Sequencing method for reverse hybridized coupling extended DNA
A DNA sequencing and DNA sequence technology, applied in the field of DNA sequencing, can solve the problems of false positives and high cost, large amount of probe synthesis, and high false positives, and achieves solutions to false positives and high cost, reliable accuracy and low cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
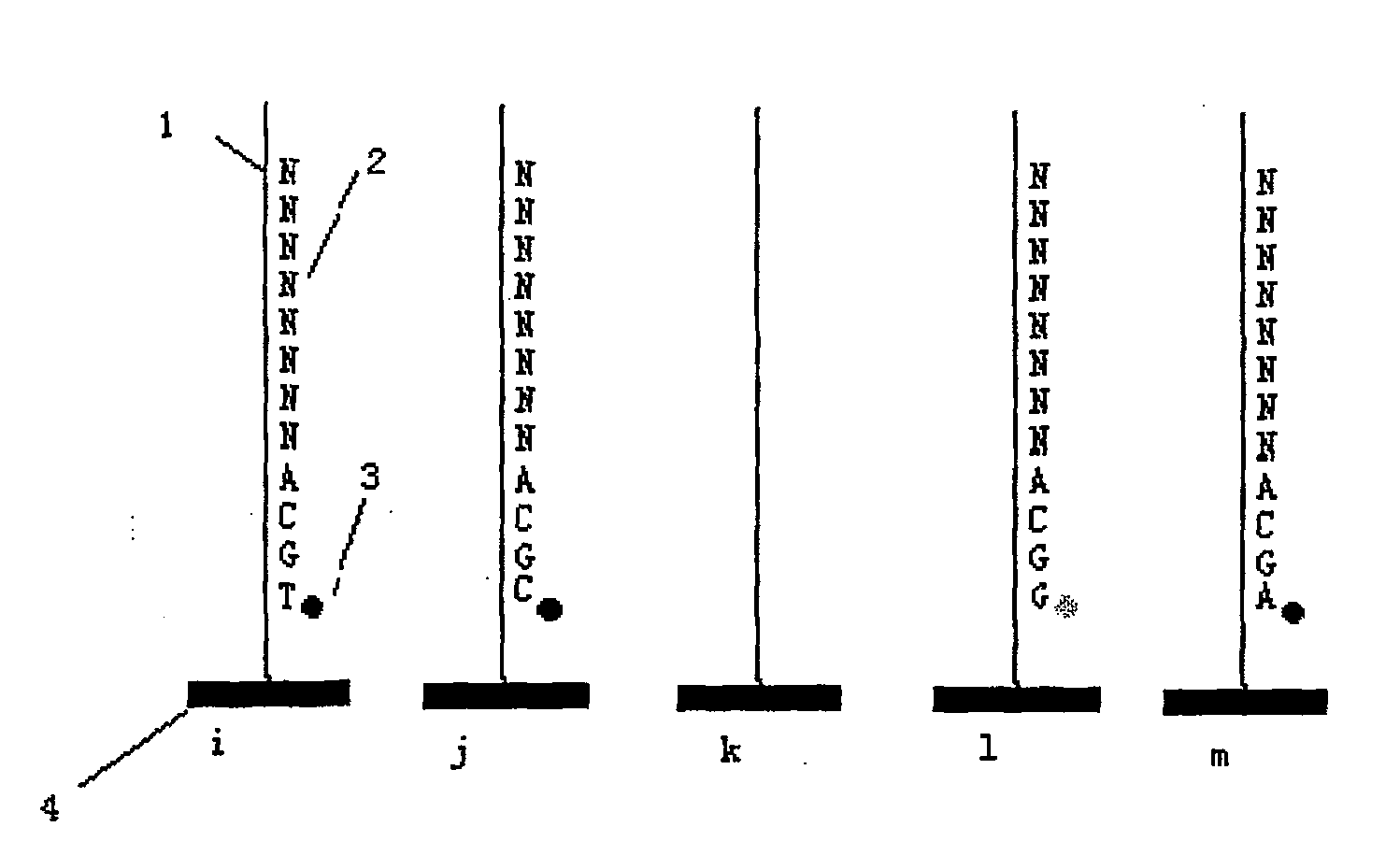
[0035] A DNA sequence to be tested is amplified by conventional PCR and fixed on an acrylamide substrate to make an unknown DNA template. Prepare 64 hybrid primers, with three known bases at the 3' end and 8 bases at the 5' end. The sequence characteristics of the hybrid primers can be expressed as 5'NNNNNNNNNXYZ 3', where N is four bases T, A , any one of G, C not limited, or can be replaced by universal base I, X, Y, Z are all selected from T, A, G, a certain base in C, such as NNNNNNNNACG, NNNNNNNNGAG etc., XYZ constituted 64 different sequences in the hybridization primers.
[0036] 1) Hybridization: hybridize the hybridization primer NNNNNNNNACG with the immobilized unknown DNA template. Dissolve the hybridization primers at 100uM concentration in 1X hybridization solution, take an appropriate amount (submerge the template to be tested completely) and place the hybridization primers in the template to be tested, denature at 60°C for 2 minutes, then anneal at 4°C for 3 mi...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Whole-genome sequencing of a single human by reverse hybridization-coupled extension DNA sequencing
[0044] DNA templates can be prepared as follows:
[0045] 1. Extract the human genome.
[0046] 2. DNA fragmentation. Use ultrasonic treatment to make the average size of DNA around 50bp.
[0047] 3. Add linker primer a. Firstly, the fragmented genomic DNA is blunted with polymerase, and its 3-terminus is treated with a protruding A. Then, under the action of ligase, the linker primer with the Mme I endonuclease recognition site is connected to the small fragment of DNA.
[0048] 4. Enzyme digestion treatment. Under the action of Mme I endonuclease, cut the whole genome into a genomic library with a fragment size of 19 bp.
[0049] 5. Same as step 3, add adapter primer b to the other end.
[0050] 6. Microemulsion PCR amplifies a single-clonal genome library.
[0051] 7. Whole genome microarray fabrication. Fix the amplified product from the previous step on an...
Embodiment 3
[0054] RNA Expression Profiling by Reverse Hybridization Coupled with Extended DNA Sequencing
[0055] DNA templates can be prepared as follows:
[0056] 1. Extract mRNA from normal cells and diseased cells respectively, and use magnetic beads to fix 30 T nucleotide chains to purify mRNA so that the magnetic beads can absorb mRNA.
[0057] 2. Reverse transcribe into cDNA, and use RNaseH, DNA polymerase, etc. to synthesize the second strand.
[0058] 3. Digest the product of step 2 with an endonuclease (Sau 3AI) that recognizes four bases. Wash the magnetic beads with binding buffer.
[0059] 4. Add linker primer A (with endonuclease Acu I recognition site on the primer) under the action of ligase.
[0060] 5. Digest the product of step 4 with Acu I. A cDNA library of adapter primer A followed by 16 unknown sequences to be tested was obtained.
[0061] 6. Add another linker primer B. Amplification was then performed using emulsion PCR.
[0062] 7. The amplified product i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com