Puerarin derivatives powder injection and its production method
A technology of puerarin derivatives and powder injection, which is applied in the directions of powder delivery, drug combination, pharmaceutical formulation, etc., can solve the problems of drug effectiveness, safety impact, unacceptable for patients, and large dosage, avoiding instability, Guaranteed safety and ease of use
Inactive Publication Date: 2008-10-22
普尔药物科技开发(深圳)有限公司
View PDF0 Cites 4 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Because the drug must be dissolved before it can be absorbed in the body, if tetraacetyl puerarin is prepared into quick-acting preparations such as dispersible tablets and dropping pills, the dosage will be large, which is difficult for patients to accept; if it is prepared into oral liquid, because tetraacetyl puerarin is in Poor stability in the solution, long-term storage, easy to degrade and precipitate out, resulting in the effectiveness and safety of the drug being affected
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
preparation example Construction
Embodiment 1
Embodiment 2
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
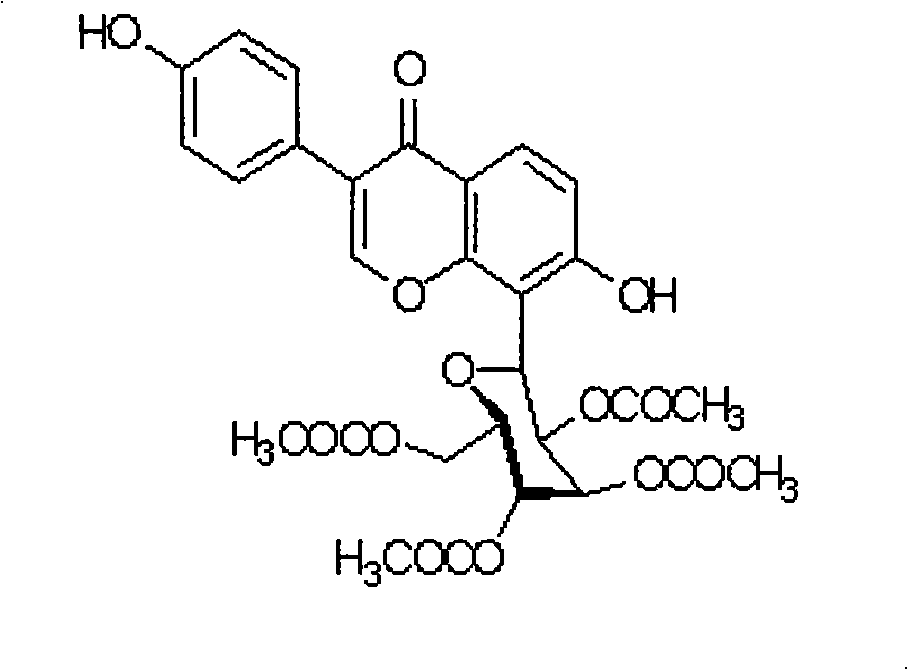
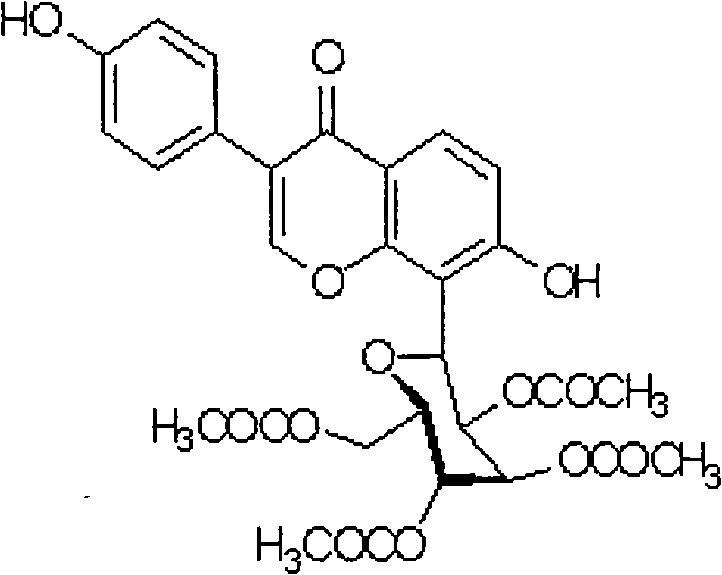
The invention provides a puerarin derivant powder injection preparation, which is characterized in that each powder injection of the powder injection preparation contains 0.001g to 0.1g of active component of puerarin derivant; the pharmaceutic adjuvants of the injection are that: one or more of polysorbate 80, kollison K30, hydroxypropul beta cyclodextrin is selected as solubilizer; one of poloxamer 188 or mannite or the combination thereof is selected as addictive agent; and the weight ratio between the puerarin derivant and the solubilizer is 1: (6-16); the weight ratio between the puerarin derivant and the addictive agent is 1: (3-20). The invention also discloses a preparation method for the puerarin derivant powder injection preparation. The preparation technique makes use of solvent method to dissolve medicine and adjuvant into a same organic solvent, the solvent is removed through evaporation and the solid dispersion freeze-dried powder is finally obtained through freeze drying. The puerarin derivant powder injection preparation solves the problem of unstable quality of puerarin derivant liquid injection preparation and has advantages of good shaping, rapid dissolution, clearance, stability and convenient use, etc.
Description
Puerarin derivative powder injection and preparation method thereof technical field The invention belongs to the technical field of natural medicine injections, in particular to an injection of puerarin derivatives and a preparation method thereof. Background technique Coronary heart disease and angina pectoris are common clinical and harmful diseases. In recent years, the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases has increased significantly, and they have become the number one killer threatening human health. They are called "the plague of the times" by the world medical community. The number of deaths due to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in my country reaches 2.6 million every year, with an average of about 300 deaths per hour, especially the age of onset and death is increasingly showing a younger trend [1]. According to data analysis, nearly one-quarter of the world's population is threatened by cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases a...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): A61K31/7048A61K9/14A61K9/19A61P9/10
Inventor 李博刘姹杨大坚陈新滋
Owner 普尔药物科技开发(深圳)有限公司
Features
- Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com