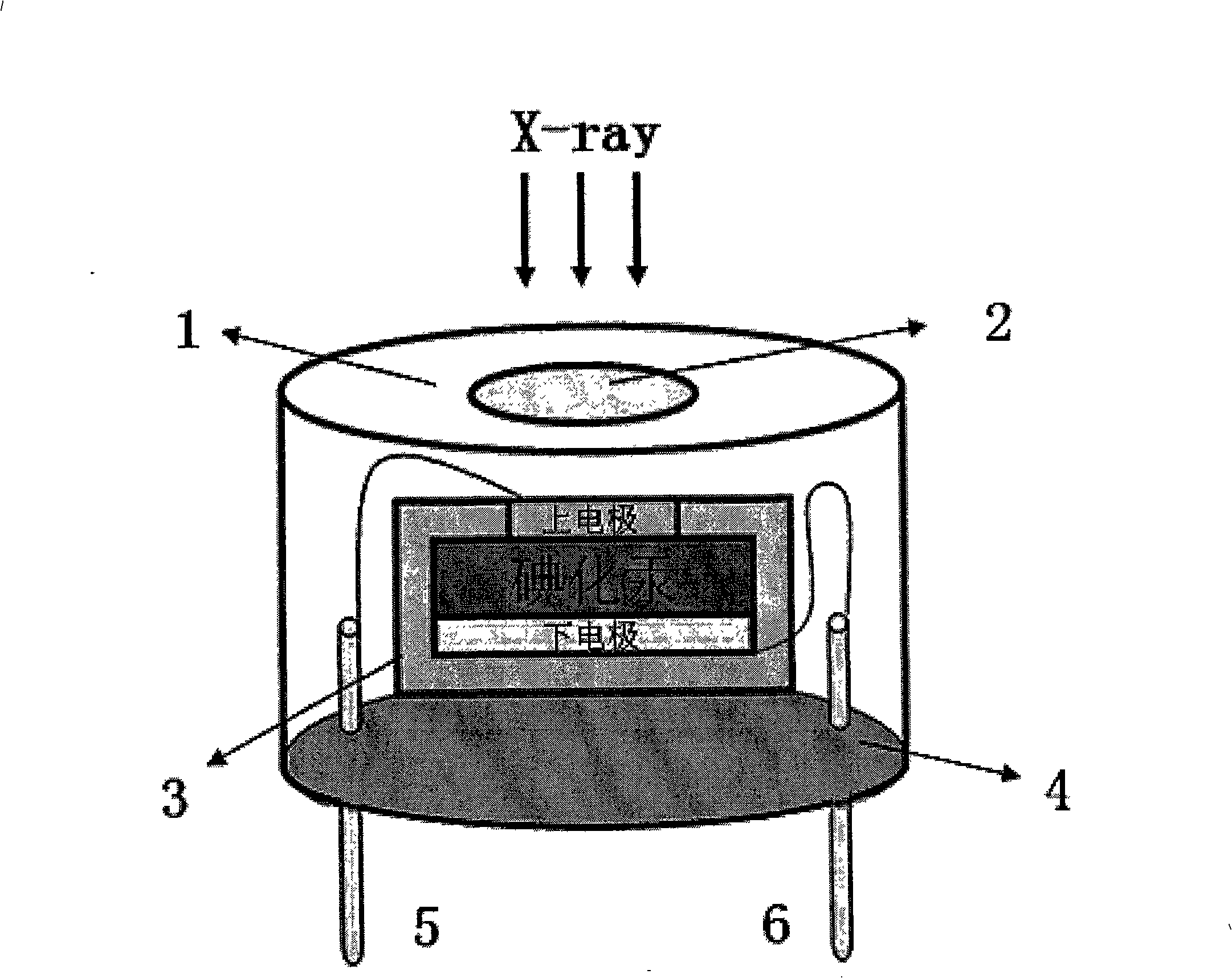
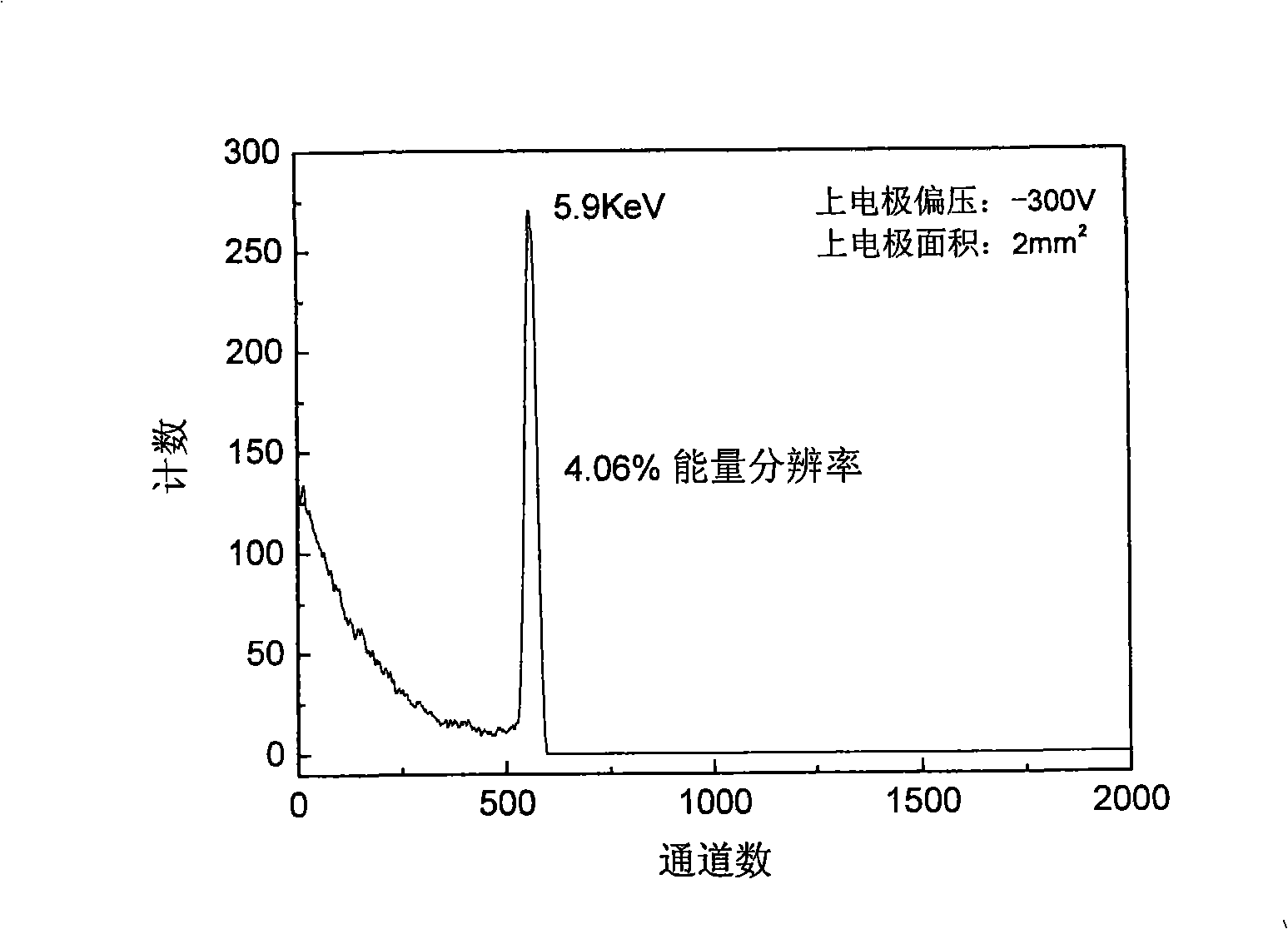
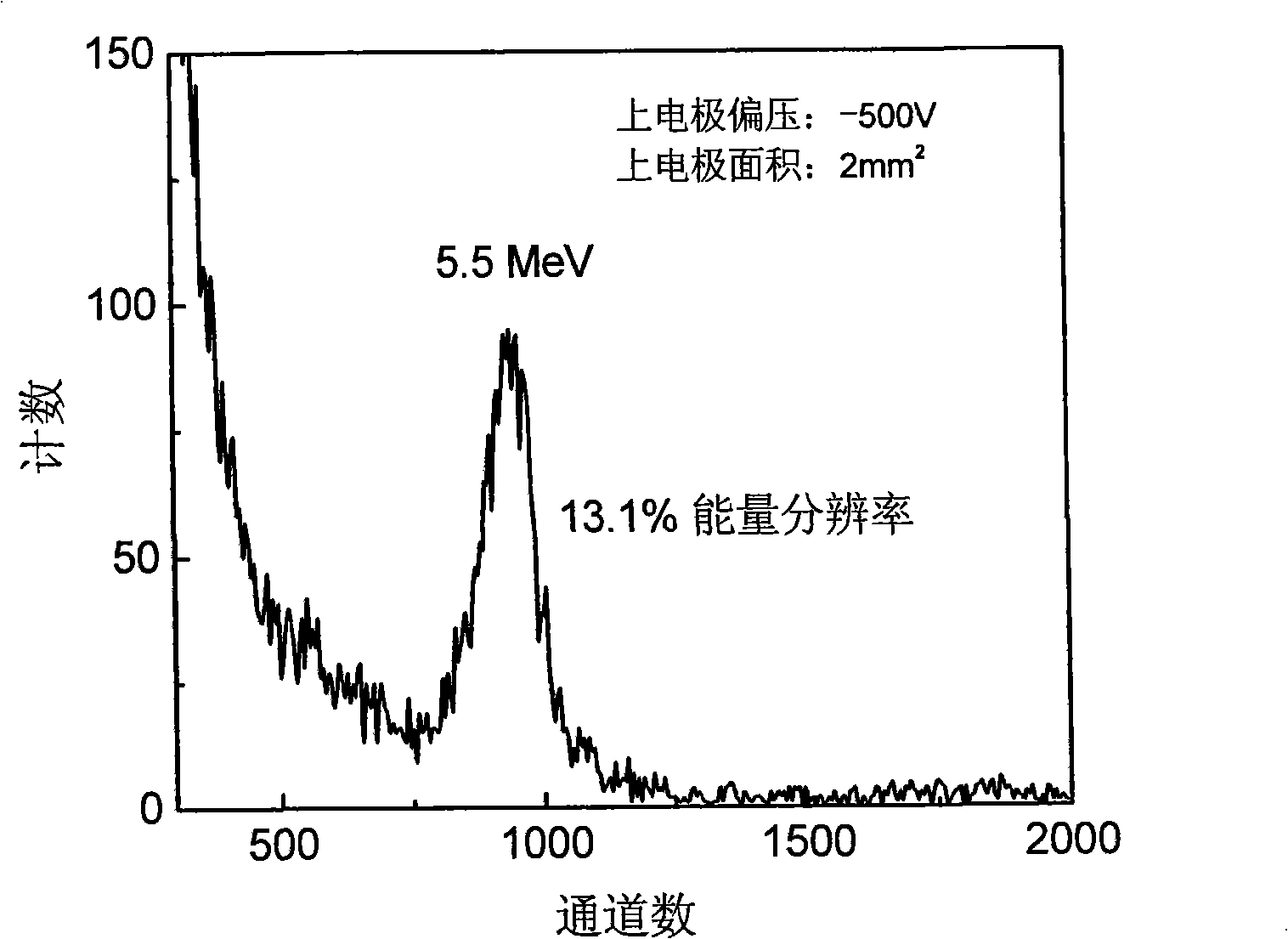
Method for making multi-crystal Hg iodide film room temperature nucleus emission detector
A nuclear radiation detector and mercury iodide technology are applied in the field of preparation of X-ray and γ-ray room temperature nuclear radiation detectors, which can solve the problem of reducing the temperature of growth, affecting the deposition speed and quality of thin films, and large stress on thin films and substrates. problem, to achieve the effect of simple process, low preparation cost and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The process and steps of the polycrystalline mercury iodide film room temperature nuclear radiation detector in this embodiment are as follows:
[0024] (1) The crystal grains prepared on the conductive glass substrate are columnar, and the crystal grain direction belongs to (001) crystal plane type polycrystalline mercury iodide film with a size of 2 inches * 2 inches. Mechanical rough polishing is performed on the film with leather paper to make the surface of the crystal grains smooth without obvious grain unevenness; then mechanical fine polishing is performed with silk cloth to remove the scratches