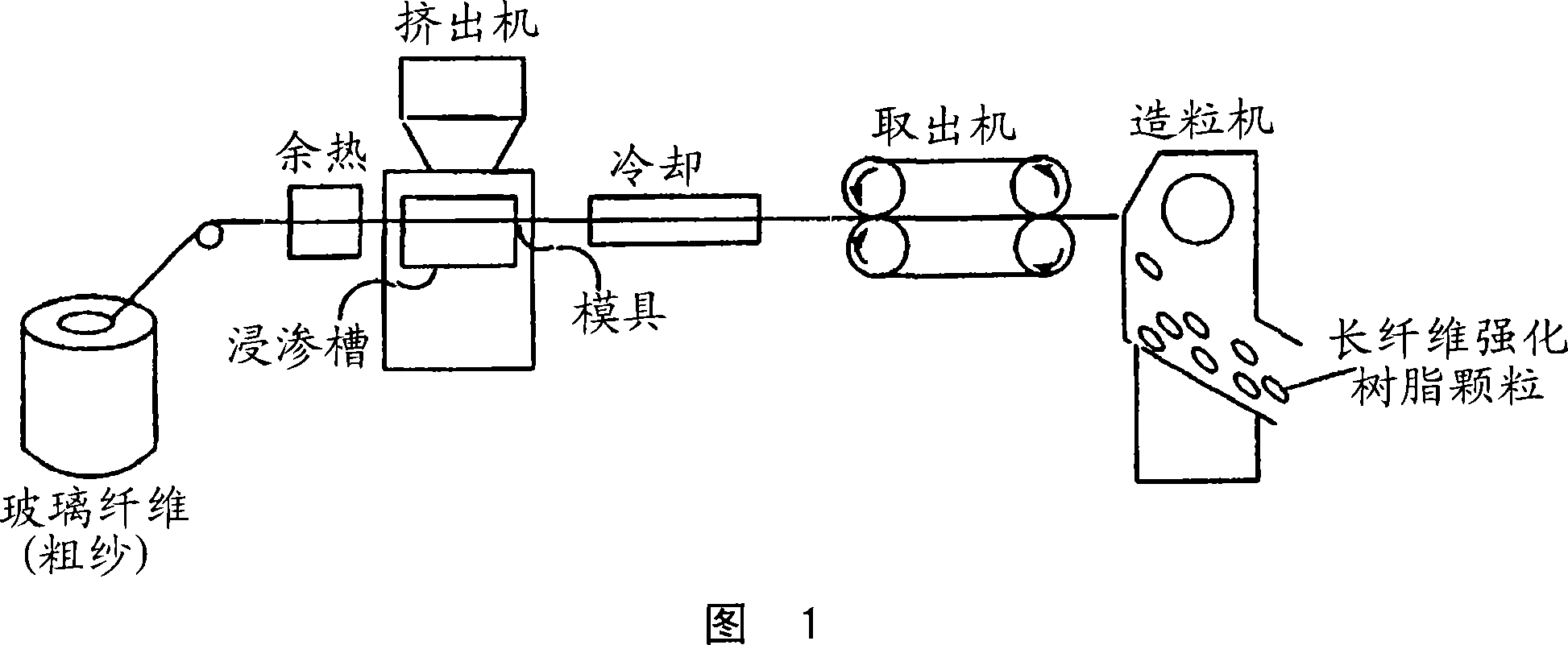
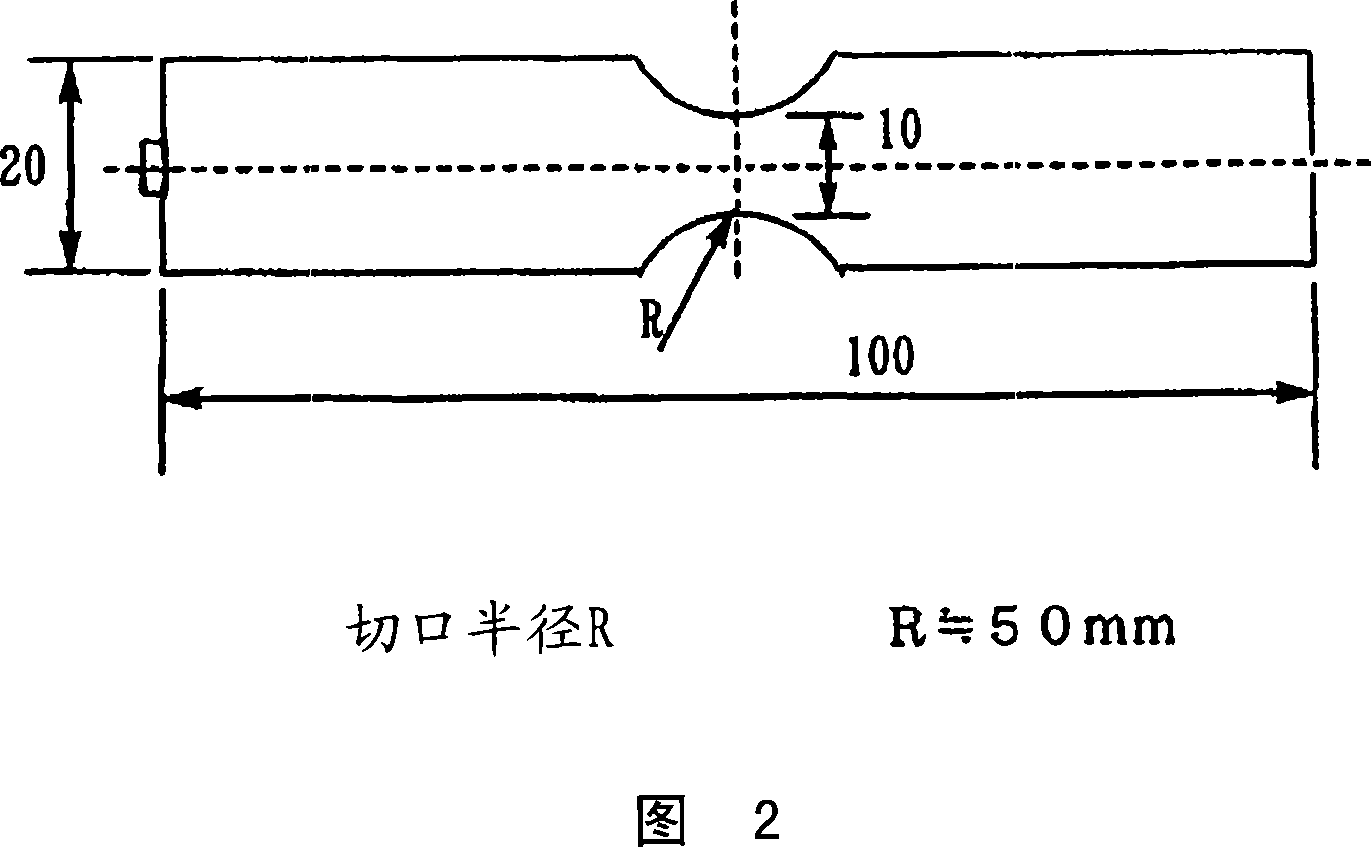
Modified polyolefin-based resin for treating glass fiber, surface-treated glass fiber and fiber-reinforced polyolefin-based resin
一种聚烯烃类树脂、酸改性聚烯烃的技术,应用在薄料处理、运输和包装等方向,能够解决界面研究、研究例子少、未能得到优异性能等问题,达到高可靠性、振动疲劳强度提高的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0129] (I-4) Preparation method of acid-modified polyolefin resin
[0130] As a method for preparing acid-modified polyolefin resins (polyolefin resins containing functional groups), Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 8-143739, Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 2002-20560, Japanese Patent Application Publication No. 7-316239, Known methods described in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 8-127697 and Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 7-232324.
[0131] The preparation method is not particularly limited. When the maleic acid modified polypropylene resin is prepared, for example,
[0132] (1) Reacting organic peroxides, maleic acid, and polypropylene in a solvent (solution method);
[0133] (2) Use Banbury mixer or extruder to melt and mix organic peroxide, maleic acid and polypropylene (melting method);
[0134] (3) Methods such as reacting maleic acid with thermally decomposed polypropylene (thermal decomposition method), (1) solution method, (3) thermal decomposition metho...
preparation example 1
[0292] Preparation Example 1: Acid-modified polypropylene resin for treating glass fiber
[0293] (1) Preparation of maleic acid modified polypropylene (EM)
