Branched succinimide dispersant compounds and methods of making the compounds
A technology of compounds and dispersants, applied in chemical instruments and methods, lubricating compositions, chemical/physical processes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
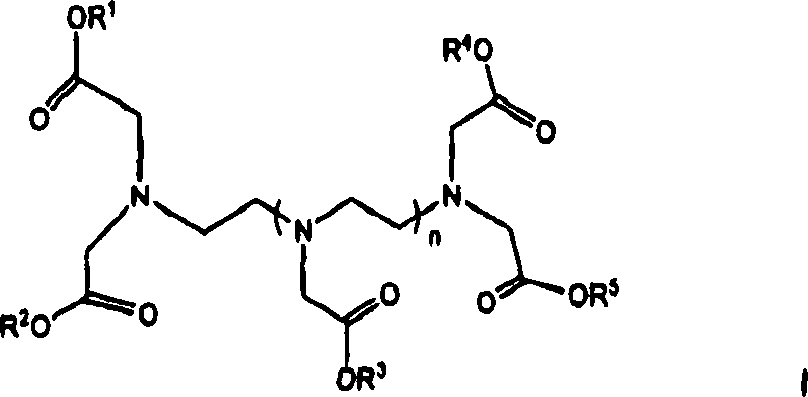
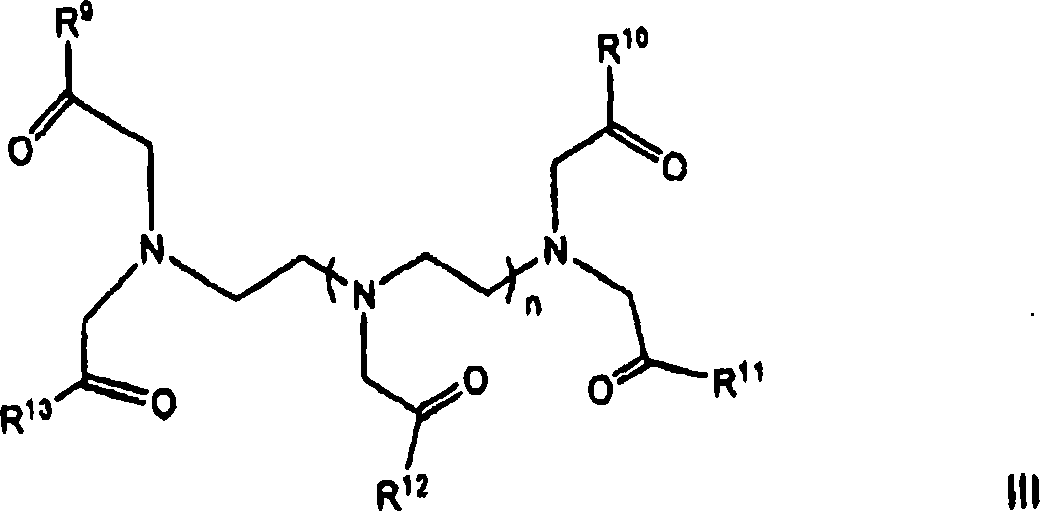
[0025] This application relates to the preparation of new dispersant compounds and their use. In one aspect of the present application, the dispersant compound comprises the reaction product of (i) a hydrocarbyl carbonyl compound, (ii) a polycarbonyl compound having at least three carbonyl acylated functional groups, and (iii) a primary amine of a polyamine part. The dispersant compounds of the present application have an extended polar region that can yield one or more advantages such as, for example, improved dispersant functionality in fuel and / or lubricating compositions.
[0026] In certain aspects, the dispersant compounds of the present application are prepared by preparing a polyamine polyamide intermediate and reacting it with a hydrocarbyl carbonyl compound. This intermediate can be prepared by reacting a polycarbonyl compound having at least three carbonyl acylation moieties with the primary amine moiety of a polyamine. Other methods suitable for forming the dispe...
Embodiment 1A
[0102] To a 1 L resin pot was added 43.8 g of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and 370 ml of water. The resulting suspension was stirred and heated to 100°C. TEPA (113.4 g) was added via addition funnel and the reaction mixture was stirred and heated under nitrogen for 3 hours. The suspension turned into a yellow solution upon addition of the amine. Water was removed from the reaction mixture in vacuo to give 156 g of a yellow viscous oil. The resulting intermediate was diluted with 100 g of water and transferred to a jar.
[0103] A proposed intermediate to the process of Example 1A is shown below as a reaction product:
[0104]
[0105] where R 20 and R 21 can be independently selected from OH, TEPA and salts of TEPA (O + H-TEPA).
Embodiment 1B
[0107] To a 3L resin pot with a stirrer on top was added 951 g of 1250Mn PIBSA. Under nitrogen, the PIBSA was heated to 160 °C with stirring. Then 248.1 g of the intermediate obtained in Example 1A were added through the addition funnel within 1 hour. The reaction mixture was stirred and heated under reduced pressure for 3 hours. The reaction mixture was diluted with 880 g process oil and filtered to give 1800 g of the desired product.
[0108] The reaction of a proposed method of Example 1B is shown below:
[0109]
[0110] where R 20 and R 21 may be independently selected from TEPA succinimide and salts of TEPA succinimide.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com