Method for treating development waste liquid
A treatment method and developing solution technology, applied in heating water/sewage treatment, electrochemical water/sewage treatment, photography, etc., can solve problems such as obstacles to long-term stable operation, low purity of TAA hydroxide aqueous solution, and rise in electrolyzer voltage , to achieve the effect of safe and effective disposal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
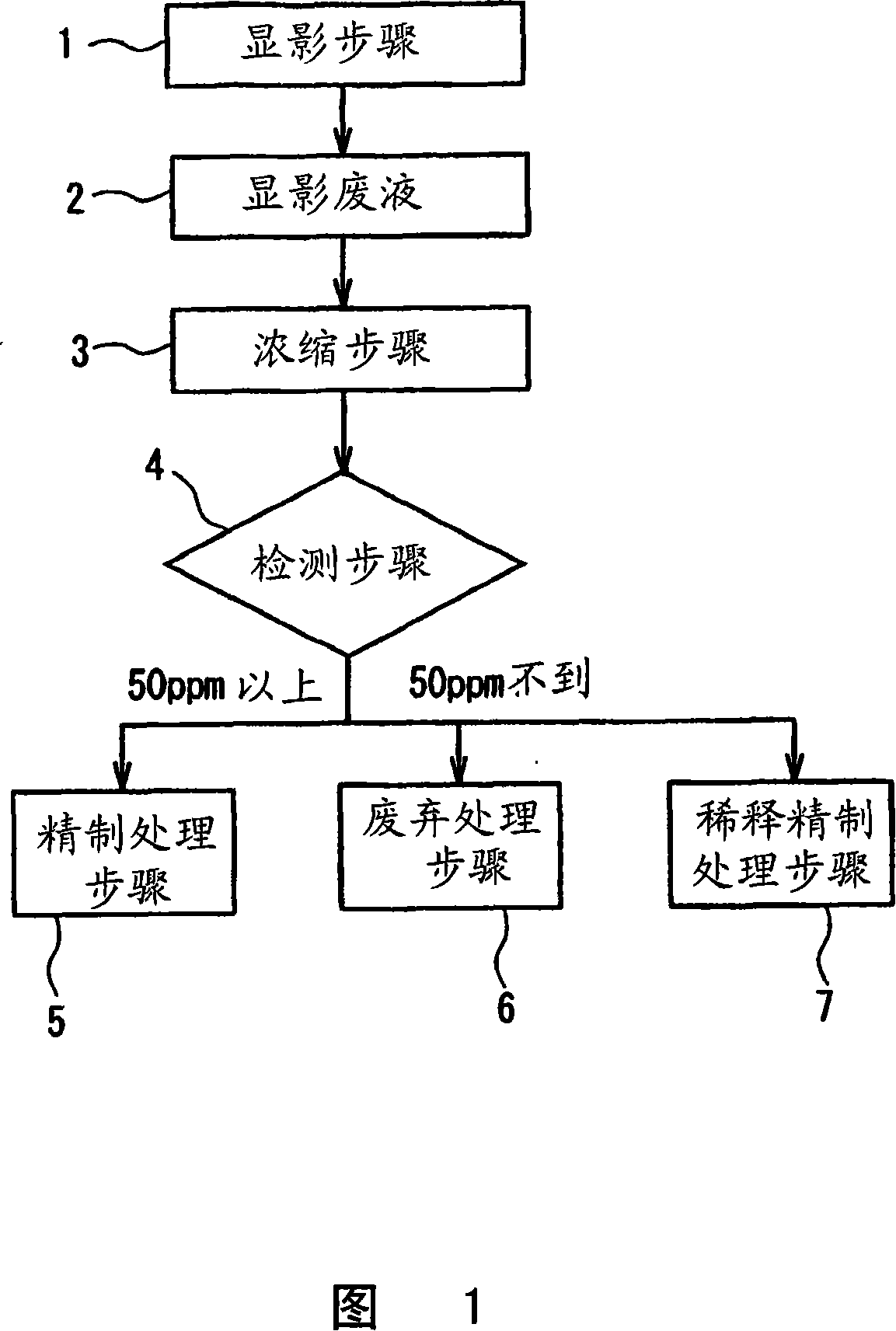
[0076] Using the thin-film concentrator 3, the liquid containing the photoresist and the tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) solution discharged from the developing step 1 of the liquid crystal display (LCD) factory was concentrated at a liquid temperature of 60° C. under a reduced pressure of 20 kPa. The waste liquid 2 was developed to obtain a brown concentrated liquid (1).
