Method for identifying textile fibers based on Raman spectra qualitative identification
A technology of textile fibers and Raman spectroscopy, applied in the field of textile materials, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, long detection period, troublesome sample preparation, etc., and achieve the effects of accurate test results, small sample volume, and short test time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Taking the qualitative identification of pure cotton fiber as an example, the steps are as follows:
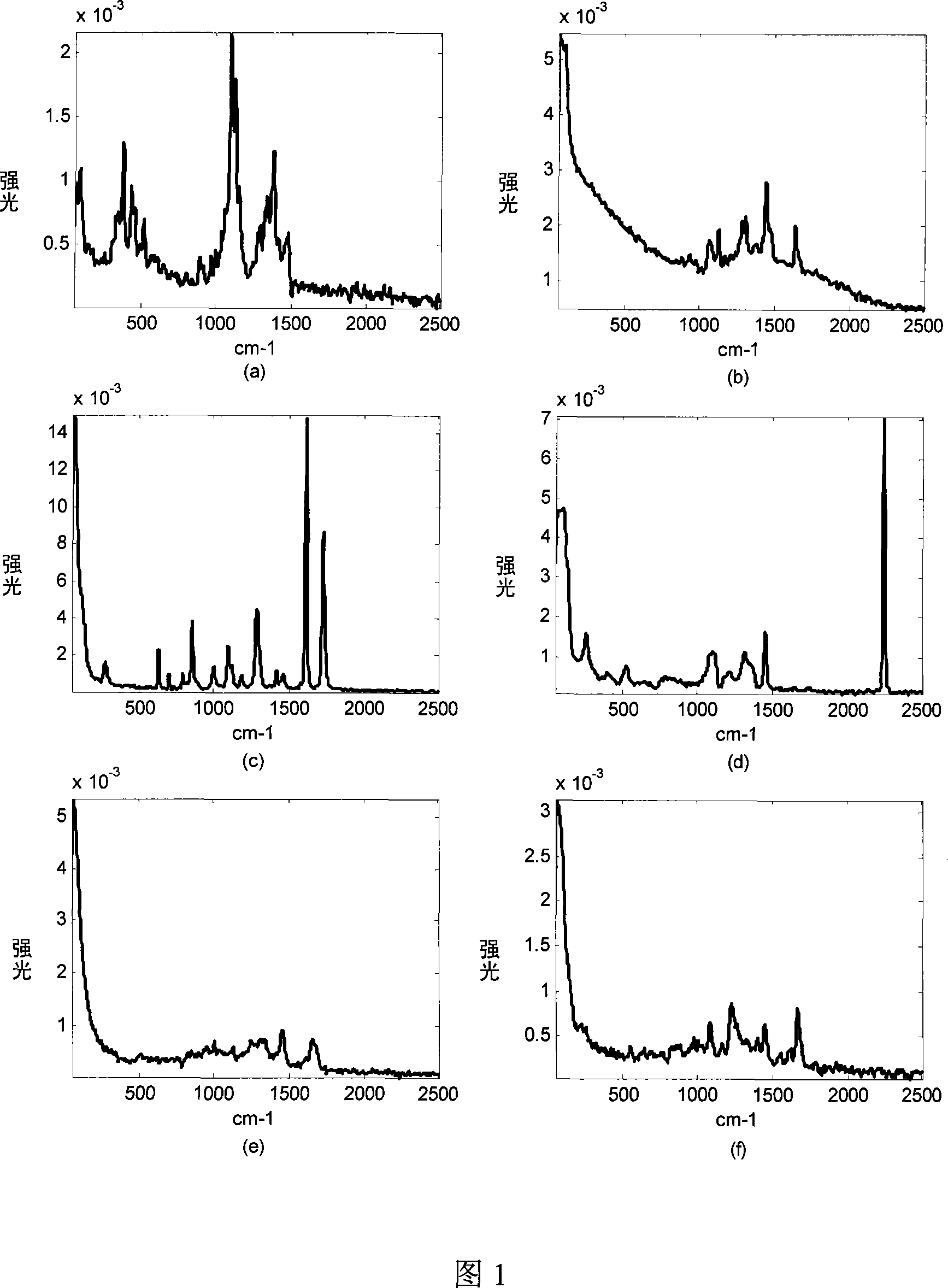
[0033] 1) directly obtain the laser Raman spectrum of pure cotton fiber with a Raman spectrometer, see Figure 1a);
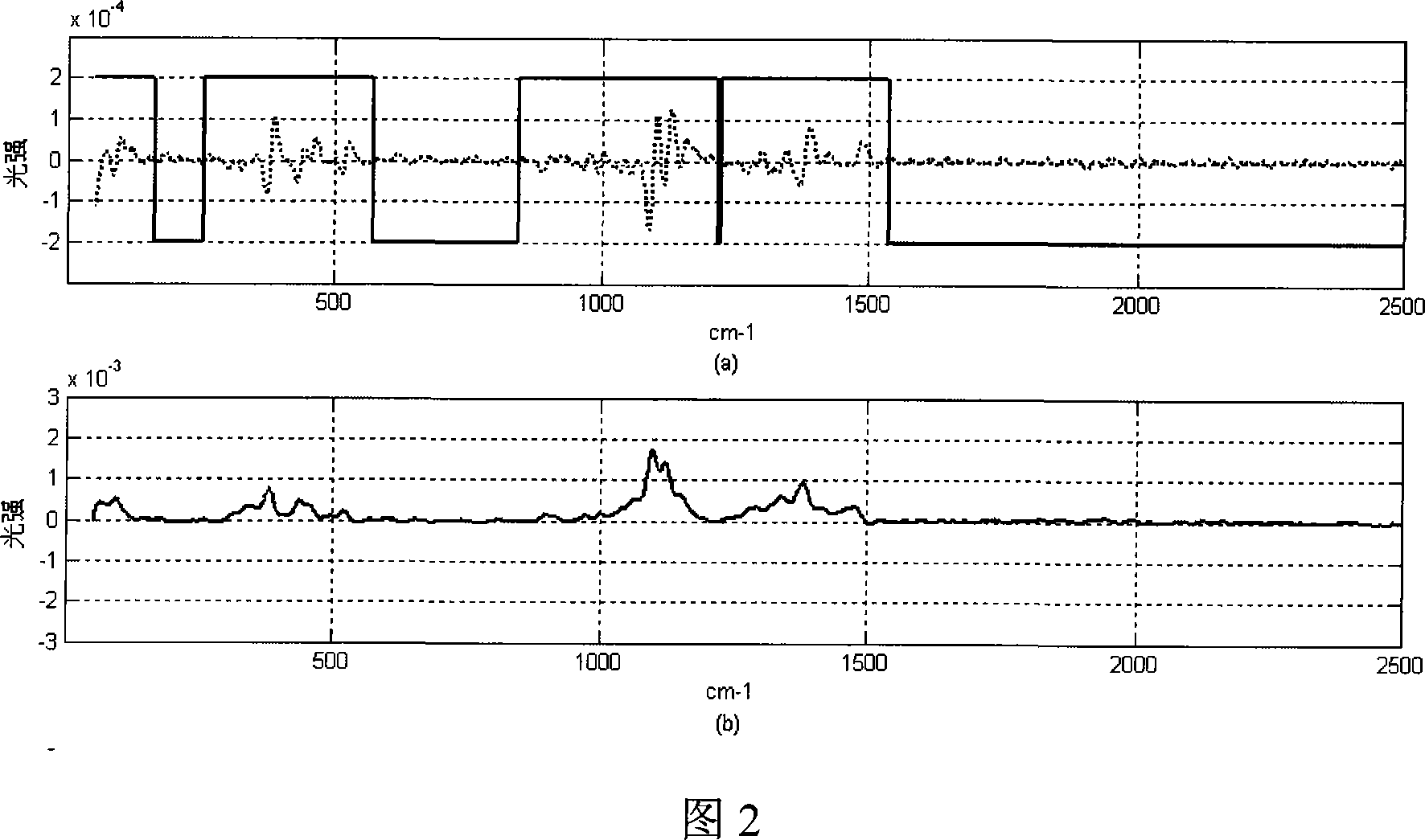
[0034] 2) Baseline correction is performed on the Raman spectrum of pure cotton fiber to eliminate the fluorescent background. The steps are as follows:
[0035] 2.1) Using the moving window polynomial differential algorithm to calculate the first-order differential spectrum of the pure cotton fiber Raman spectrum:
[0036] (2.1.1) For each data point in the pure cotton fiber laser Raman spectrum, select 2×h+1 data points with the point as the center and a half window width of h to form a moving window;
[0037] (2.1.2) carry out polynomial fitting to the data in this window;
[0038] (2.1.3) Deriving the polynomial and calculating the first order differential value of a certain spectral point.
[0039] The result of polynomial differentiation with a m...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Taking the qualitative identification of acrylic fiber as an example, the steps are as follows:
[0050] 1) directly obtain the laser Raman spectrum of the acrylic fiber with a Raman spectrometer, see Figure 1d);
[0051] 2) Baseline correction is performed on the Raman spectrum of the acrylic fiber to eliminate the fluorescent background, and the processing steps in Example 1 are used to perform baseline correction. The selection of processing parameters is exactly the same. The half-window width of the polynomial differential of the moving window is 4 data points, and the order of the polynomial is the second order; the reference area without effective peaks is 1850-2150cm -1 The data points within; the half-window width w of the validity discrimination window is 20 data points, and the relative threshold of validity discrimination K=3.
