Digital camera
A digital camera and functional technology, which is applied in the field of digital cameras, can solve the problems of different brightness levels of subjects and no uniform benchmark of brightness signal levels, etc., and achieve the effect of maintaining fineness and improving recognition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
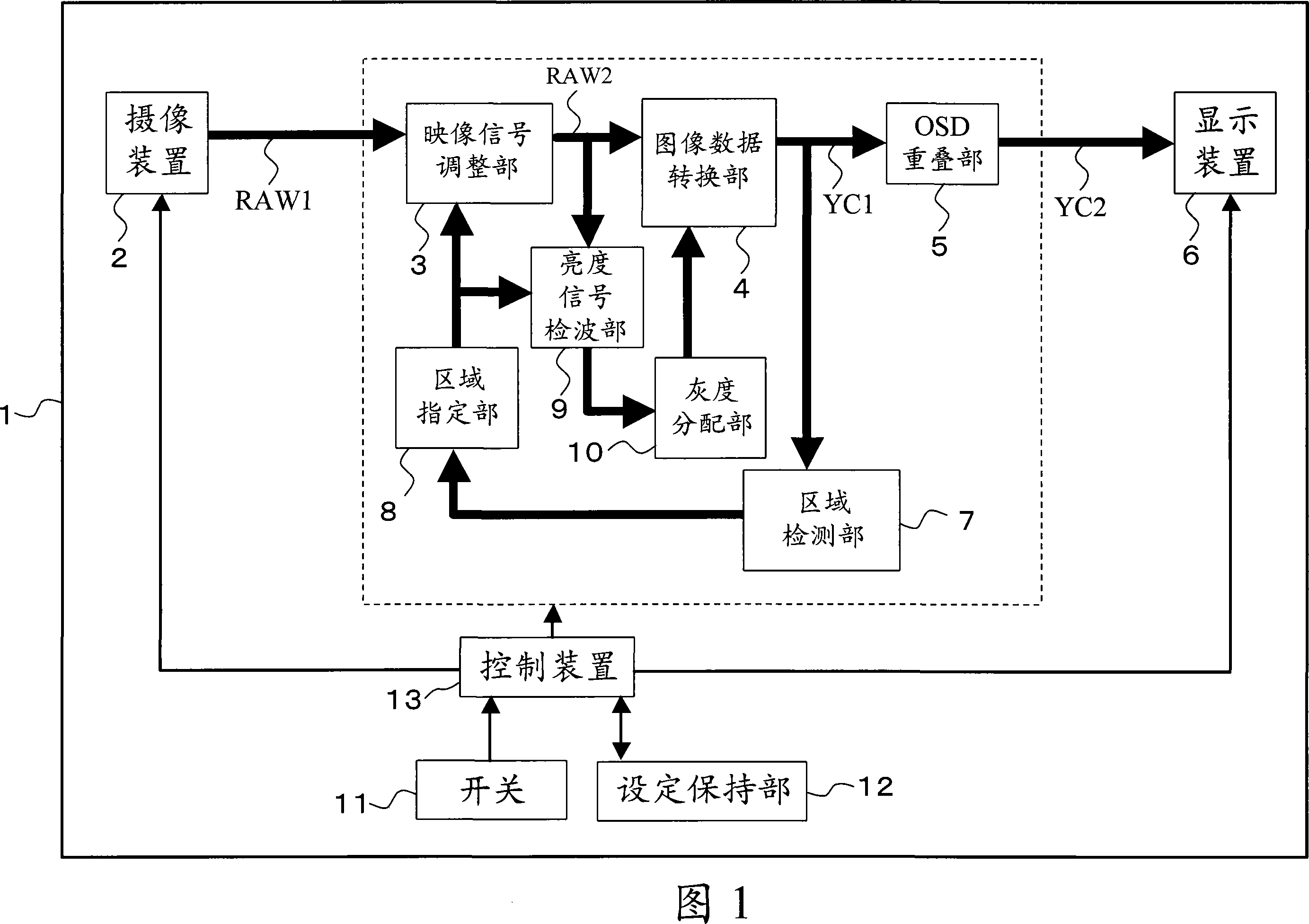
[0037] The configuration of the digital camera of the first embodiment is shown in FIG. 1 . This digital camera 1 includes: an imaging device 2, an image signal adjustment unit 3, an image data conversion unit 4, an on-screen video control system superimposition unit 5, a display device 6, an area detection unit 7, an area designation unit 8, and a brightness signal detection unit 9 , a gradation distribution unit 10, a switch 11, a setting holding unit 12, and a control device 13.
