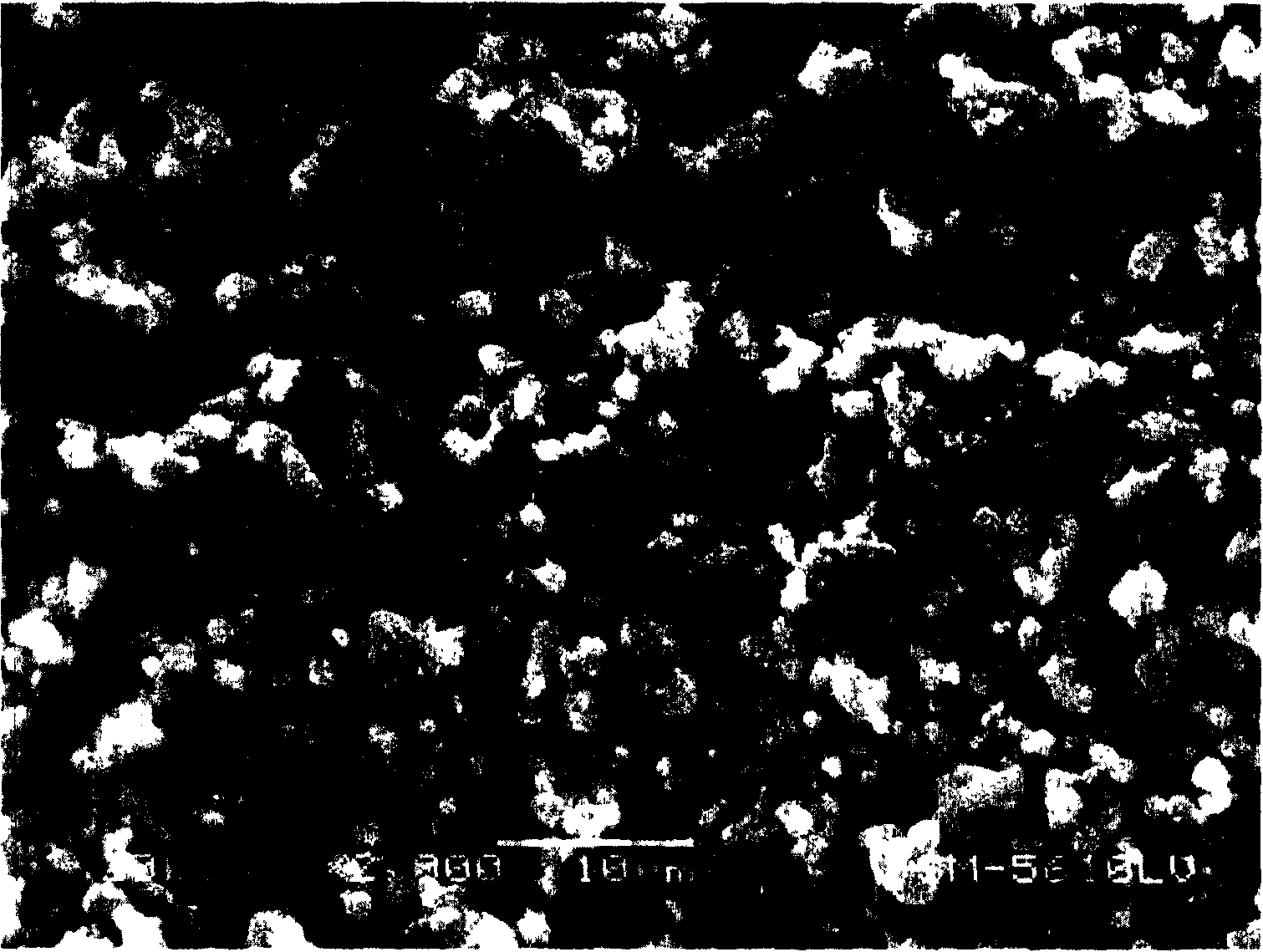
Preparation method for lithium ion secondary battery positive pole active substance lithium iron phosphate
A cathode active material, lithium iron phosphate technology, applied in battery electrodes, chemical instruments and methods, circuits, etc., can solve the problem of poor high-current discharge performance of batteries, and achieve good high-current discharge performance, good uniformity, and high efficiency. High volume effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
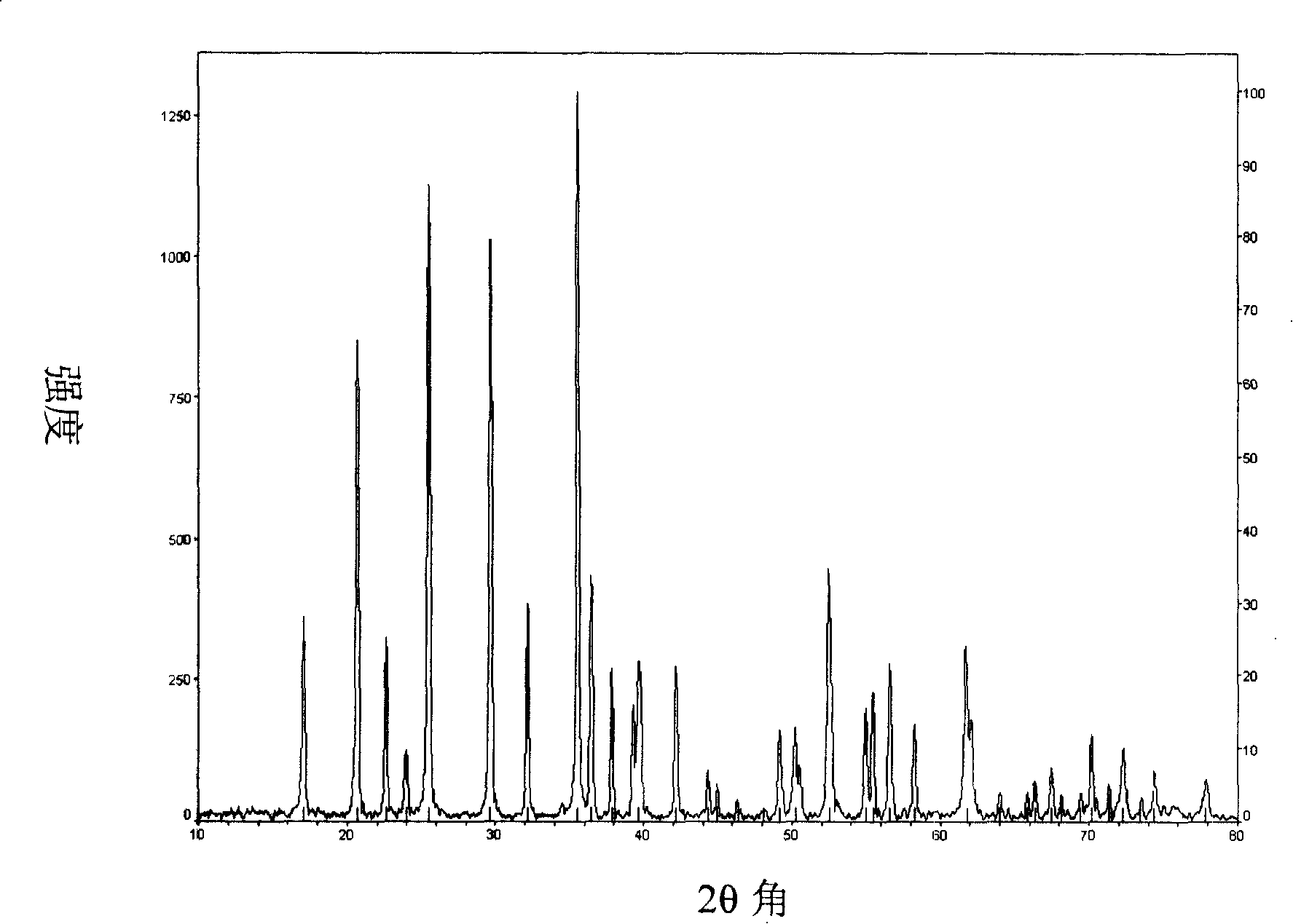
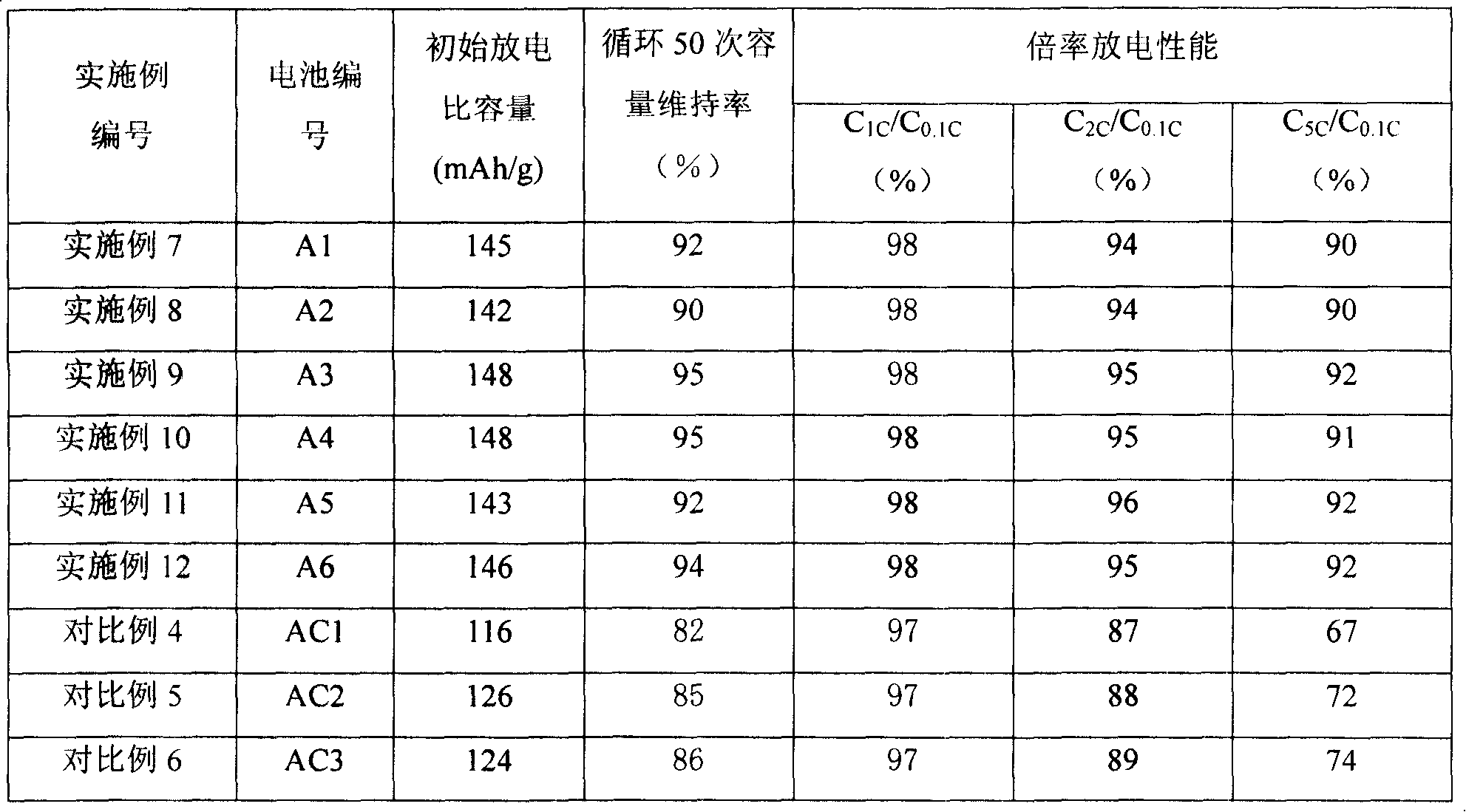
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] This embodiment illustrates the preparation of the positive electrode active material lithium iron phosphate provided by the invention
[0035] (1) Add 0.1 mole of Li 2 CO 3 , 0.2 mol FePO 4 Mix 1.2 grams of carbon black with 250 milliliters of absolute ethanol (Li: Fe: P molar ratio is 1:1:1), ball mill for 8 hours at a speed of 300 rpm in a ball mill jar, take it out, and dry it at 70°C ;
[0036] (2) Under the protection of argon with a flow rate of 10 liters / minute, the mixture in step (1) was heated to 650° C. for sintering at a constant temperature at a rate of 5° C. / minute