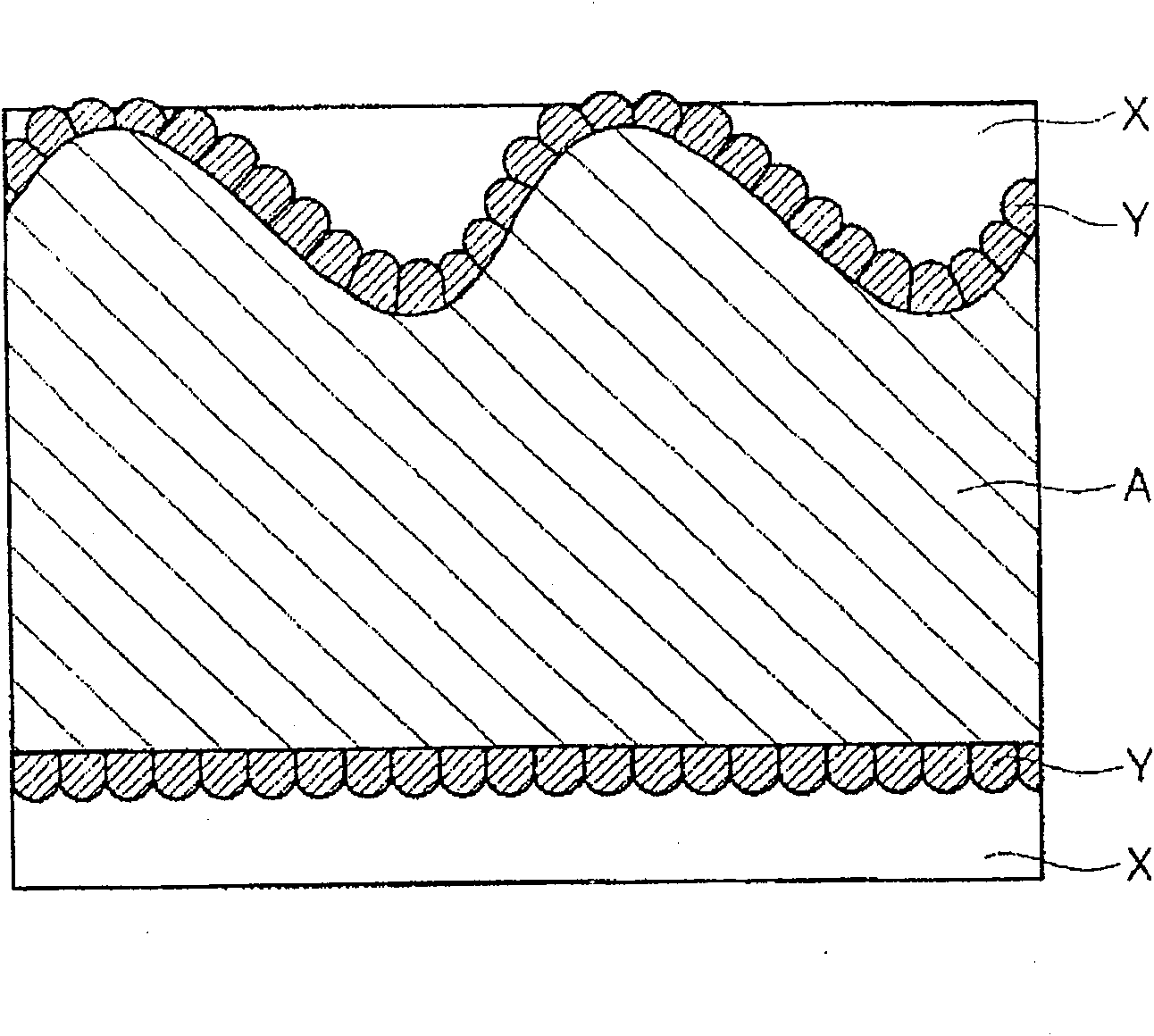
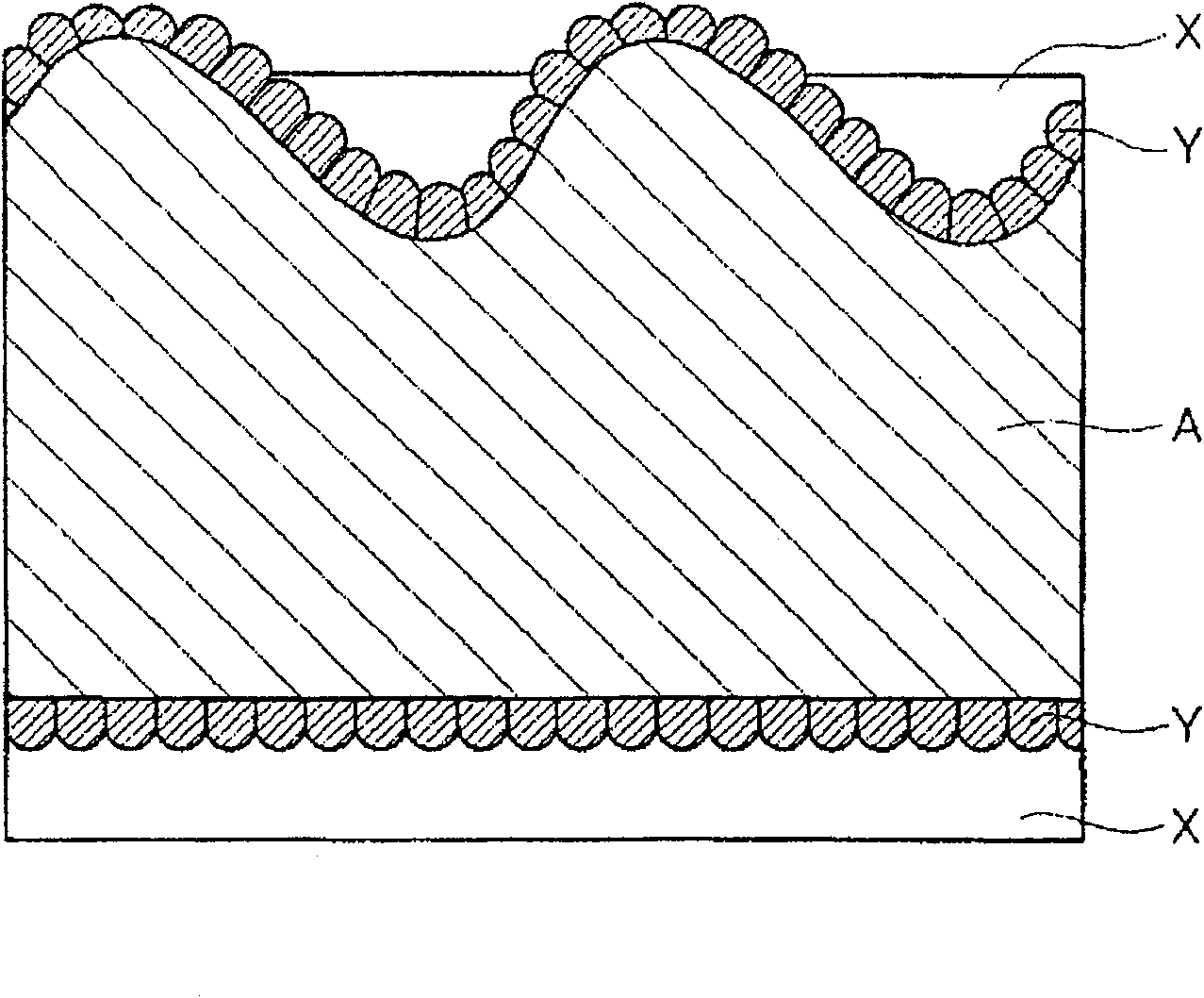
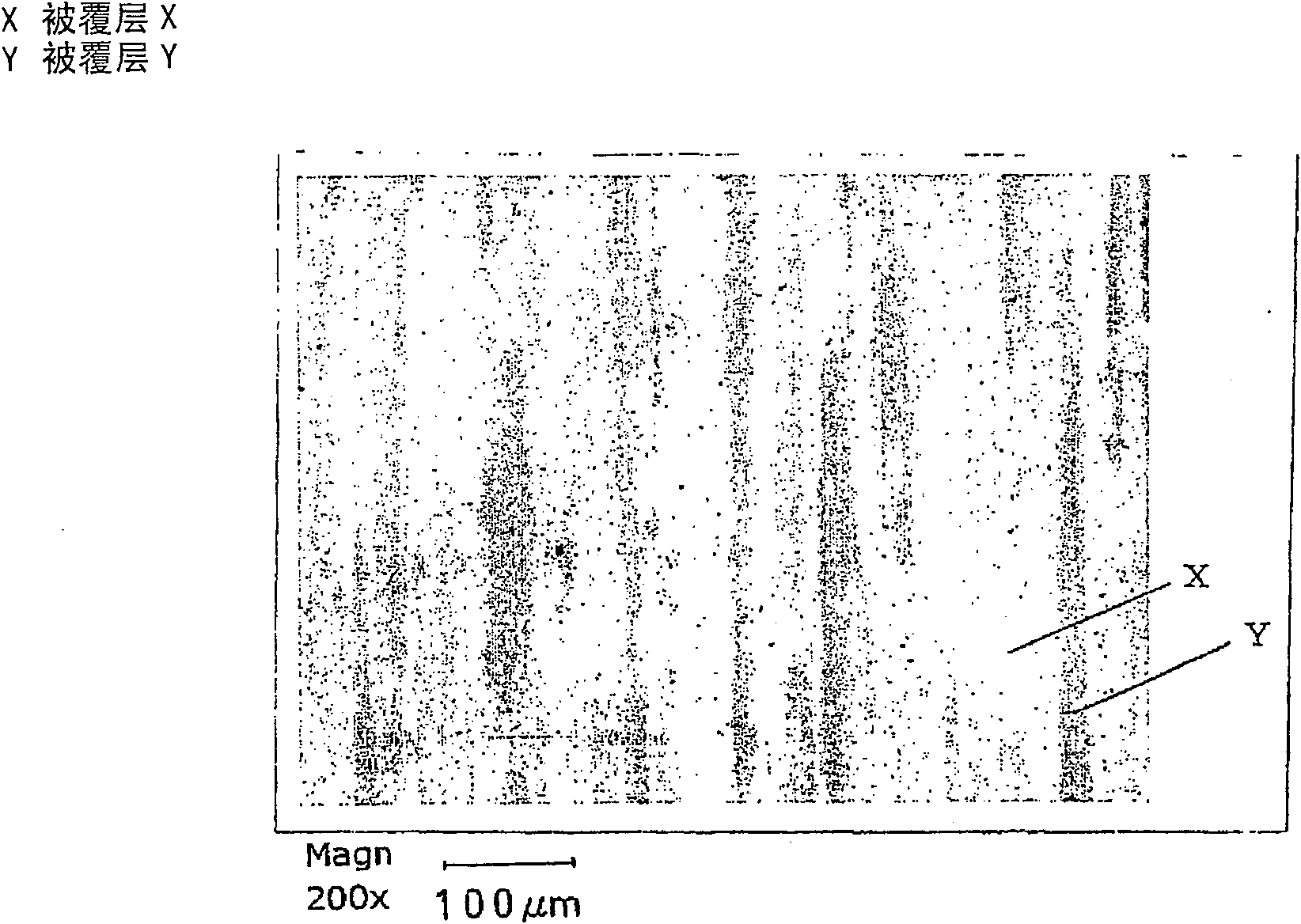
Conductive material for connecting part and method for manufacturing the conductive material
A technology for connecting parts and conductive materials, applied in the field of conductive materials for connecting parts, can solve the problems of micro-sliding wear, corrosion resistance and solderability reduction, terminal insertion force reduction, etc., and achieves low contact resistance, excellent electrical properties. Reliability and friction coefficient reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] [Production of Cu alloy base material]
[0096] Table 1 shows the chemical components of Cu alloys (No. 1, 2) used. In this example, these Cu alloys were subjected to surface roughening treatment by mechanical means (rolling or grinding) to a Cu alloy base material having a thickness of 0.25 mm and a predetermined surface roughness. In addition, the surface roughness was measured in the following manner.
[0097] [Measurement method of surface roughness of Cu alloy base material]