[0038] The imaging device 2 converts light from a subject into an image signal RAW1 corresponding to R·G·B by a solid-state image sensor such as a CCD or a CMOS, and outputs the image signal RAW1. The video signal adjustment unit 3 performs individual gain adjustment of various color components (R·G·B) of the video signal RAW1 from the imaging device 2, white balance adjustment, offset addition, and defect correction etc., and output as the adjusted image signal RAW2. The image data converting u...
no. 2 approach
[0048] The configuration of the digital camera of the second embodiment is shown in FIG. 14 . This digital camera 1 further includes an automatic exposure (AF=Auto-Focus) control unit 20 in addition to the components shown in FIG. 1 . The automatic exposure control unit 20 performs control to focus on a subject. Fig. 15 shows images and correction areas in the digital camera 1 of the present embodiment.
[0049] Usually, when performing auto-focus control, there are several auto-focus areas (Auto-Focus areas) to focus on. In this case, the seven quadrangular ranges (Auto-Focus ranges) in FIG. 15(a) correspond to auto-focus areas. Here, if the auto-focus area is selected as the specified area, as shown in FIG. 15( b ), the image in the focused auto-focus area is corrected as the correction target area. Since the focus is generally on the desired area of the subject, as long as the AF area is designated as the designated area, the trouble of specifying the correction target...
no. 3 approach
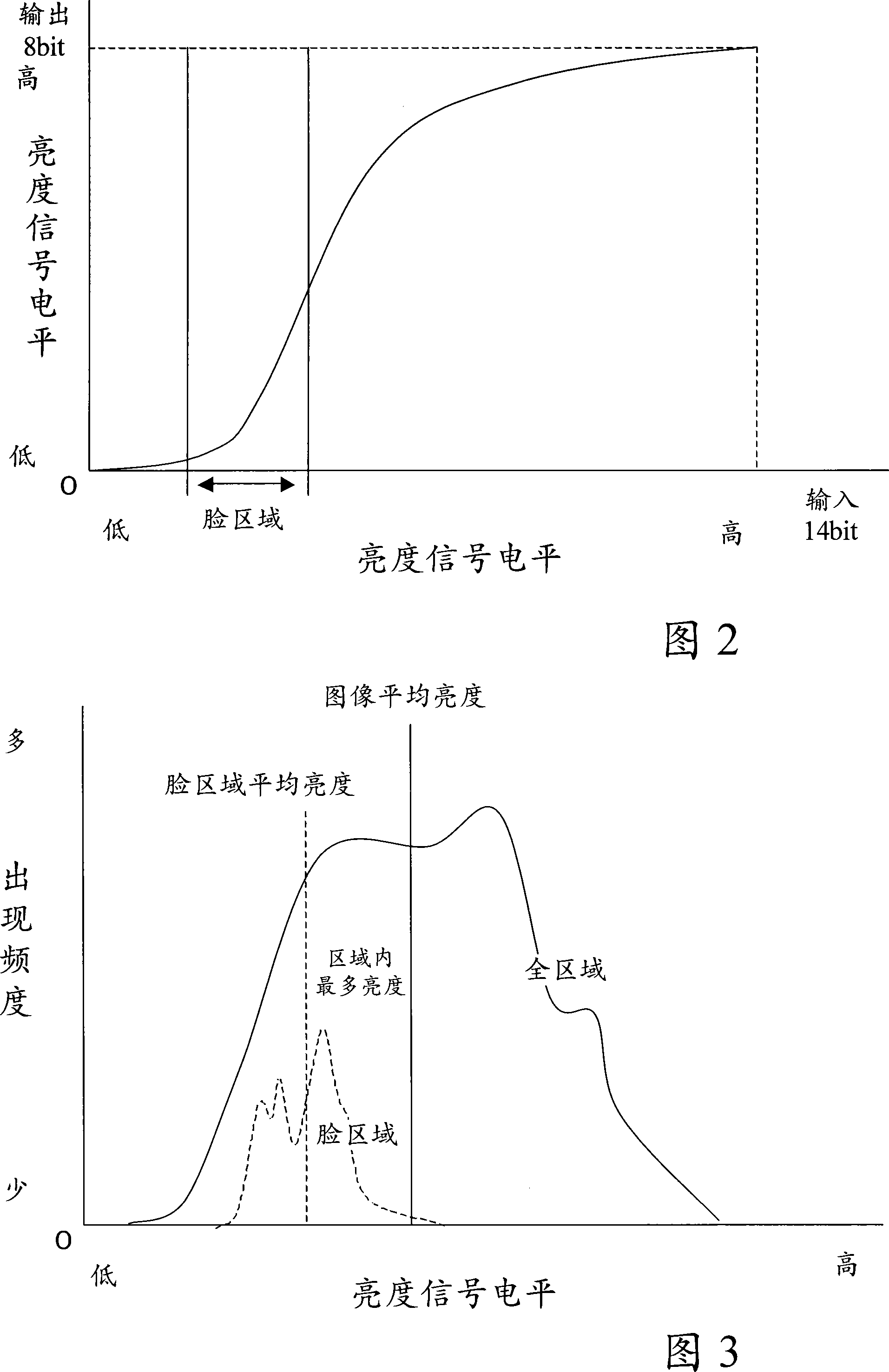
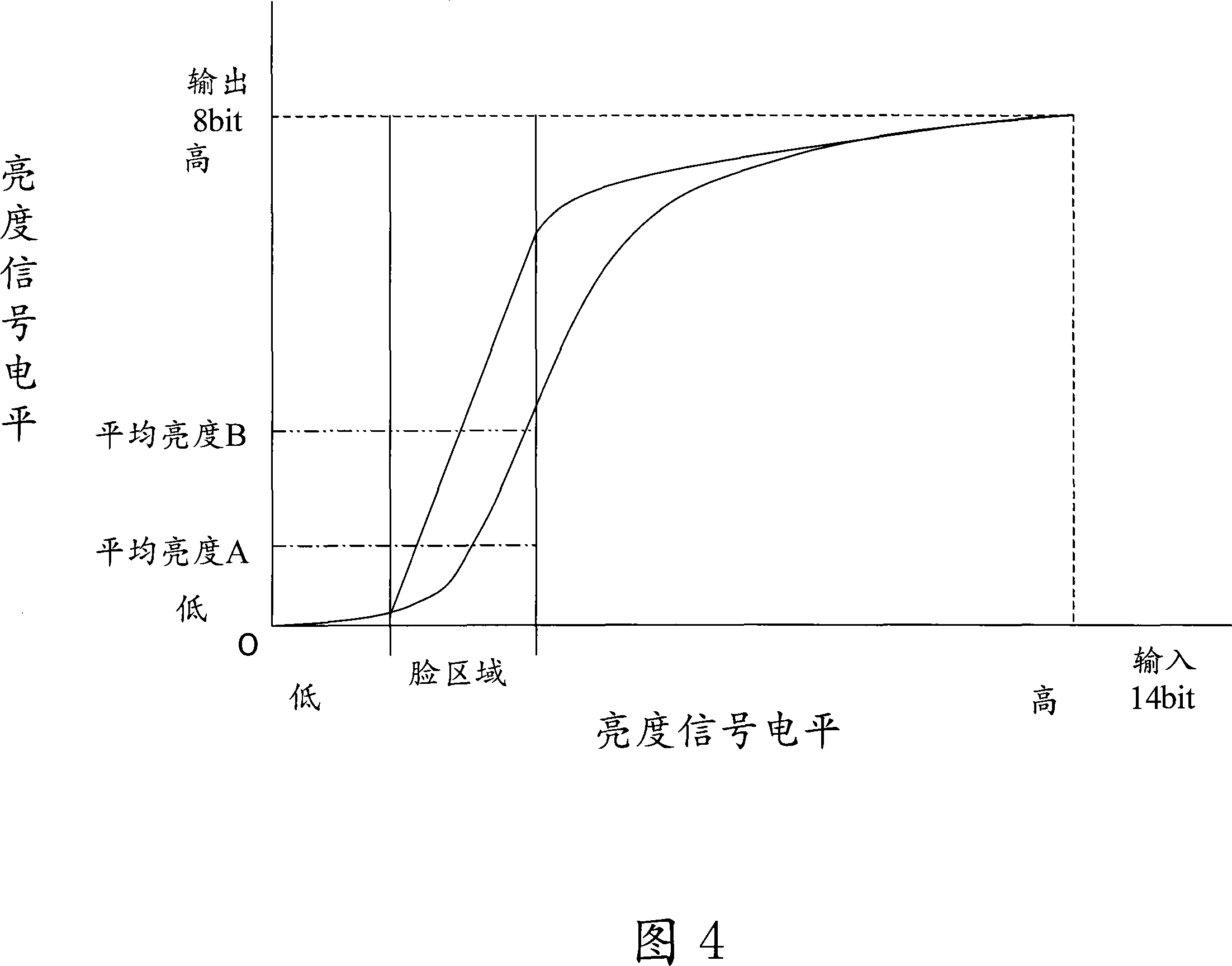
[0051] The configuration of the digital camera of the third embodiment is shown in FIG. 16 . This digital camera 1 includes, in addition to the components shown in FIG. 1 , a memory device 30 for storing video signals and the like, and a memory access unit 31 for storing / retrieving video signals in the memory device 30 . Furthermore, the image data conversion unit 4 converts the video signal from the memory access unit 31 into image data. The control device 13 controls each processing unit that generates image data from the video signal repeatedly until the luminance signal (average luminance, maximum luminance, minimum luminance) of the area specified by the area specifying unit 8 reaches a predetermined value.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com