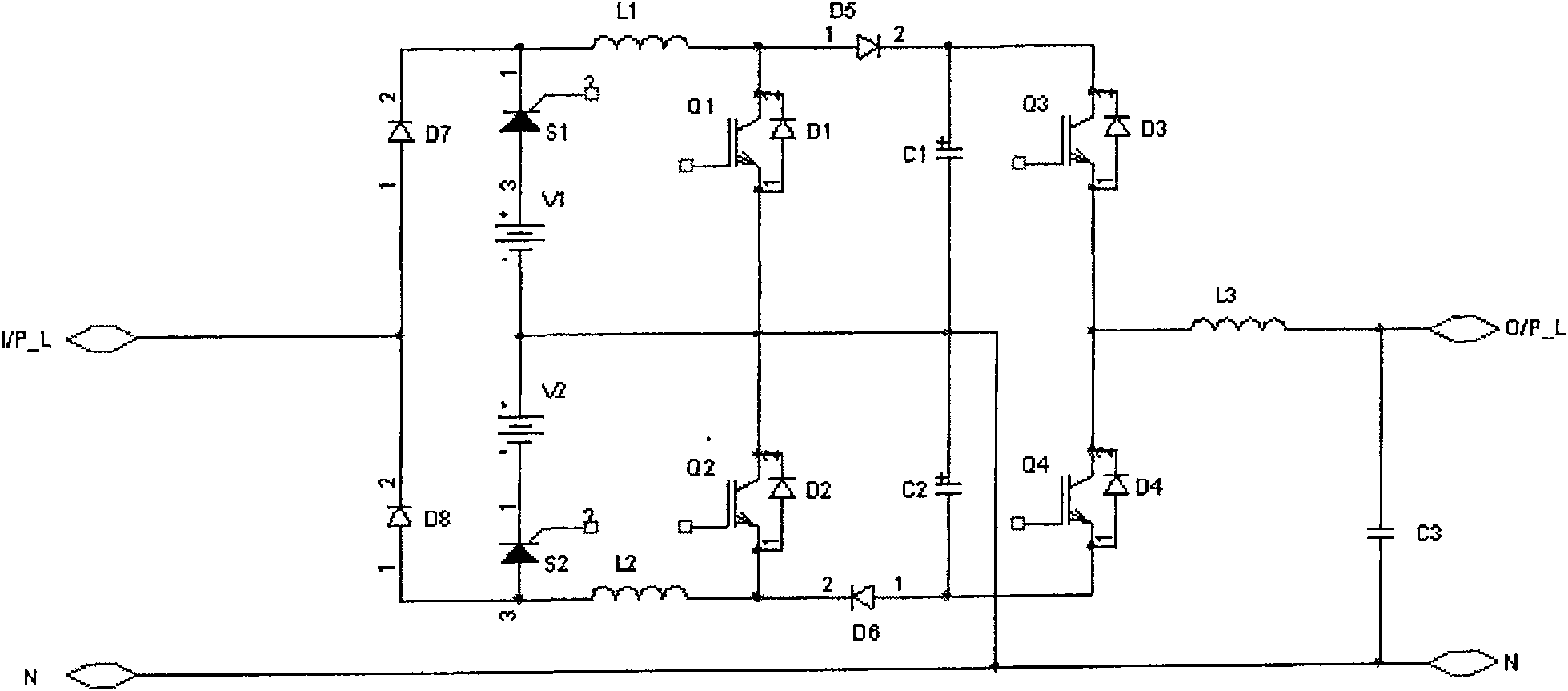
[0030] Such as figure 2 As shown, an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) includes an AC power input, a DC power supply, a controllable switch, a boost module and an inverter module, and the controllable switch is configured to selectively input AC power or The DC power supply is connected to the boost module, and the boost module is used to boost the AC power input or the input voltage provided by the DC power supply and output it to the inverter module, and the inverter module is used to output the boost module The voltage is converted into an AC voltage output. The DC power supply is composed of a group of batteries BAT, and the boost module includes an inductor L1, a first switching tube Q1, a second switching tube Q2, a first capacitor C1, a second capacitor C2, a rectifier tube D11, a twelfth Diode D12, third diode D3 and fourth diode D4. The rectifier is a diode. The twelfth diode D12 is used to prevent current from flowing through the first switch tube Q1 when the AC...
