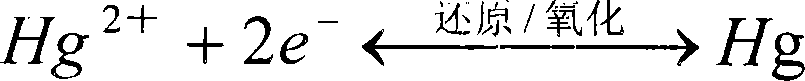Method for detecting lead content in tea-leaf
A technology of lead content and tea, which is applied in the field of qualitative or quantitative detection of heavy metal lead content in tea, which can solve problems such as difficulty in adapting, expensive detection instruments, and cumbersome detection steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Weigh 0.5000g of tea sample 1 to be tested in a conical flask, add 5ml of HNO 3 and 2ml H 2 o 2 , using a sealed pressurized microwave digestion tank with a household microwave oven, heating at low heat (119W) for 10 minutes, medium and low heat (231W) for 8 minutes, medium and low heat (231W) for 5 minutes, and high fire (385W) for 1 minute. Remaining acid is driven away with low heat, and digestive juice is obtained.
[0056] The isotopic mercury plating method and square wave stripping voltammetry were used to detect lead ions in the sample solution. Take the tea digestive juice with 0.1mol / L NH 4 Set the volume of Cl to 25 mL, put it in the electrolytic cell, add 100 μl of 0.1 mol / L mercury plating solution, adjust the pH value to 5.0 with concentrated ammonia water, fill with nitrogen to remove oxygen, and stir with a magnetic stirrer at a speed of 400 r / min. The screen-printed electrode was inserted into the electrolytic cell (the auxiliary electrode of the sc...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Weigh 0.5000g of the tea sample 2 to be tested in the Erlenmeyer flask, and the parameters of the digestion, detection method, data acquisition and processing system are the same as those in Example 1.
[0070] Apply a voltage to the working electrode, and detect the current value between the auxiliary electrode and the working electrode. Record the square wave stripping voltammetry peak height.
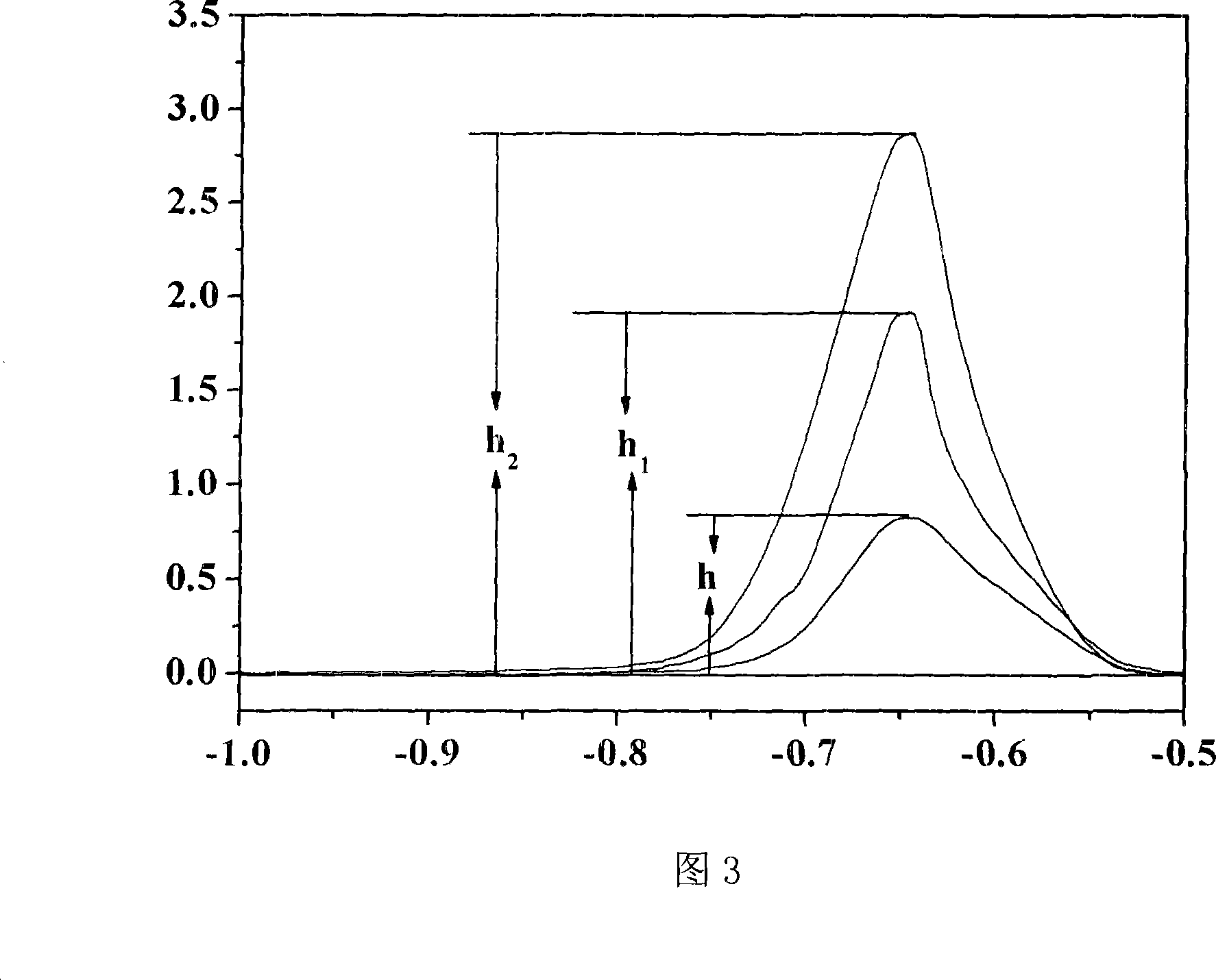
[0071] Add 100 μl of lead standard solution with a concentration of 10 μg / mL (ie: a=1.00 μg) into the electrolytic cell; apply voltage to the working electrode, and detect the current value between the auxiliary electrode and the working electrode; record the square wave dissolution after adding the standard solution Volt-ampere peak height.
