Drive device for vehicle and method of assembling the same
A drive system and vehicle technology, applied in the direction of traction, transmission, power unit, etc. driven by an engine, can solve the problem that the axial size of the drive system cannot be sufficiently reduced, the configuration cannot be fully configured, and the accuracy and efficiency of the assembled drive system can be reduced. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
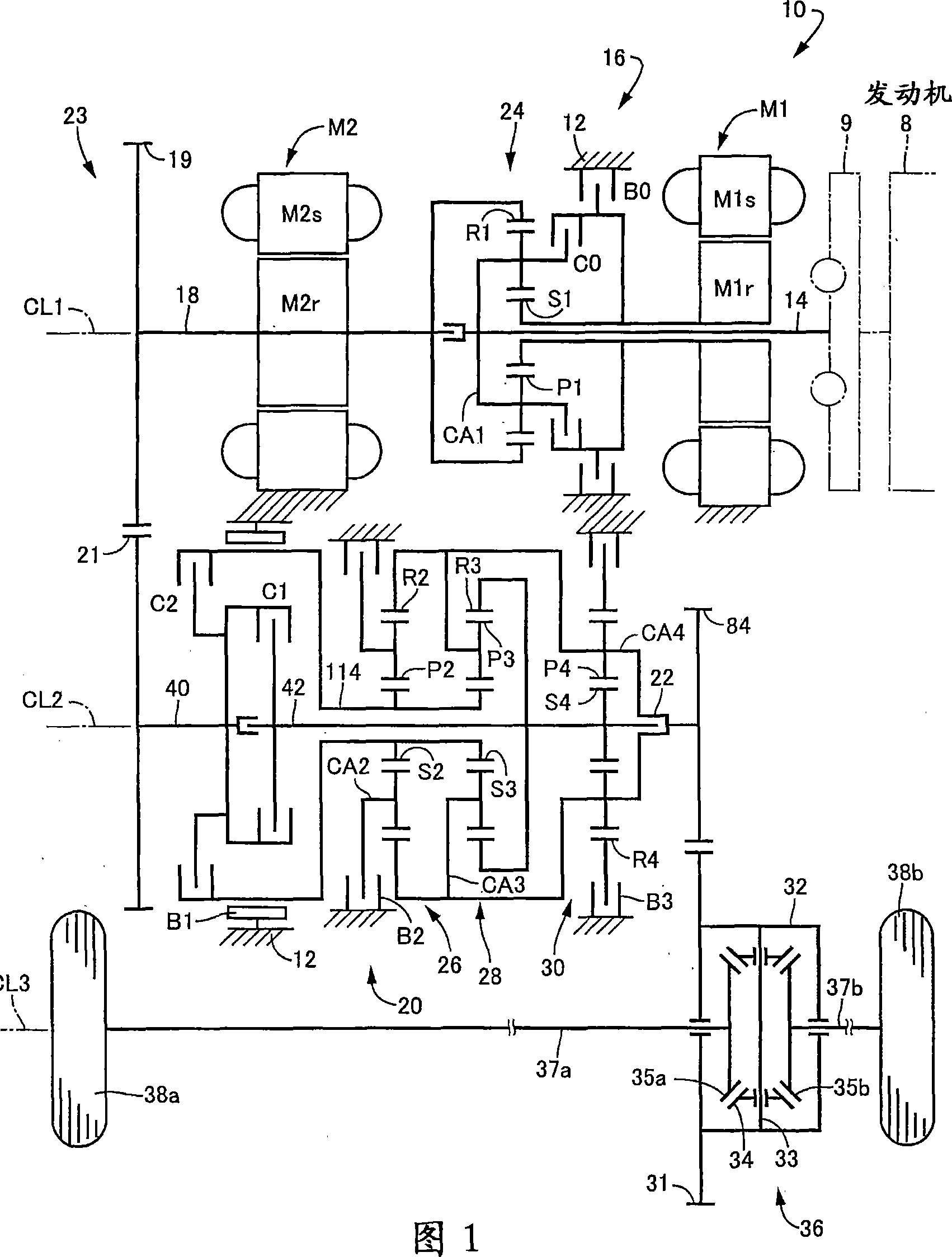
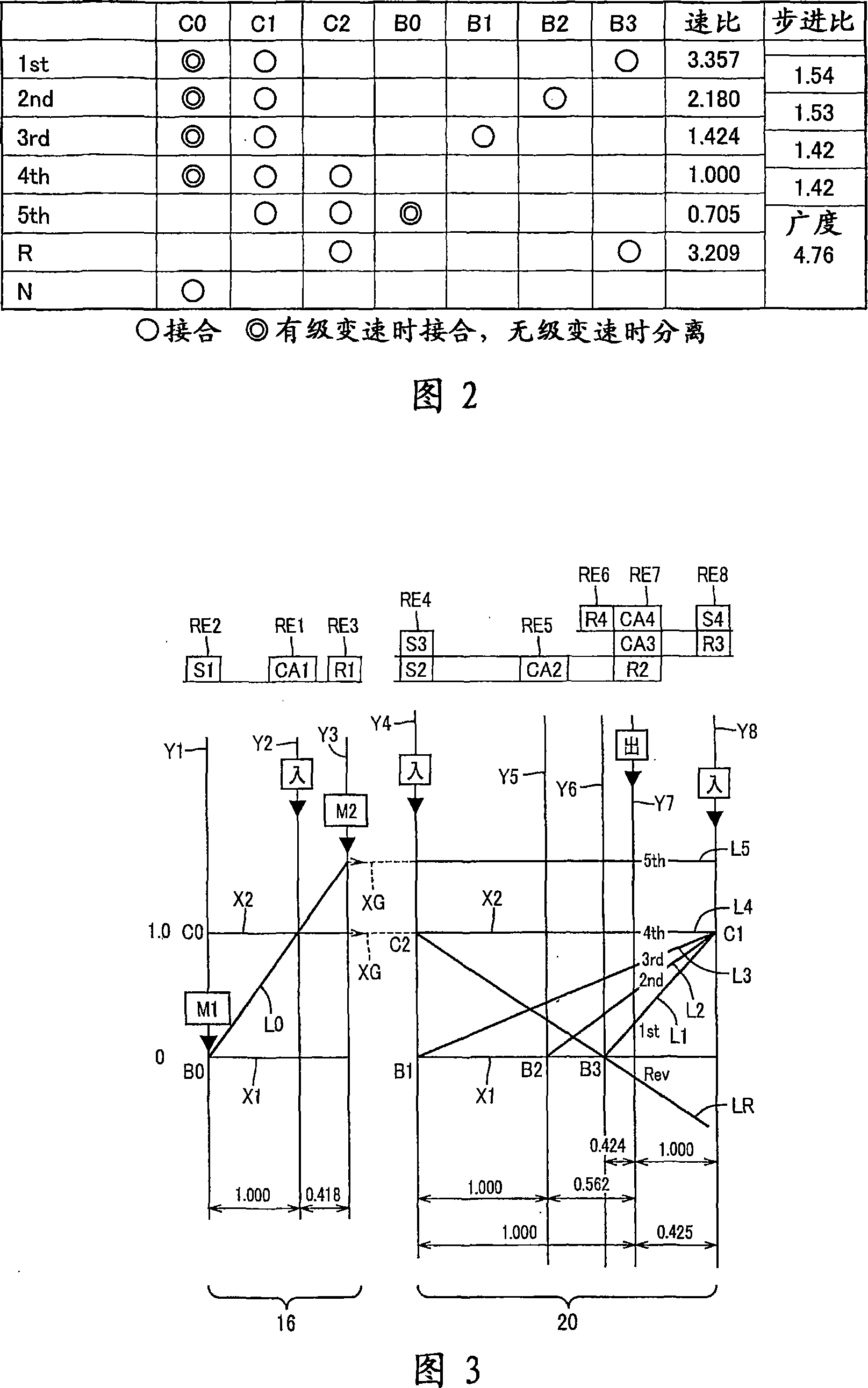
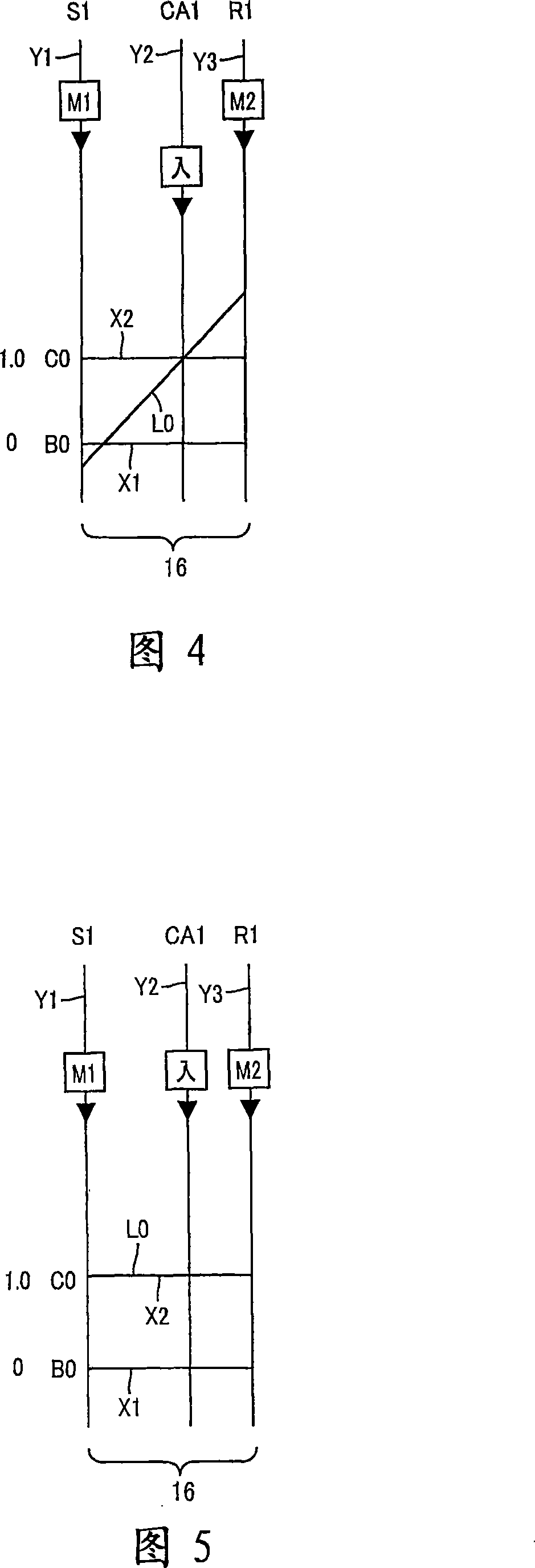
[0087] Reference is first made to the schematic diagram of FIG. 1 , which illustrates a drive system 10 for a hybrid vehicle constructed in accordance with one embodiment of the present invention. The drive system 10 shown in FIG. 1 includes: an engine 8; a transaxle housing 12 (hereinafter simply referred to as "housing 12"), which is a fixed member mounted on the vehicle body; a pulsation absorbing damper (vibration damping device) 9; an input shaft in the form of an input rotary member 14 connected to the engine 8 via the pulsation absorbing damper 9 and receiving the output of the engine 8 via the pulsation absorbing