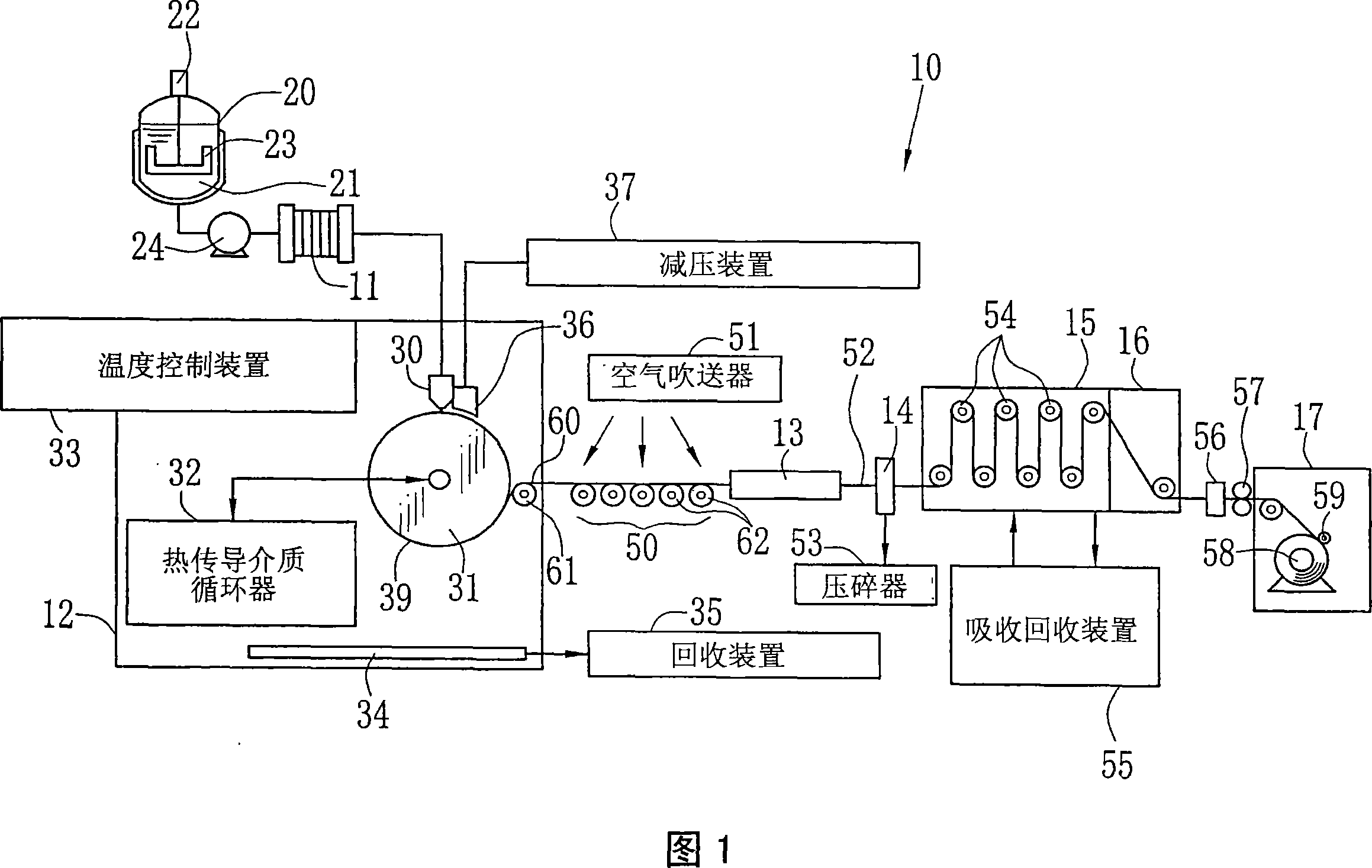
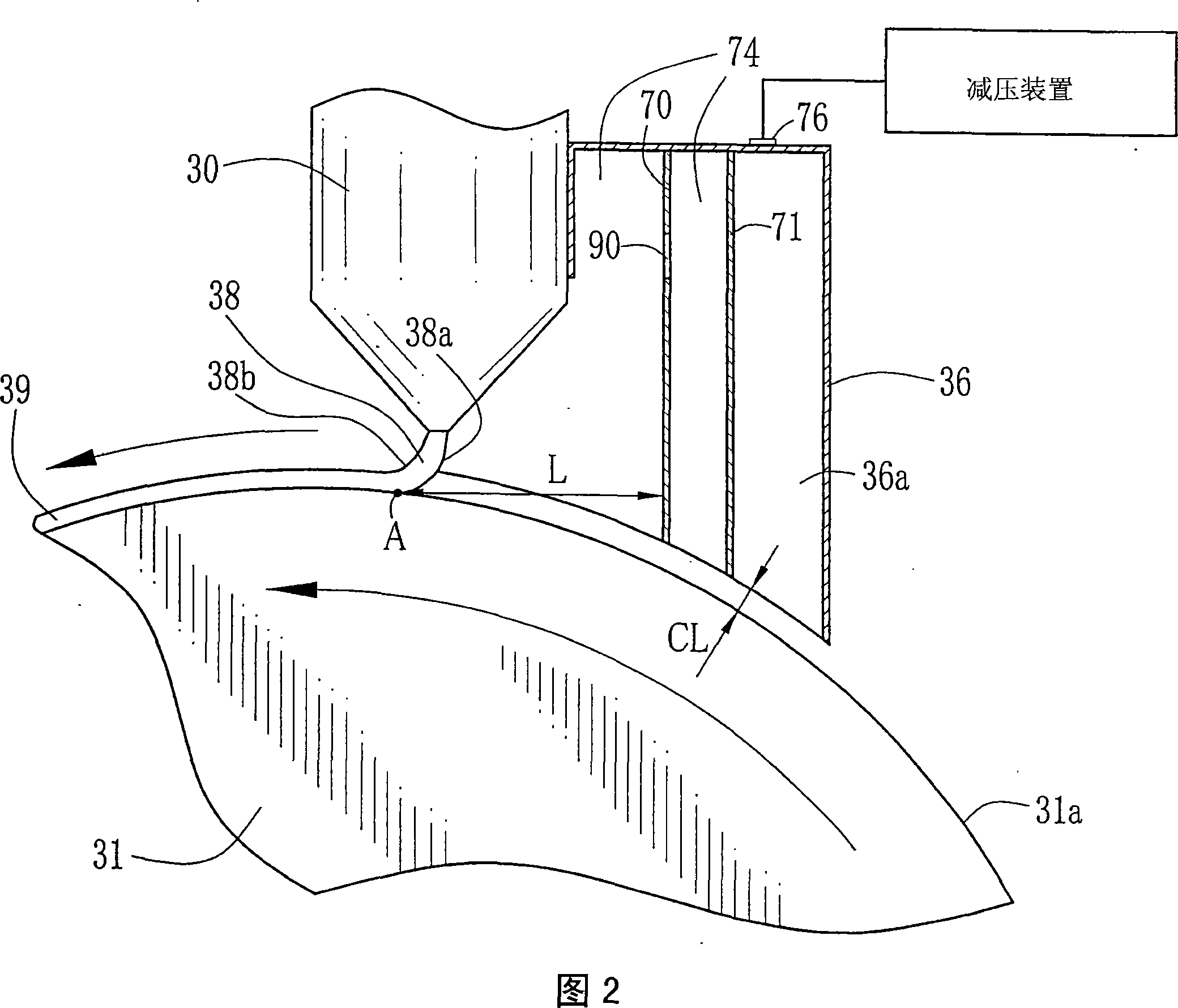
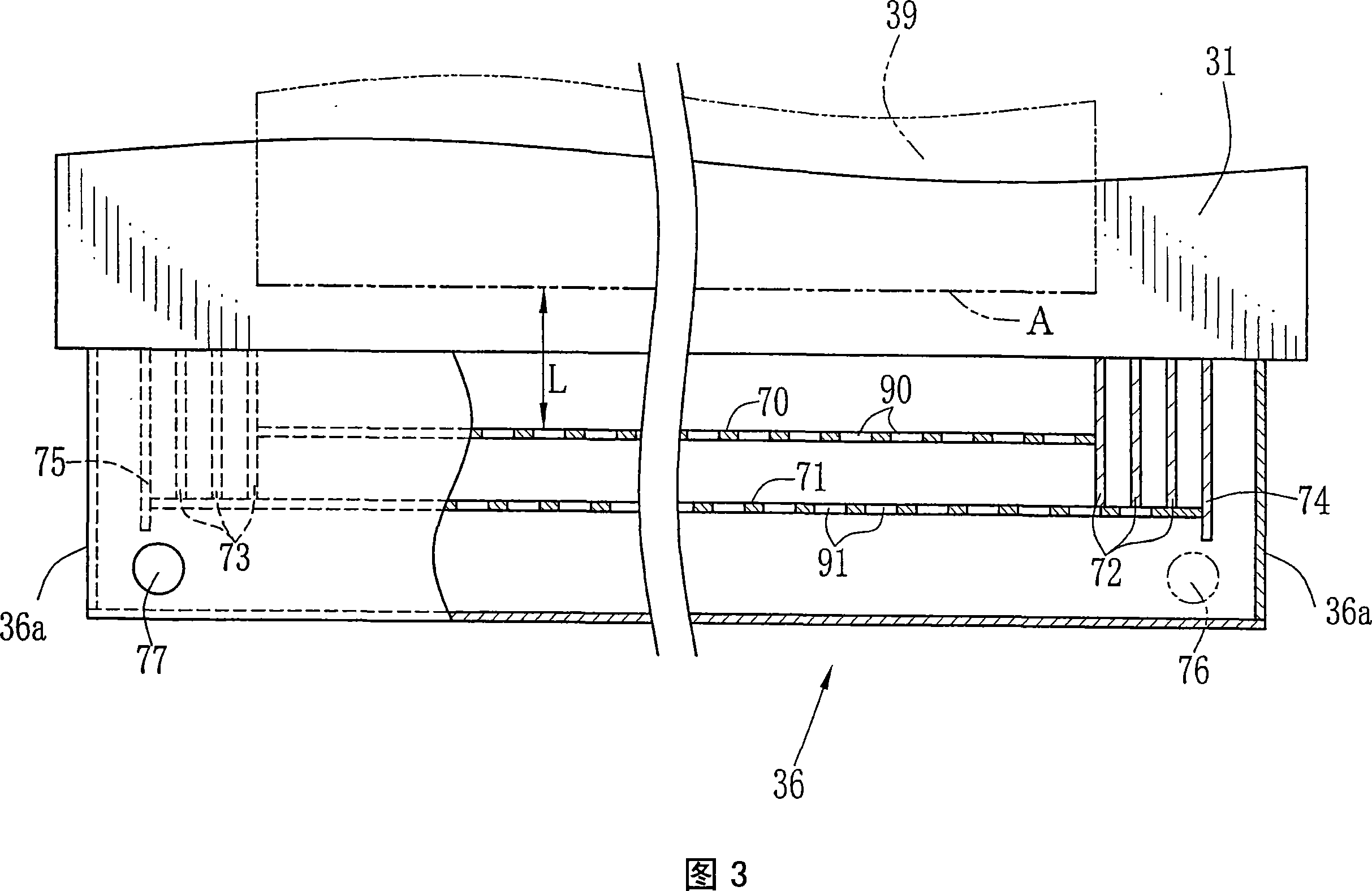
Solution casting method of film
A solution and casting liquid technology, applied in the field of film manufacturing, can solve the problems of film surface deterioration, difficulty, uneven film thickness, etc., and achieve the effects of helping air flow control, reducing trouble, and preventing unevenness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] Example 1 is described below. However, the present invention is not limited to Example 1. Note that a detailed explanation is given in Experiment 1. Regarding Experiments 2 to 17 according to the present invention and Comparative Experiment 18, the experimental conditions are shown in Table 1 together with the results.