[0098] It measured based on JISB0601-1994 using the contact surface roughness meter (Tokyo Seiki Co., Ltd., SURFCOM1400). The surface roughness measurement conditions were as follows: a cutoff value of 0.8 mm, a reference length of 0.8 mm, an evaluation length of 4.0 mm, a measurement speed of 0.3 mm / s, and a stylus tip radius of 5 μmR. In addition, the surface roughness measurement direction is a direction at right angles to the rolling or polishing direction performed during the surface ...
Embodiment 2
[0132] For each base material of Cu alloy No. 1 that has undergone surface roughening treatment, Cu plating with a thickness of 0.15 μm is applied, and after Sn plating with various thicknesses is performed, reflow treatment is performed at 280°C for 10 seconds. Thus, test materials (No. 11-19) were obtained. Table 4 shows the production conditions thereof. In addition, among the surface roughness parameters of the base material, the average interval Sm with respect to unevenness is all within the above-described preferable range (0.01 to 0.5 mm). In addition, the average thickness of the Cu plating and Sn plating described in Table 4 was measured in the same manner as in Example 1 above.
[0133] [Table 4]
[0134]
[0135] Next, Table 5 shows the structure of the coating layer of the obtained test material. The average thickness of the Cu—Sn alloy coating layer, the Cu content, the exposed area ratio, and the average thickness of the Sn coating layer were measured in t...
Embodiment 3
[0142] For the base material of Cu alloy No. 1 with surface roughening treatment, Cu plating with a thickness of 0.15 μm was applied, and Sn plating with various thicknesses was applied, and various reflow treatments were performed to obtain test materials. (No. 20-26). Table 6 shows the production conditions thereof. In addition, among the surface roughness parameters of the base material, the average interval Sm with respect to unevenness is all within the above-described preferable range (0.01 to 0.5 mm). In addition, the average thickness of the Cu plating and Sn plating described in Table 6 was measured in the same manner as in Example 1 above.
[0143] [Table 6]
[0144]
[0145] Next, Table 7 shows the structure of the coating layer of the obtained test material. In addition, the average thickness of the Cu—Sn alloy coating layer, the Cu content, the exposed area ratio, and the average thickness of the Sn coating layer were measured in the same manner as in Exampl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com