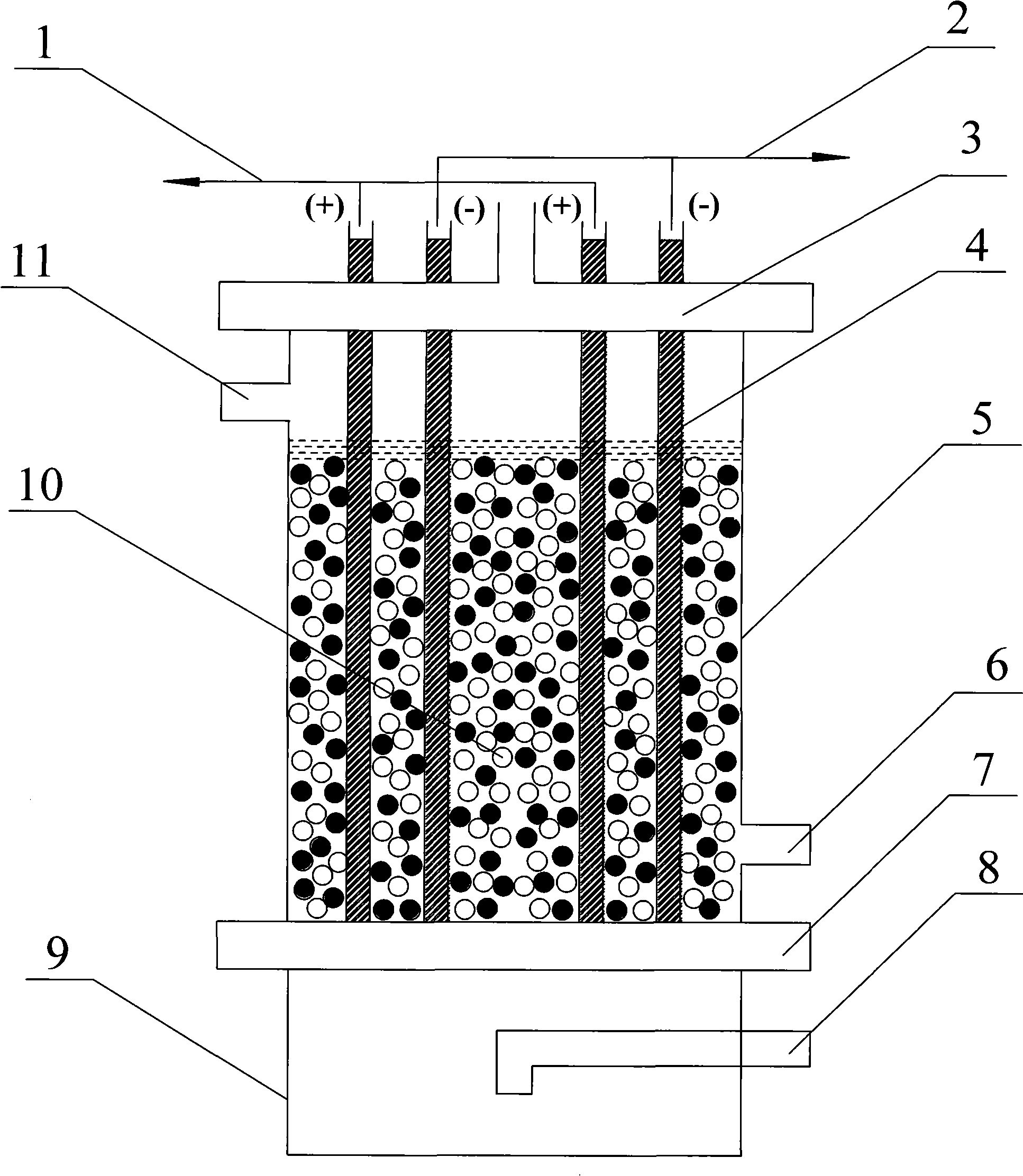
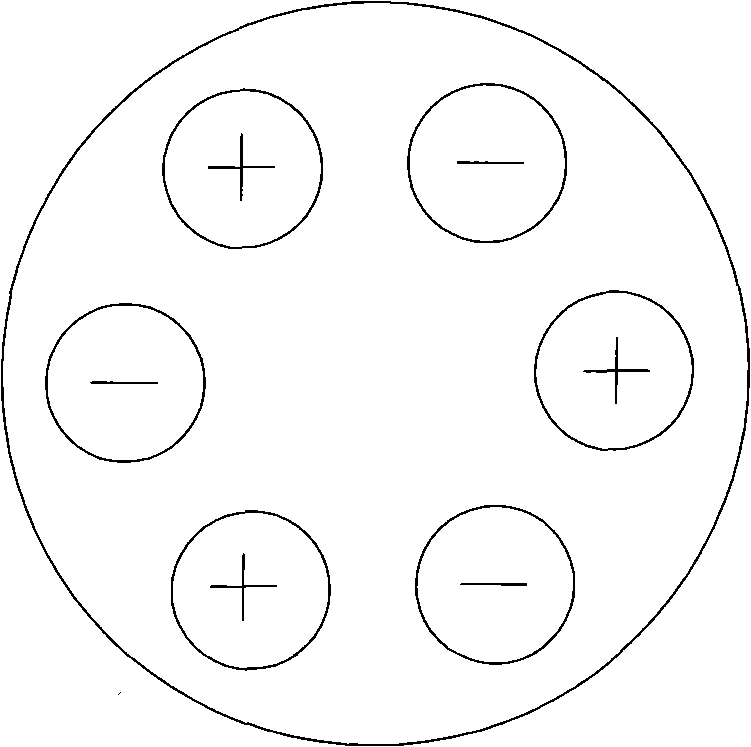
Electric regeneration method of non-film ion-exchange resin based on equate filter element electrode
An ion exchange resin and electric regeneration technology, applied in the direction of ion exchange regeneration, ion exchange, electric regeneration, etc., can solve the problems of unutilized electrode reaction, power consumption, negative scaling, etc., and achieve the effect of simplifying the recovery and regeneration operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1: introduce 600ml of 001×7 styrene series strongly acidic cation exchange resin 201×7 styrene series strongly basic anion exchange resins that are deactivated by NaCl. The regeneration conditions are: voltage 40V, current 3-5A, regeneration time 3h. After the regeneration is completed, the resin is exported and separated, and the exchange capacity of the cation resin is measured by GB8144-87 "Method for Determination of Exchange Capacity of Cation Exchange Resin", and the exchange capacity of anion resin is determined by GB5760-88 "Method for Determination of Exchange Capacity of Anion Exchange Resin". The results are as follows: the exchange capacity of the cation resin is 3.4 (dry) mmol / g; the exchange capacity of the anion resin is 2.1 mmol / g (dry); both achieve the regeneration effect of chemical agents. The pH value of the anode outlet liquid is less than 3, which can kill pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses. During the regeneration ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: the sample is chelating resin D751, and the regeneration process is as follows: at first only the cathode water is exported, and after a certain period of time, the pole is reversed and the anode water is exported, and continues until the predetermined requirement.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com