for 6 hours, cooled to room temperature naturally, and then 2.6 glucose was added, and mixed with 150 milliliters of absolute ethanol, ball milled at a speed of 250 rpm for 6 hours in a ball mill jar, taken out, and dried at 70°C; the amount of glucose made the obtained lithium ferrous phosphate contained about 3 weight%.
[0037] (3) Under the protection of argon gas with a flow rate of 1...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This embodiment illustrates the preparation of the positive electrode active material lithium iron phosphate provided by the invention
[0042] (1) Add 0.1 mole of Li 2 CO 3 , 0.2 mol FePO 4 Mix 1.2 grams of carbon black with 250 milliliters of absolute ethanol (Li: Fe: P molar ratio is 1:1:1), ball mill for 8 hours at a speed of 300 rpm in a ball mill jar, take it out, and dry it at 70°C ;
[0043] (2) Under the protection of argon with a flow rate of 10 liters / minute, the mixture in step (1) was heated to 650° C. for sintering at a constant temperature at a rate of 5° C. / minute for 6 hours, cooled to room temperature naturally, and then 2.6 glucose was added, and stir evenly; the amount of glucose makes the carbon content in the obtained lithium iron phosphate about 3% by weight.
[0044] (3) Under the protection of argon gas with a flow rate of 10 liters / minute, the mixture in step (2) was heated to 750° C. for 10 hours at a heating rate of 10° C. / minute and sint...
Embodiment 3
[0047] This embodiment illustrates the preparation of the positive electrode active material lithium iron phosphate provided by the invention
[0048] (1) Add 0.1 mole of Li 2 CO 3 , 0.198 mol FePO 4 , 0.002 mole Mg(OH) 2 Mix 1.2 grams of carbon black with 200 milliliters of absolute ethanol (Li: Fe: Mg: P molar ratio is 1: 0.99: 0.01: 1), ball mill at a speed of 300 rpm for 12 hours in a ball mill jar, take it out, and Dry at 70°C;
[0049] (2) Under the protection of argon with a flow rate of 10 liters / minute, the mixture in step (1) was heated to 670° C. for sintering at a constant temperature at a rate of 8° C. / minute for 6 hours, cooled to room temperature naturally, and then 3.2 glucose was added, and mixed with 200 milliliters of absolute ethanol, ball milled at a speed of 200 rpm for 6 hours in a ball mill jar, taken out, and dried at 70°C; weight%.
[0050] (3) Under the protection of argon gas with a flow rate of 10 liters / minute, the mixture in step (2) was he...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com