damper 9; a first electric motor M1; a hydraulically operated differential speed limiting device which is A form of a switching clutch C0 and a switching brake B0; a differential gear mechanism or a differential portion, which is in the form of a power distribution mechanism 16 connected to an input rotation member 14; a power transmission member 18, which is a...
Embodiment 2
[0166] Other embodiments of the present invention will be described below. In the following description of other embodiments, the same reference numerals as in the first embodiment are used to denote elements with the same function, and redundant descriptions thereof will be omitted.
[0167] Referring to FIG. 19 , which is a partial cross-sectional view showing a portion of a drive system 186 for a vehicle according to a second embodiment of the present invention. The drive system 186 differs from the drive system 10 of the first embodiment only in that a drive connection 188 is provided instead of the drive connection 23 . As shown in FIG. 19 , the driving connection device 188 includes a driving sprocket 190 , a driven sprocket 192 and a transmission belt 194 made of metal or resin and connecting the driving sprocket 190 and the driven sprocket 192 . The drive sprocket 190 is mounted on an axial end portion of the power transmission member 18 via the connection member 118 ...
Embodiment 3
[0169] Reference is next made to the partial cross-sectional view of FIG. 20 showing a portion of a drive system 196 for a vehicle according to a third embodiment of the present invention. The drive system 196 differs from the drive system 10 of the first embodiment in that the axial position of the engine 8 is opposite to that of the first embodiment, and between the differential drive gear 84 and the large diameter gear 31 of the final reduction gear unit 36 An idler gear 200 is arranged between them. The idler gear 200 is rotatably supported by the first and second housing parts 12a, 12b via bearings 198 . In the third embodiment, the fourth axis CL4 is disposed between and parallel to the second and third axes CL2, CL3, the idler gear 200 is rotatably supported around the fourth axis CL4, and is connected to the differential drive gear 84. It meshes with the large-diameter gear 31 of the final reduction gear unit 36 . The idler gear 200 transmits the rotational motion ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com