left by the mechanical rough polishing of the grains; mechanical fine polishing with silk cloth After polishing, use a 15% KI solution at 15°C for 1 minute of chemical corrosion polishing to make the surface of the grains smooth and there are no obvious concave holes between the grain boundaries; then perform mechanical fine polishing with silk cloth, and use 10 %KI solu...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The process and steps of the polycrystalline mercury iodide film room temperature nuclear radiation detector in this embodiment are as follows:
[0032](1) The crystal grains prepared on the amorphous silicon thin film glass substrate are columnar, and the crystal grain direction belongs to the (001) crystal plane type polycrystalline mercury iodide thin film with a size of 2 inches * 2 inches. Use fine sand paper to mechanically polish the film to make the grain surface smooth without obvious grain unevenness; then perform mechanical fine polishing with silk cloth to remove the scratches left by the grain after mechanical rough polishing; After mechanical fine polishing of silk cloth, chemical corrosion polishing was carried out with 20% KI solution at 10°C for 1 minute, so that the surface of the grains was smooth and there were no obvious concave holes between the grain boundaries; then mechanical fine polishing was performed with silk cloth, and the 15% KI solution ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The process and steps of the polycrystalline mercury iodide film room temperature nuclear radiation detector in this embodiment are as follows:
[0037] (1) The crystal grain prepared on the conductive glass substrate substrate with gold thin film in advance is columnar, and the crystal grain direction belongs to the polycrystalline iodide of 2 inches * 2 inches in size of the (001) crystal plane type Mercury film, first use fine sandpaper to mechanically polish the film to make the surface of the grains smooth without obvious grain unevenness; then perform mechanical fine polishing with silk cloth to remove the mechanical rough polishing left by the grains Scratches; after mechanical fine polishing with silk cloth, chemical corrosion polishing is carried out with 18% KI solution at 15°C for 1 minute, so that the surface of the grains is smooth and there is no obvious concave hole between the grain boundaries; and then mechanically polished with silk cloth For fine poli...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breakdown voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com