[0294] (1-1) Modification method-1: Melting method (EM-1~9, EM-11 and EM-12)
[0295] As shown in Table 2 below, polypropylene, maleic acid, and organic peroxide were put into a twin-screw extruder with vents, and melt-kneaded under specified conditions to obtain maleic acid-modified polypropylene.
[0296] The components that can be extracted with boiling methyl ethyl ketone contained in the obtained maleic acid-modified polypropylene are removed by the following purification method or washing method.
[0297] (1-2) Purification method (EM-1~8)
[0298] The maleic acid-modified polypropylene obtained above was heated (about 130°C) while stirring in p-xylene to completely dissolve it, and the solution was poured into methyl ethyl ketone for reprecipitation. After filtration, vacuum drying (130°C x 6 hours) was performed.
[...
manufacture example 2
[0364] Production Example 2: Production of surface-treated glass fiber (GFEM)
[0365] As shown in Table 4 below, a sizing agent containing maleic acid-modified polypropylene and a silane coupling agent for glass fiber treatment prepared by the above-mentioned production example 1 was used to treat E-glass fibers with a diameter of 17 μm (specific gravity 2.55 g / cm 3 ) After heating and drying, the roving is made.
[0366] [Table 4]
[0367] Sizing agent
Of treated glass fiber
EM adhesion amount
(Mass%)
(CP)
Surface treatment resin
(EM)
Proportion
EM / CP
GFEM-1
CP-1
EM-1
6
0.40
GFEM-2
CP-1
EM-1
6
0.40
GFEM-3
CP-2
EM-1
6
0.40
GFEM-4
CP-1
EM-2
6
0.40
GFEM-5
CP-1
EM-3
6
0.40
GFEM-6
CP-1
EM-4
6
0.40
GFEM-7
CP-1
EM-5
6
0.40
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com