Ecological agriculture domestic fungus resource cyclic utilization method
A technology of ecological agriculture and edible fungi, applied in agriculture, application, preparation of organic fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems of loss of nutrients, pollution of drinking water sources, unreasonable agricultural production methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
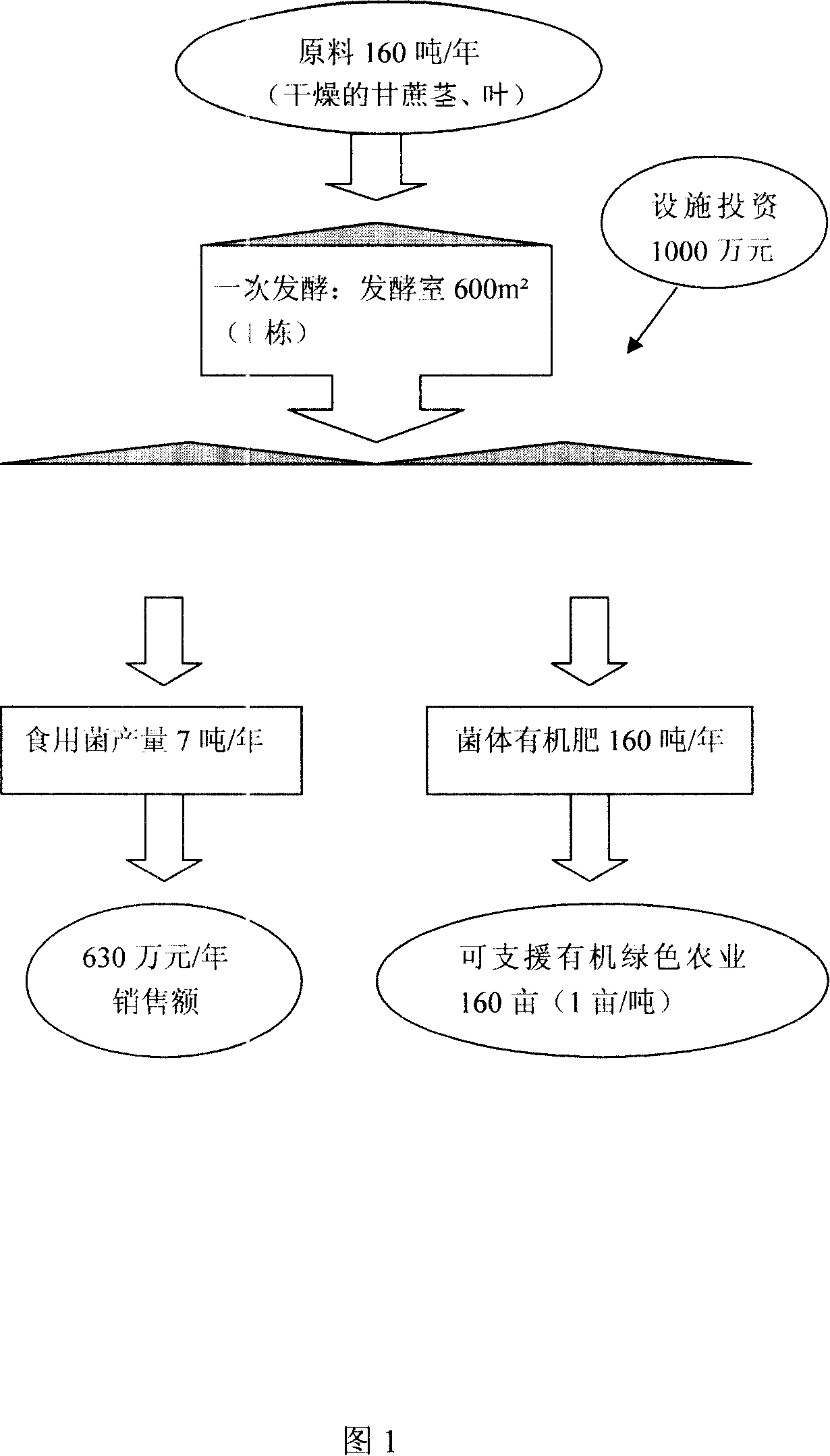
[0045] Embodiment 1 is shown in Figure 1:
[0046] 1. Raw materials: 160 tons of dry sugarcane stems and leaves are used. Cut into 6-7 cm, soak in the water tank according to the amount used once until the water content reaches 75%.
[0047] 2. The first fermentation room is a building with an area of 600 square meters. The sugarcane stems and leaves with a water content of 75% are adjusted to 45 with urea or the like, and fermented with natural ventilation at high temperature.
[0048] 3. The second fermentation room implements cultivation and management facilities with an area of 2,800 square meters and 420 square meters. After the first fermentation is completed, bacteria are planted after high-pressure steam insecticidal and sterilizing treatment.
[0049] The specific cultivation measures of matsutake mushroom (CJ-01) are as follows:
[0050] Spread the fermented compost evenly on the mushroom bed with a thickness of 20cm. When sowing, adopt the method of hole sow...
Embodiment 2
[0058] 1. Raw materials: 160 tons of dry sugarcane stems and leaves are used. Cut into 6-7 cm, soak in the water tank according to the amount used once until the water content reaches 75%.
[0059] 2. The first fermentation room, implementing a building with an area of 600 square meters. The sugarcane stems and leaves with a water content of 60% are adjusted to 50 with urea or the like, and then naturally ventilated and fermented at high temperature.
[0060] 3. The second fermentation room implements cultivation and management facilities with an area of 2,800 square meters and 420 square meters. After the first fermentation is completed, bacteria are planted after high-pressure steam insecticidal and sterilizing treatment.
[0061] The specific cultivation measures of matsutake mushroom (CJ-01) are the same as in Example 1.
[0062] 4. After 6 months of cultivation, it can be harvested 8 times, that is, about 6.5 tons of dried matsutake mushroom (CJ-01) per year.
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com