[0077] The various components of the obtained concentrate (1) were analyzed, and the results are shown below.
[0078] TMAH concentration: 20.6wt%
[0079] Concentration of metal impurities:
[0080] Al: 3800ppb (unit TAA is 22.7ppm)
[0081] Na: 40ppb (unit TAA is 0.24ppm)
[0082] Cu: 650ppb (unit TAA is 3.88ppm)
[0083] Fe: 800ppb (unit TAA is 4.78ppm)
[0084] The total content of unit TAA: 31.60ppm
[0085] Total concentration of organic impurities: 3800ppm
[0086] The TMAH concentration was measured by potentiometric titration, the metal concentration was measured by ICP-MS, and the tota...
Embodiment 2
[0128] The concentrate (2) of Comparative Example 1 was diluted by adding a high-purity TMAH aqueous solution. The analysis results of the high-purity TMAH aqueous solution and diluent used are as follows.
[0129] High-purity TMAH aqueous solution
[0130] TMAH concentration: 20.1wt%
[0131] Al: less than 5ppb
[0132] Na: less than 5ppb
[0133] Cu: below 5ppb
[0134] Fe: below 5ppb
[0135] Total concentration of organic impurities: below 10ppm
[0136] Diluent
[0137] TMAH concentration: 20.3wt%
[0138] Al: 6000ppb (unit TAA is 36.3ppm)
[0139] Na: 60ppb (unit TAA is 0.36ppm)
[0140] Cu: 2100ppb (unit TAA is 12.7ppm)
[0141] Fe: 1500ppb (unit TAA is 9.01ppm)
[0142] The total content of unit TAA: 58.37ppm
[0143] Total concentration of organic impurities: 3800ppm
[0144] The content of each metal impurity in this diluted solution is below the reference value (50 ppm) of the present invention.
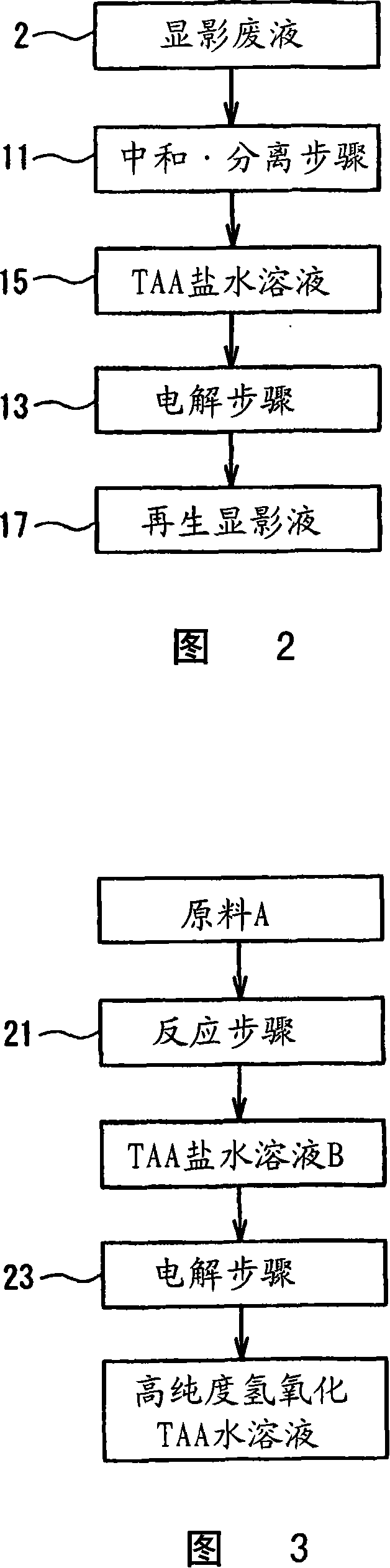
[0145] Using this diluted solution, neutralization, sep...
Embodiment 3
[0156] The concentrated solution (2) (developing waste solution) of Comparative Example 1 was supplied in the form of droplets or mist at the positions shown in Table 1 in the cement manufacturing process (while giving the temperature). In addition, the input amount of developing waste liquid is 10g / Nm relative to the gas flow rate at the input position. 3 Continuous supply from left to right.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com