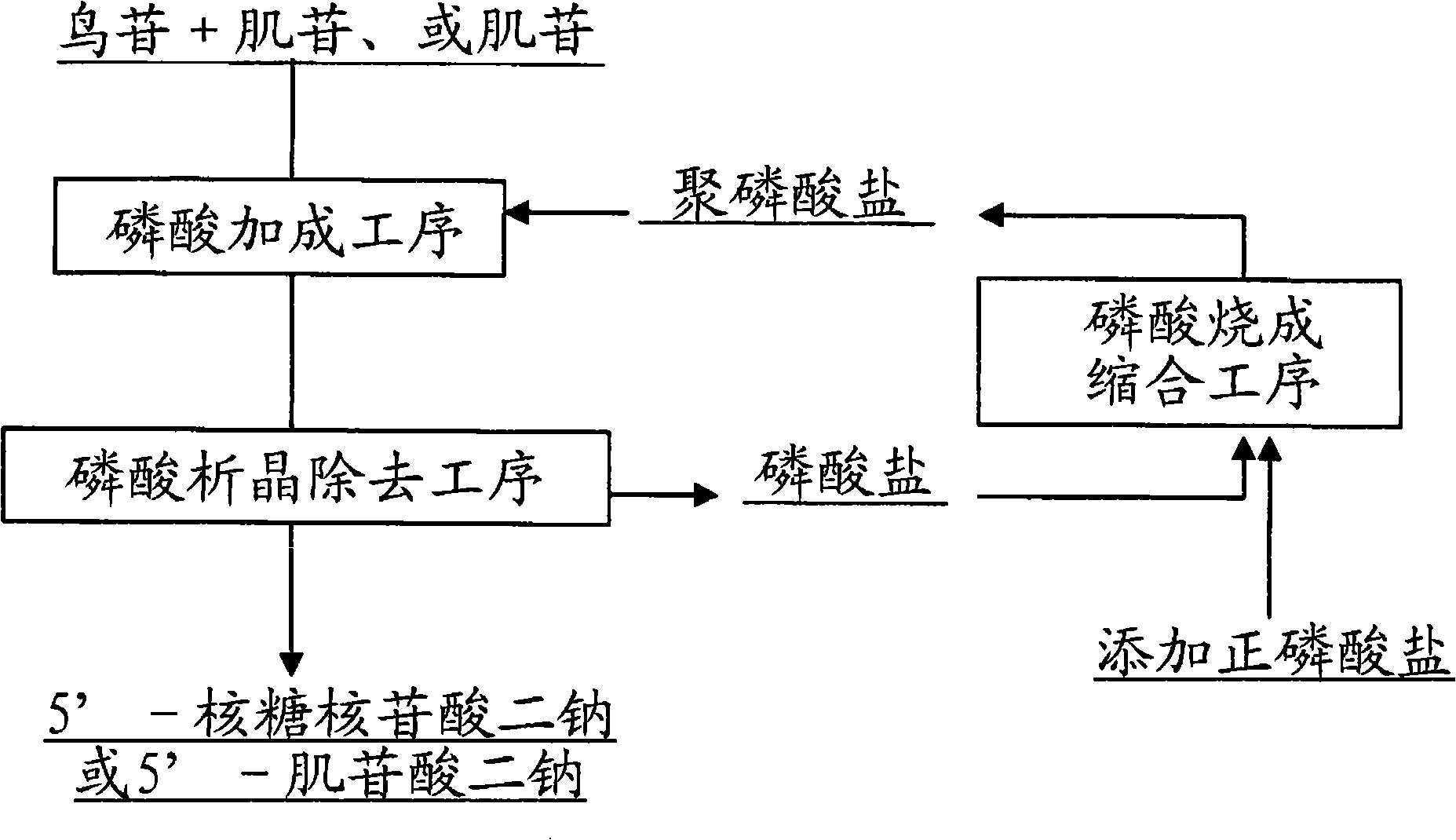
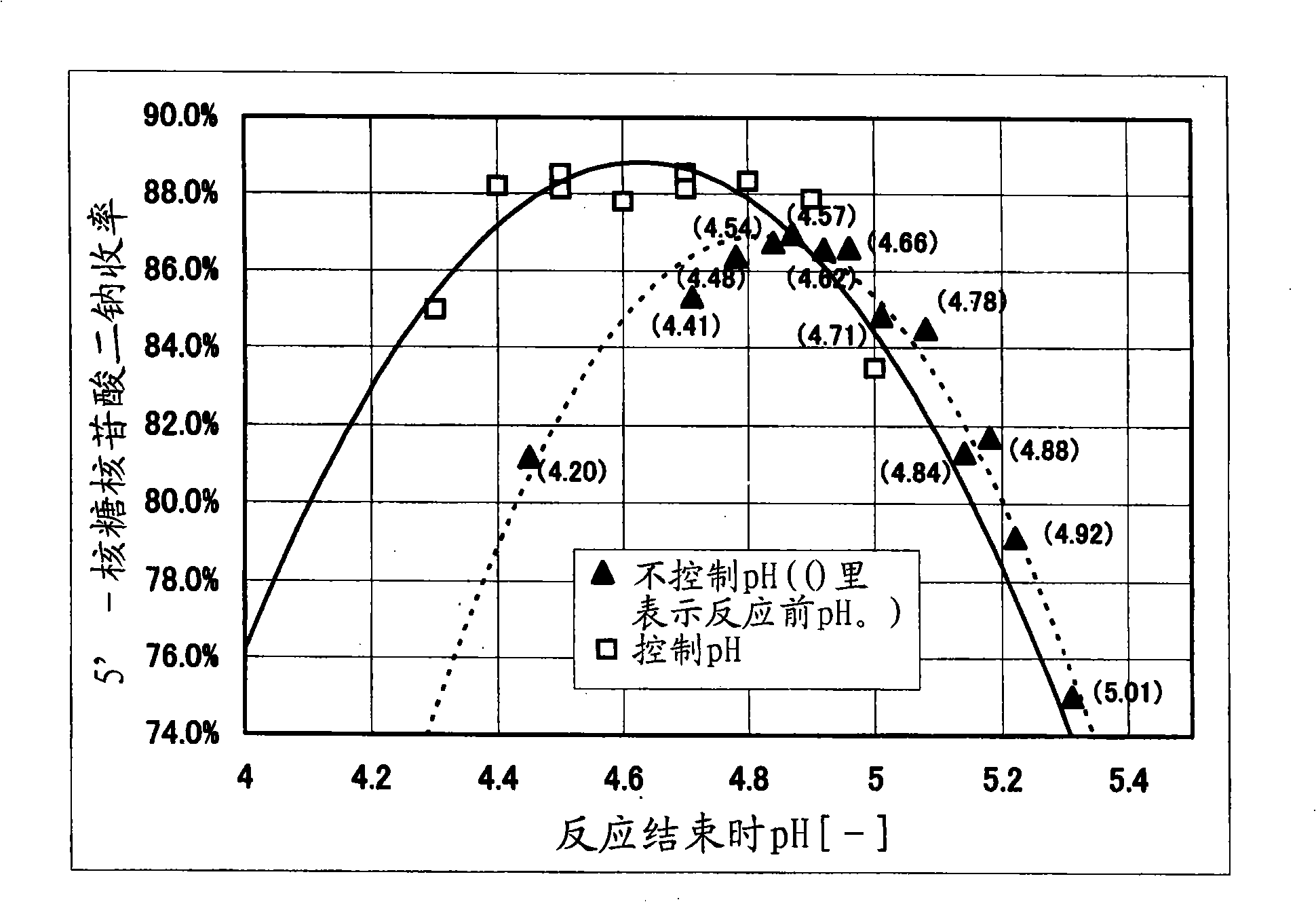
Method for preparing nucleotide using phosphoric acid circulation
A manufacturing method and nucleotide technology, applied in the field of nucleotide manufacturing, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining high phosphorylation yield and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1: Using basic sodium condensed phosphate with an average degree of polymerization of about 3 to 4 to increase the phosphorylation yield when adding phosphoric acid to nucleosides
[0040] (1) Preparation of bacteria containing acid phosphatase
[0041] Escherichia coli JM 109 / pEPI370 carrying the plasmid pEPI370 shown in Reference Example 1 described in JP-A-2002-289 was inoculated in 50 ml of L medium, cultured at 37° C. for 16 hours, and the culture solution was used as Enzyme solution is used. The enzyme solution contains bacterial cells containing acid phosphatase. Enzyme solutions in the following examples all use enzyme solutions prepared by this method.
[0042] (2) Preparation of phosphoric acid addition reaction raw material slurry
[0043] The method disclosed in JP 2002-289 A was used. That is, the guanosine crystal is made into a 27.1wt% slurry in water, and the pulverization process of the crystal is carried out by a pulverizer (DYNO MILL produ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2: reclaim the mixture of orthophosphate and pyrophosphate from the manufacturing process of 5'-ribonucleotide disodium, and regenerate the recovered phosphate into condensed sodium phosphate with an average degree of polymerization of about 3 to 4, Re-use in the production of 5'-ribonucleotide disodium