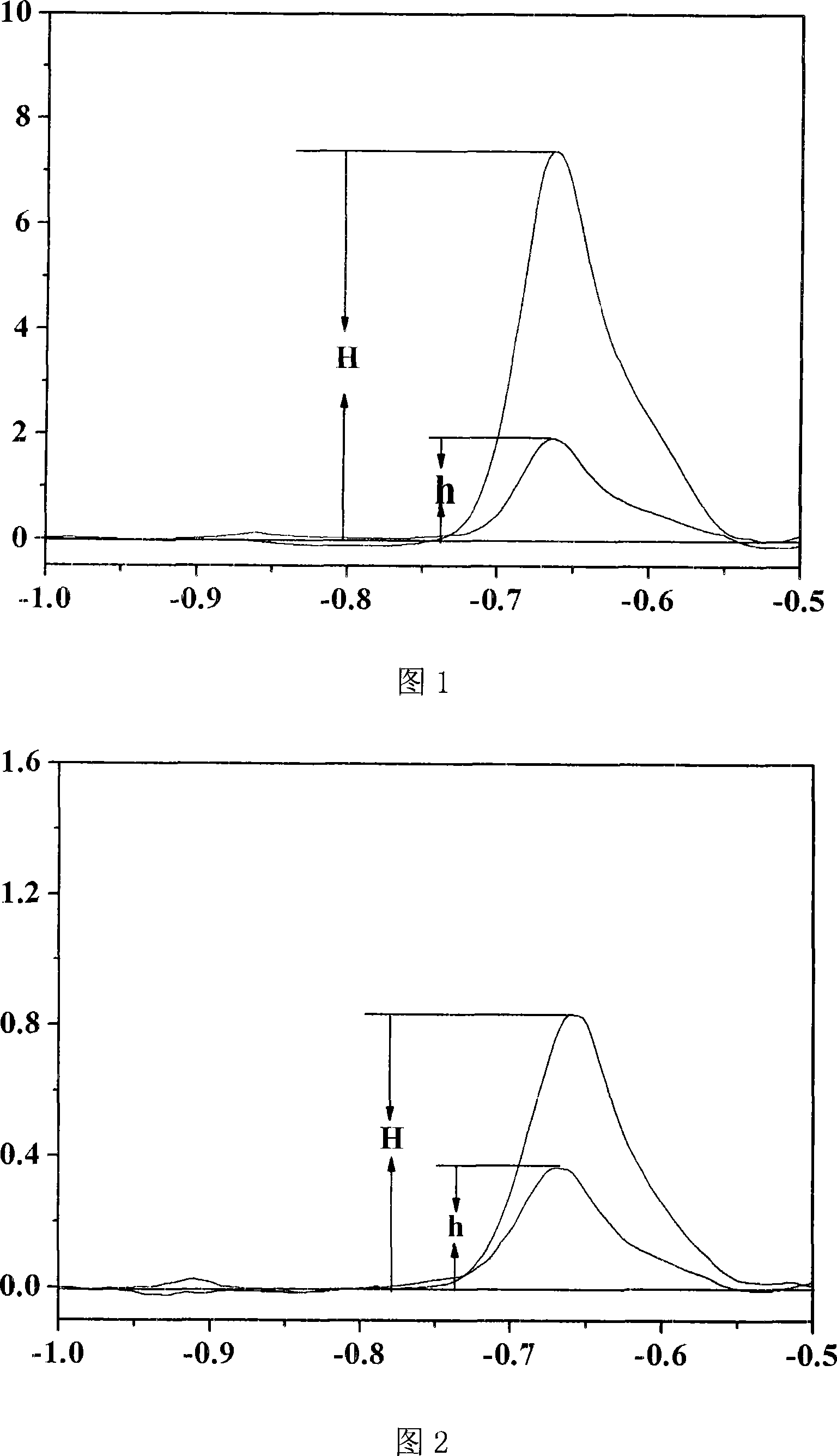
[0072] The square wave stripping peak peak figure of lead as shown in Figure 1. Among them, curve 1-0.10mol / L blank NH 4 Cl bottom solution (pH value 5.0); Curve 2-the square-wave dissolution peak of lead in the sample to be tested; C...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Weigh 0.5000g of the tea sample 3 to be tested in the Erlenmeyer flask, and the parameters of the digestion, detection method, data acquisition and processing system are the same as those in Example 1.
[0081] Apply a voltage to the working electrode, and detect the current value between the auxiliary electrode and the working electrode. Record the square wave stripping voltammetry peak height.
[0082] Add 50 μl of lead standard solution with a concentration of 100 μg / mL into the electrolytic cell (ie: a=5.00 μg); apply voltage to the working electrode, and detect the current value between the auxiliary electrode and the working electrode; record the square wave dissolution after adding the standard solution Volt-ampere peak height.
[0083] Add 50 μl of lead standard solution with a concentration of 100 μg / mL into the electrolytic cell again (ie: a=5.00 μg); apply voltage to the working electrode, and detect the current value between the auxiliary electrode and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com