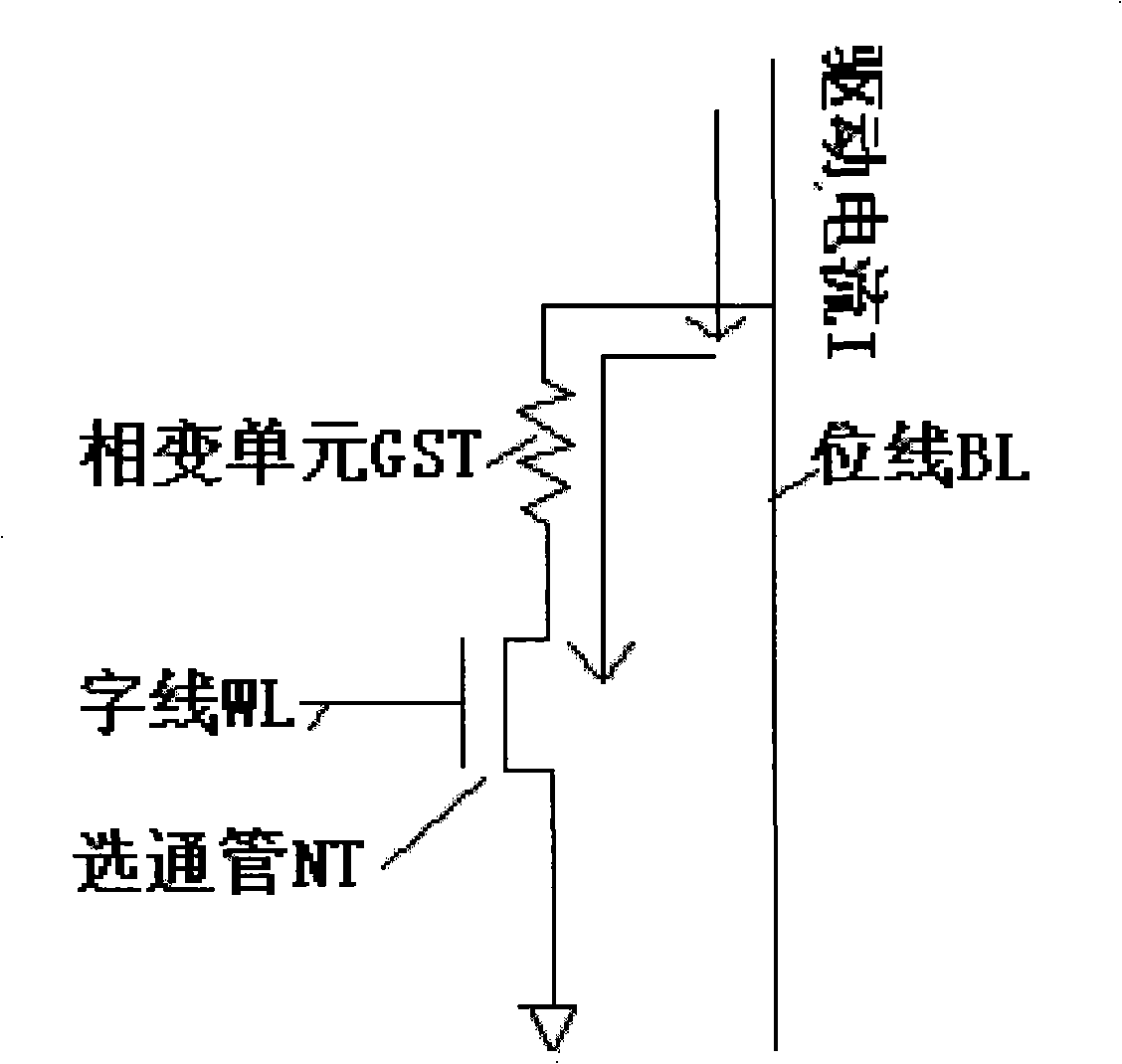
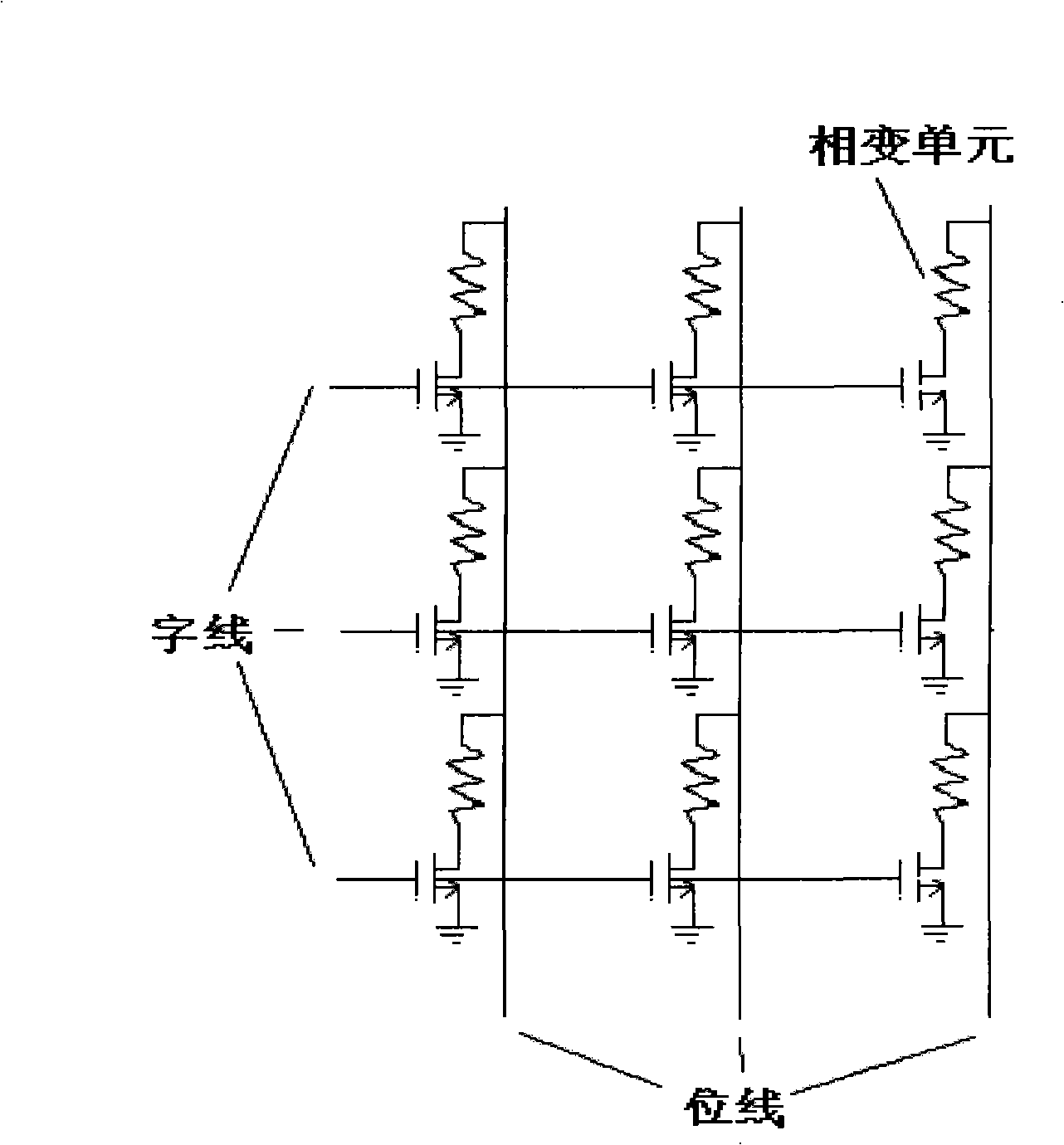
Phase-change memorizer 1R1T structure and its driver circuit design method
A phase change memory, 1R1T technology, applied in static memory, read-only memory, digital memory information and other directions, can solve the problems of high cost, unfavorable integration of phase change memory, large area, etc., to increase the implementation method, increase the scale and complexity performance, and the effect of reducing manufacturing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
