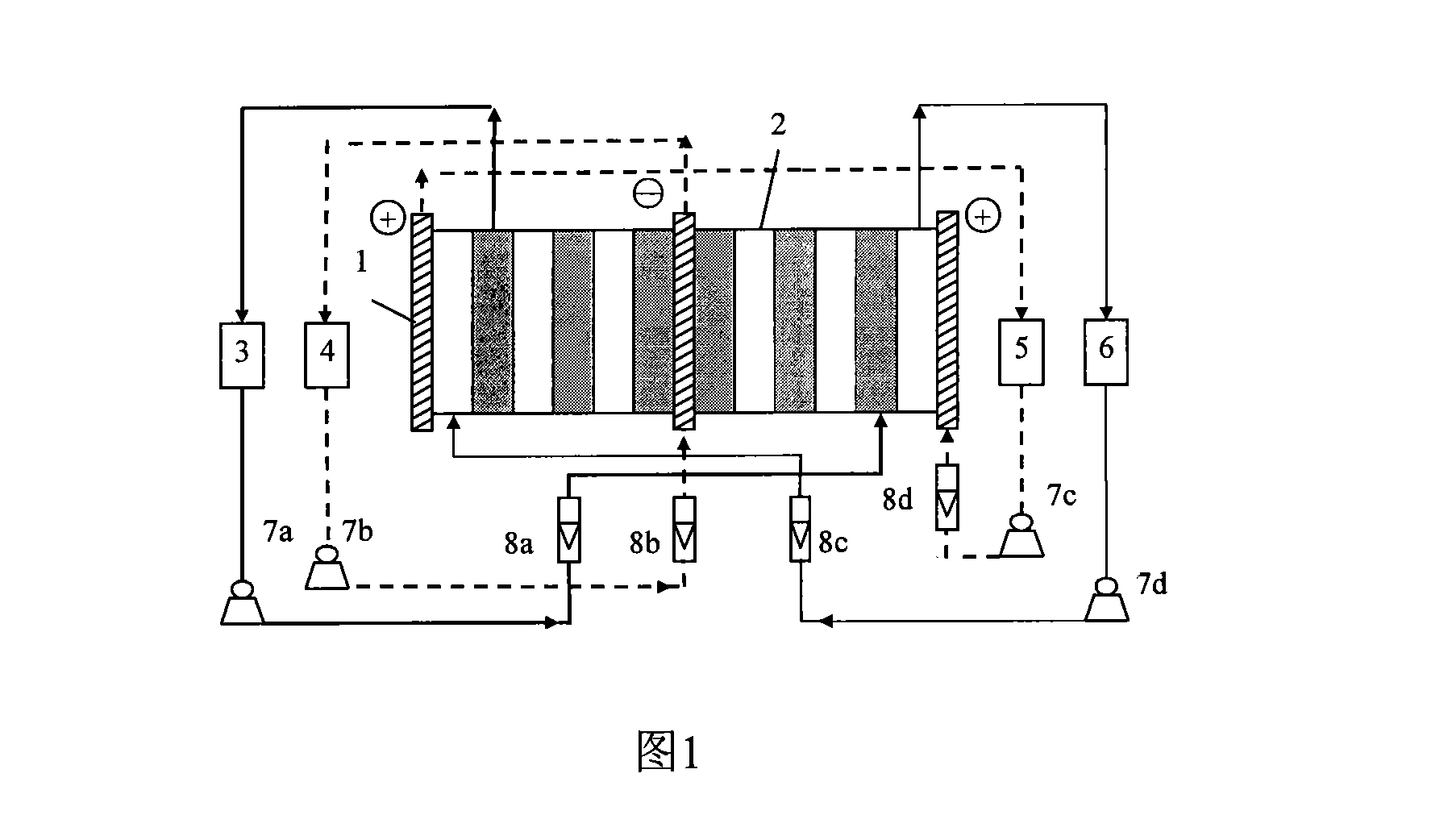
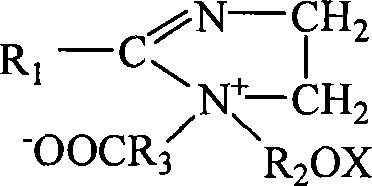
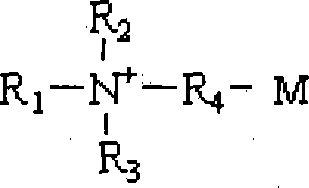Method for purifying ampholytic surface active agent with electric dialyze desalinisation
A surfactant and electrodialysis technology, applied in the field of membrane separation, can solve the problems of low cost, low energy consumption, restricted development, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1 Electrodialysis desalination of α-decyl betaine solution
[0020] The pH value of the α-decyl betaine solution containing NaCl was adjusted to 7.5. It is measured that the mass percentages of α-decyl betaine and inorganic salts are 10% and 3% respectively. Put 1L of the above solution into the storage tank of the dilute chamber, use 1L of 0.05mol / L NaCl solution as the initial solution of the concentrated chamber, and use 1L of sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid solutions with a concentration of 0.05mol / L as the cathode and anode chambers respectively. Solution, under the operating conditions of 10V operating voltage and 20L / h flow rate of the dilute chamber, the α-decyl betaine solution is desalted in a cycle. The dialysis ends when the conductivity of the dilute solution no longer decreases. The desalination rate was 97%, and the recovery rate of α-decyl betaine was 82.7%.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2 Electrodialysis desalination of dodecylsulfopropyl betaine solution
[0022] Adjust the pH value of the dodecylsulfopropyl betaine solution containing unknown inorganic salt to 7.2. The mass percentages of dodecylsulfopropyl betaine and inorganic salts were measured to be 31% and 13% respectively. Put 0.9L of the above solution plus 0.1L of water into the storage tank of the dilute chamber, use 1L of 0.05mol / L NaCl solution as the initial solution of the concentrated chamber, and use 1L each of sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid solutions with a concentration of 0.05mol / L As the cathode and anode chamber solutions, the dodecyl sulfopropyl betaine solution is desalted in circulation under the operating conditions of 14V operating voltage and 23L / h dilute chamber flow rate. The dialysis ends when the conductivity of the dilute solution no longer decreases. The desalination rate is 95%, and the recovery rate of dodecyl sulfopropyl betaine is 73.6%.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Embodiment 3 Electrodialysis desalting of lauryl amidopropyl betaine solution
[0024] Adjust the pH of the lauryl amidopropyl betaine solution containing unknown inorganic salts to 6.5, and measure the mass percentages of lauryl amidopropyl betaine and inorganic salts to be 5% and 1% respectively. Put 1L of the above solution into the storage tank of the dilute room, and add 1L of 0.05mol / L NaNO 3 The solution is used as the initial solution of the concentrated chamber, and each 1 L of sodium hydroxide and sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 0.05 mol / L is used as the solution of the cathode and anode chambers respectively. The solution is cyclically desalinated. The dialysis ends when the conductivity of the dilute solution no longer decreases. The desalination rate was 97%, and the recovery rate of lauryl amidopropyl betaine was 78.2%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com