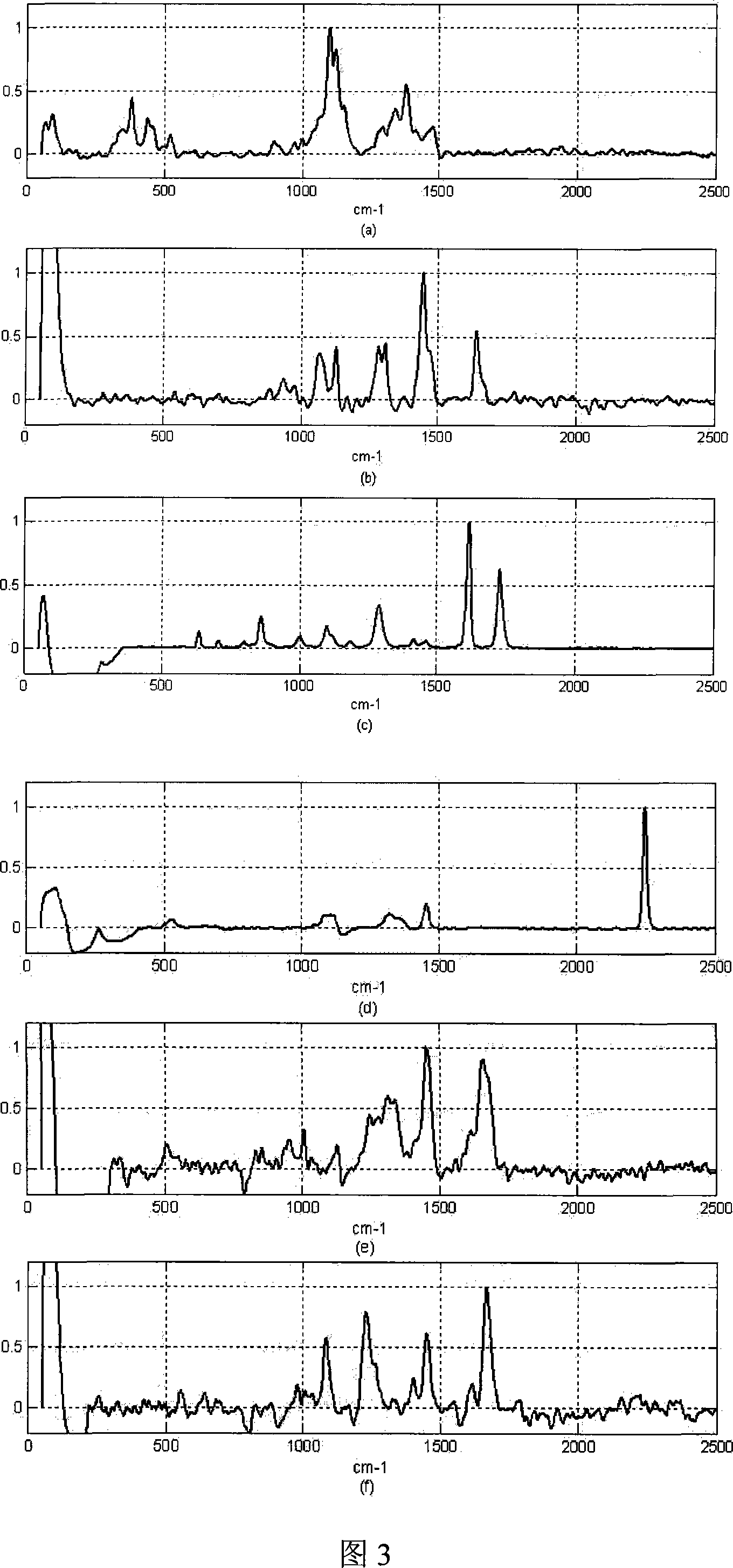
[0052] 3) Perform maximum value normalization on the baseline-corrected Raman spectrum, and use the processing steps in Example 1...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Taking the qualitative identification of polyester fiber as an example, the steps are as follows:
[0055] 1) directly obtain the laser Raman spectrum of the polyester fiber with a Raman spectrometer, see Figure 1c);
[0056] 2) Perform baseline correction on the Raman spectrum of the polyester fiber to eliminate the fluorescent background, and use the processing steps in Example 1 to perform baseline correction. The selection of processing parameters is exactly the same. The half-window width of the polynomial differential of the moving window is 4 data points, and the order of the polynomial is the second order; the reference area without effective peaks is 1850-2150cm -1 The data points within; the half-window width w of the validity discrimination window is 20 data points, and the relative threshold of validity discrimination K=3.
[0057] 3) Perform maximum value normalization on the baseline-corrected Raman spectrum, and use the processing steps in Example 1 to ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com