specific Embodiment approach 2
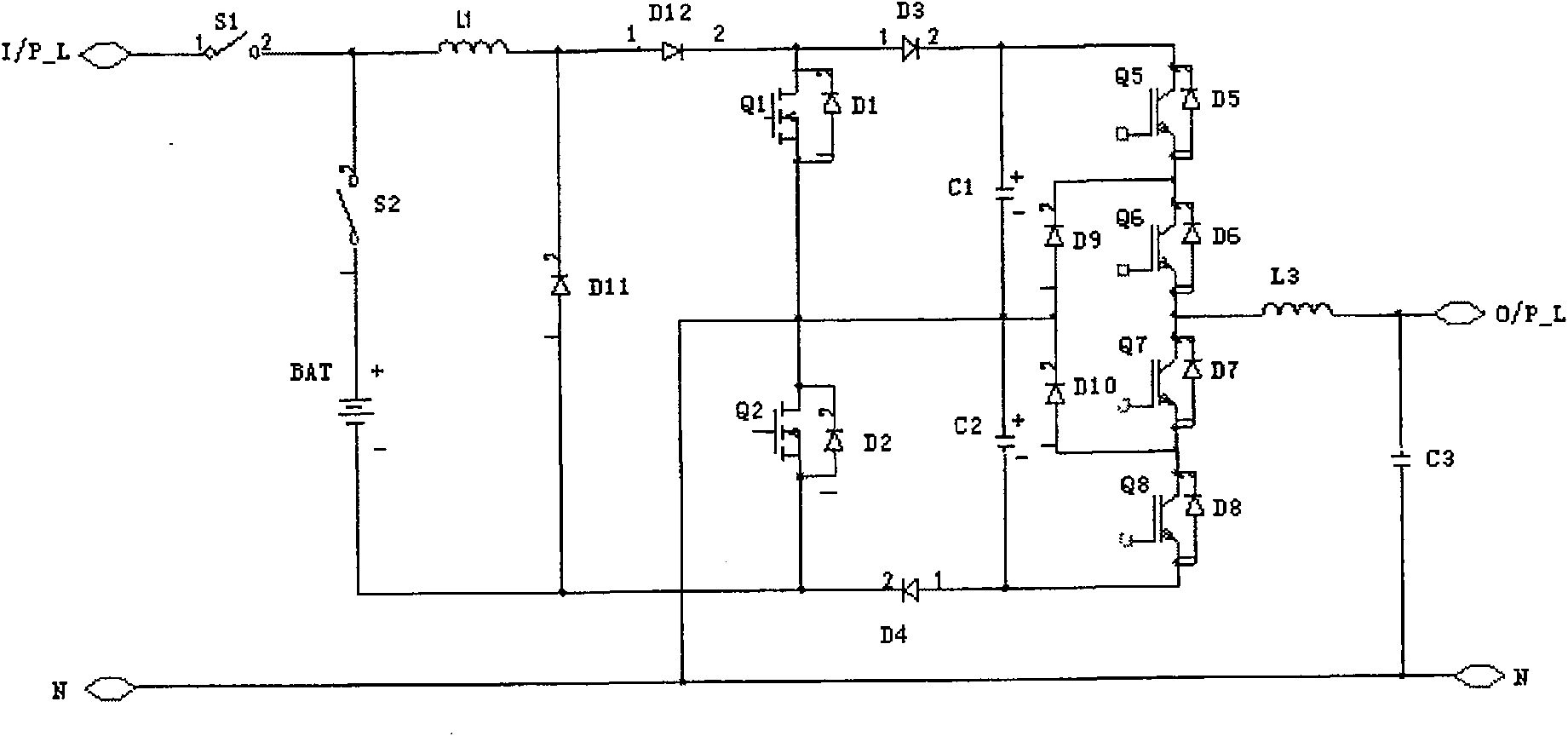
[0048] Such as Figure 11 As shown, the difference between this specific embodiment and the first specific embodiment is that the position of the twelfth diode D12 is changed. In this specific embodiment, the twelfth diode D12 is moved to the first switch tube Between the source of Q1 and the drain of the second switching transistor Q2. That is: the anode of the twelfth diode D12 is connected to the source of the first switching tube Q1, and the cathode of the twelfth diode D12 is connected to the drain of the second switching tube Q2 and the neutral line N of the AC power input. In this way, when the first switch tube Q1 is turned off and the third diode D3 is turned on, a diode loss can be saved.