[0094] The raw material used for each mass part of embodiment 1 is as follows:
[0095] [Element]
[0096] Cellulose triacetate (microparticle, its degree of substitution is 2.84, the viscosity-average degree of polymerization is 306, the moisture content is 0.2% (mass), the viscosity of the dichloromethane solution of 6% (mass) is 315mPa·s, and the average particle diameter is 1.5mm and the average deviation of particle size is 0.5mm)
[0097] 100 parts by mass
[0098] Dichloromethane (first solvent) 384 parts by mass
[0099] Methanol (second solvent) 94 parts by mass
[0100] 1-butanol (the third solvent) 2 parts by mass
[0101] Plasticizer...
Embodiment 2
[0144] Embodiment 2 is described below. However, the present invention is not limited to Example 2. Note that this is described in detail in Trial 19. However, the description of the same test conditions as Test 1 is omitted. Furthermore, with regard to Tests 20 to 27 according to the present invention and Comparative Test 28, the experimental conditions and results are shown together in Table 2 below.
[0145] Each part by mass of raw materials used in Test 19 is shown below.
[0146] [Element]
[0147] Cellulose triacetate (the degree of substitution is 2.83, the viscosity-average degree of polymerization is 320, the moisture content is 0.4% (mass), and the viscosity of a 6% dichloromethane solution with a mass content is 305mPa·s)
[0148] 28 parts by mass
[0149] 75 parts by mass of methyl acetate
[0150] Cyclopentanone 10 parts by mass
[0151] Acetone 5 parts by mass
[0152] Methanol 5 parts by mass
[0153] 5 parts by mass of ethanol
[0154] Plasticizer A ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com