[0048] (1) Response to nucleoside addition of phosphate
[0049] Using the guanosine slurry after the same crushing treatment as in Example 1, 92g inosine, 79g guanosine and 228g sodium tripolyphosphate were suspended in 760g water, and then 95g35% hydrochloric acid was added to adjust the pH to 4.5. Add 228ml of enzyme solution at 0.5°C to start the reaction. During the reaction, 30 g of 35% hydrochloric acid was intermittently added to maintain the pH at 4.5. About 19 hours after the start of the reaction, an enzyme reaction solution containing 289 g of 5'-ribonucleotides was obtained.
[0050] (2) Phosphate crystallization removal process
[0051] The...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3: Reclaim the mixture of orthophosphate and pyrophosphate from the manufacturing process of 5'-disodium inosinate, condense and regenerate the recovered phosphate into condensed sodium phosphate with an average degree of polymerization of about 3 to 4, and again When used in the production of disodium 5'-inosinate
[0057] (1) Response to nucleoside addition of phosphate
[0058] Suspend 55g of inosine and 54g of sodium tripolyphosphate in 97g of water, add 15g of 35% hydrochloric acid, adjust the pH to 4.5, add 50ml of enzyme solution at 35±0.5°C, and start the reaction. During the reaction, 12 g of 35% hydrochloric acid was intermittently added to maintain the pH at 4.5. About 26 hours after the start of the reaction, an enzyme reaction liquid containing 101 g of disodium 5'-inosinate was obtained.
[0059] (2) Phosphate crystallization removal process
[0060] The pH of the above reaction solution was adjusted to 9.7 with 34% sodium hydroxide aqueous s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com