specific Embodiment approach 3
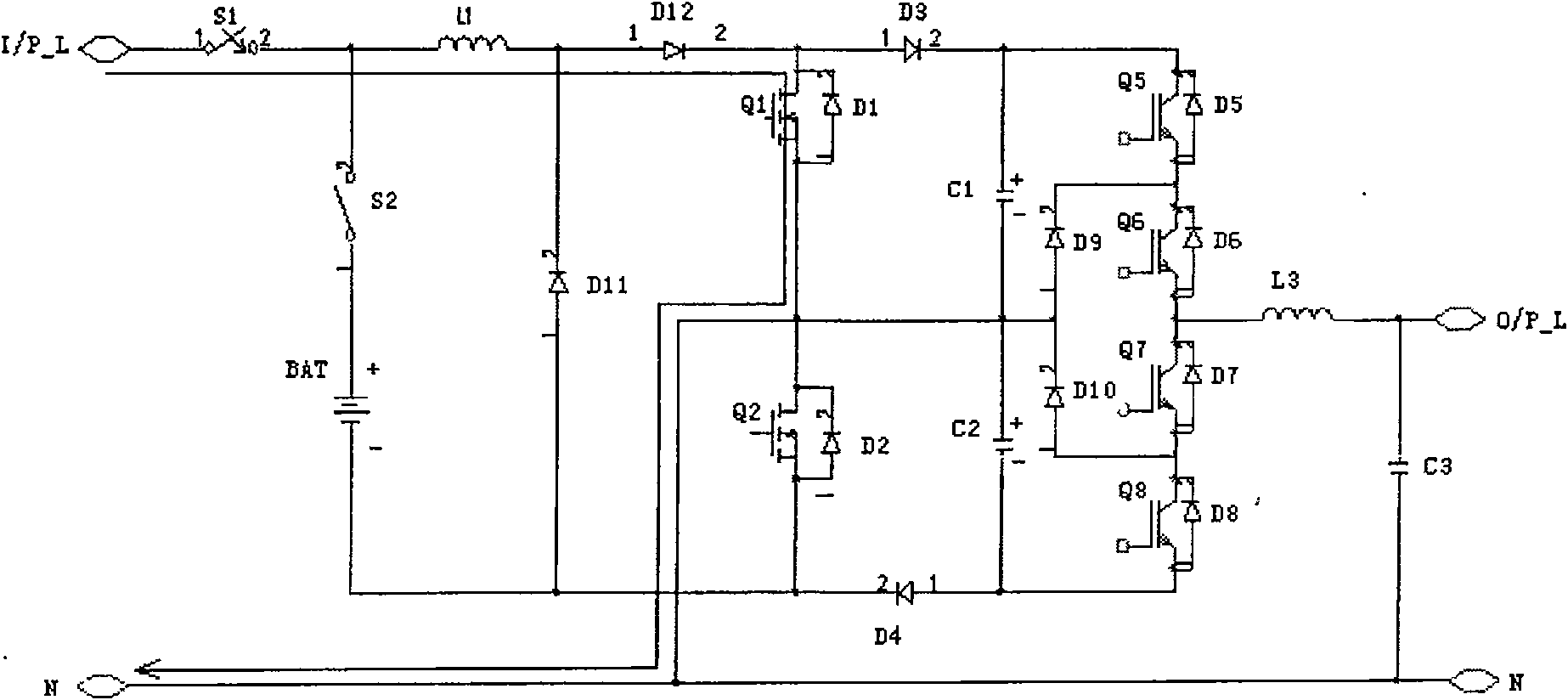
[0049] Such as Figure 12 As shown, the difference between the present embodiment and the second embodiment is that the rectifier uses a power field effect transistor (MOS) with a body diode or an insulated gate bipolar transistor (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor, IGBT for short) with a body diode. ) instead. In the mains mode, the body diode D11 of the transistor Q11 is used as a rectifier diode; in the battery mode, the inductance L1 is charged and discharged by controlling the opening and closing of the Q11, and Figure 11 Compared with charging and discharging the inductor L1 by controlling the on-off of the first switching tube Q1 and the second switching tube Q2, the loss of another MOS tube can be saved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com