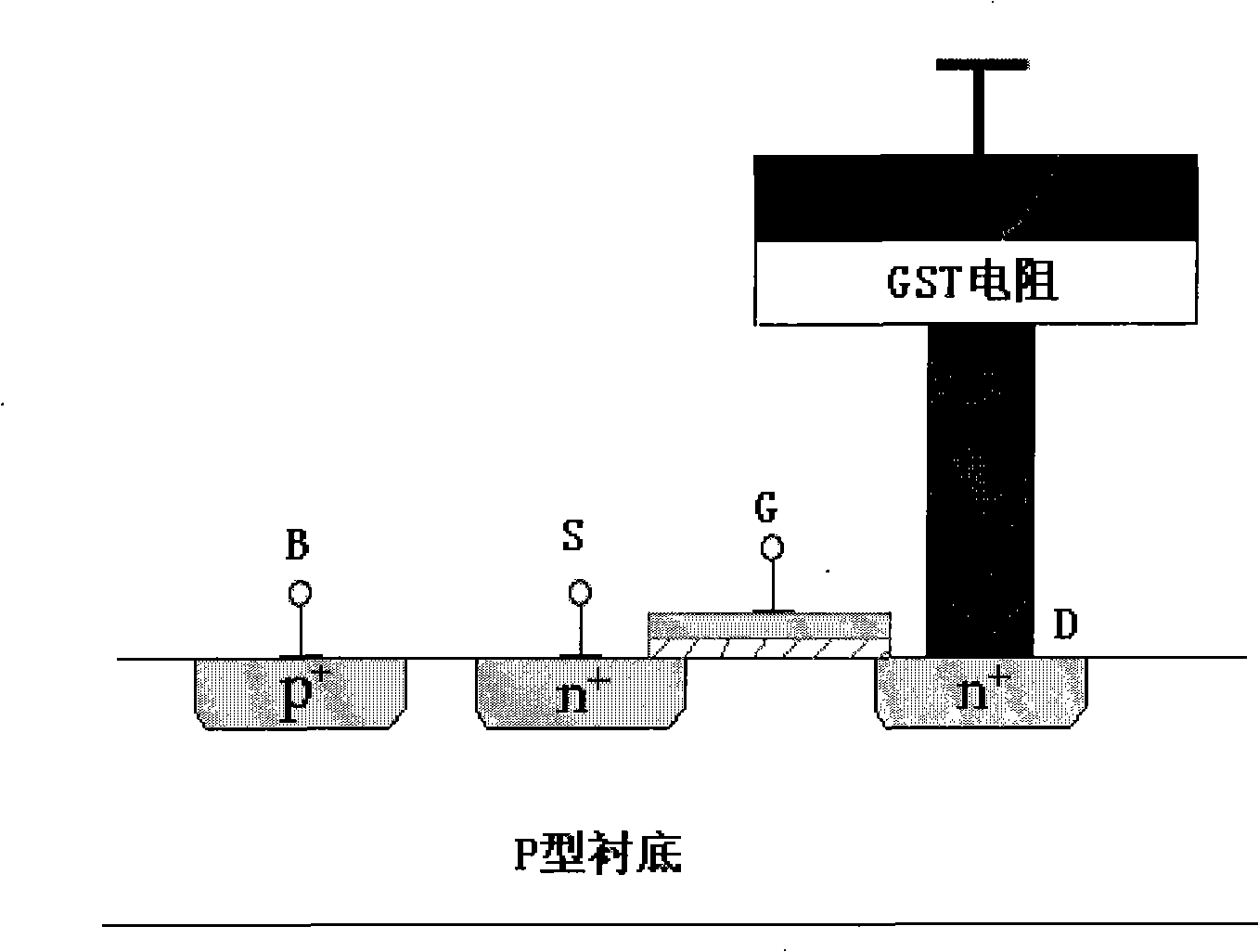
[0032] A specific embodiment of the specific implementation of 1R1T of the present invention, such as Figure 4 As shown, first the basic circuit part is completed through the standard CMOS process line, the drain end of the gate tube is connected through the outermost layer of metal, and then SiO is deposited on the layer of metal 2And etch a smaller through hole 3, and fill it with metal tungsten (as the lower electrode), and next to this smaller through hole is another slightly larger through hole 4, so far, all are completed by standard CMOS technology of. Then use the GST process line, first sputter a layer of phase change material GST to cover the larger through hole above, and then etch away the excess GST, (a layer of SiO can be added 2 ), and then grow a layer of metal aluminum (Al) on it as the upper electrode 5, etch, and finally cover a passivation layer of silicon dioxide.
[0033] In this way, except for the phase change resistor GST part in the storage array, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com