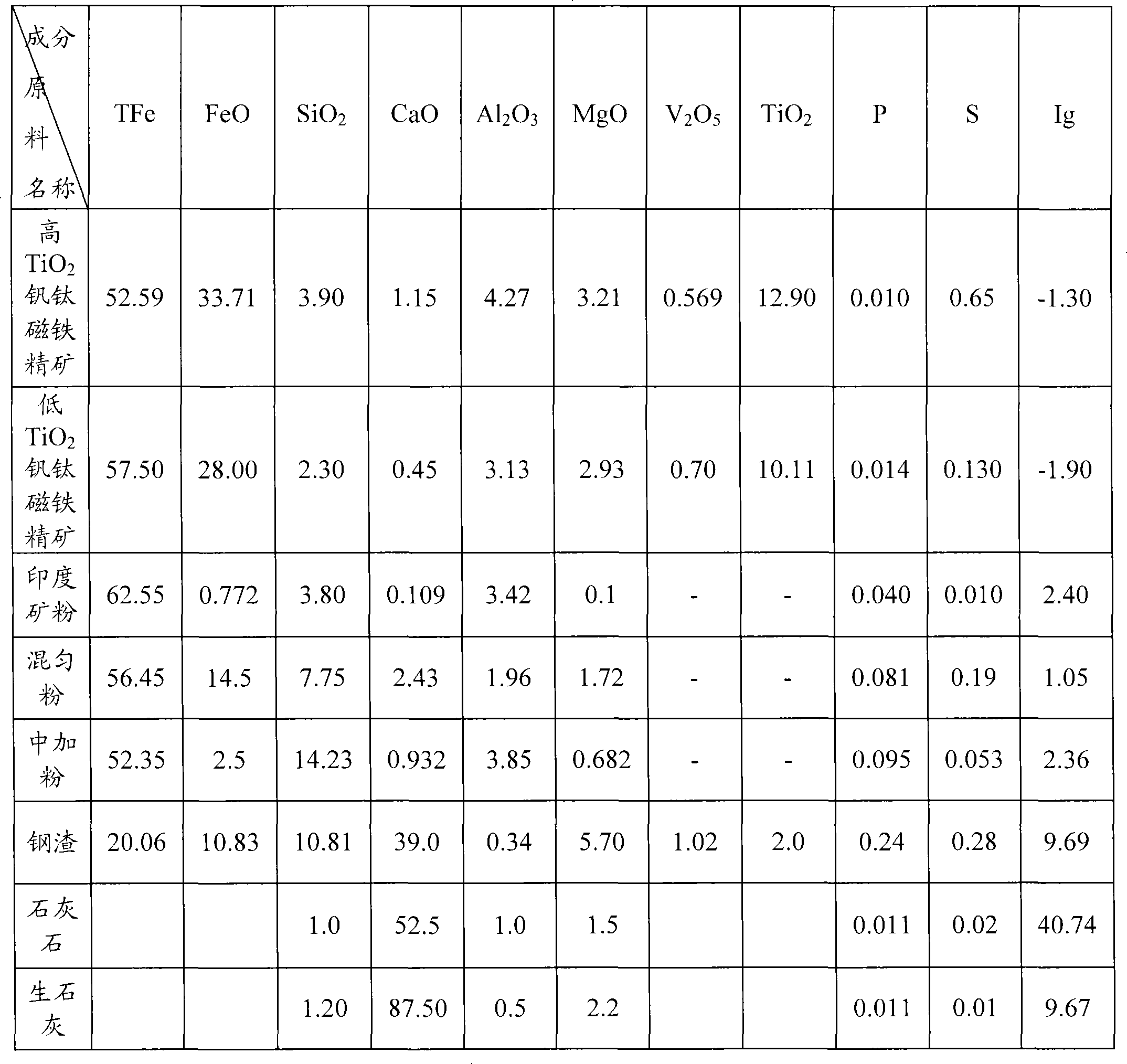Blast furnace ironmaking raw material and method for preparing same
A blast furnace ironmaking and raw material technology, which is applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy, can solve problems that do not involve improving the quality of sintered ore, difficult sintering mixture granulation, and low sintering strength, so as to improve mineral composition and structure and reduce fuel consumption. , Improve the effect of metallurgical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0021] The preparation method of blast furnace ironmaking raw material according to the embodiment of the present invention comprises preparing TiO 2 A step of sintering ore with a content of 5.91% to 4.7% and a step of preparing pellets.
[0022] Can be made of TiO 2 Sintered ore is prepared from sintered raw materials with a content of 5.91% to 4.7%, wherein the sintered raw materials may contain high TiO 2 (Content 12%~13%) Vanadium Titanium Magnetite Concentrate, Low TiO 2 (Content 10%~11%) Vanadium Titanium Magnetite Concentrate, TiO 2 Steel slag with 2% content, return ore with the same composition as sinter and no TiO 2 Iron ore powder, flux and sinter fuel. High TiO 2 Vanadium Titanium Magnetite Concentrate and Low TiO 2 The sum of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate can account for 42%-45% of the total weight of sintering raw materials, the weight of steel slag can account for 3.2% of the total weight of sintering raw materials, and the weight of returned or...
Embodiment 1
[0026] Preparation of sinter
[0027] First, prepare TiO 2 The raw material for sintering with a content of 5.91% uses limestone and quicklime as the sintering flux, coke oven gas as the ignition fuel, and coke powder as the sintering fuel. 2 The belt-type sintering machine sinters the sintering raw material, and the sintering air volume is 92m 3 / m 2 ·min, the negative pressure of the supervisor is 12600Pa. After the sintering is completed, the sintered ore is unloaded from the tail of the machine, crushed by a single-roller crusher, then screened by a thermal vibrating screen, then cooled by a ring cooler, and finally screened by a fixed screen. After being sieved by a fixed sieve, the sintered ore with a particle size of not less than 10 mm is used as a part of the blast furnace ironmaking raw materials according to this embodiment (among them, a small part of sintered ore with a size of 10 mm to 16 mm is separated as the bottom material for the sintering machine), and...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The raw materials for blast furnace ironmaking were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the proportioning percentage of sintered raw materials and the weight ratio of sintered ore to pellets were different. Wherein, the proportioning percentage of embodiment 2 is as shown in table 1, and in sintering raw material and sintering ore, TiO 2 The content of sintered ore is 5.50%, and the weight ratio of sintered ore and pelletized ore is 75:25.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com