Inhibition of viral gene expression using small interfering RNA
A technology of small interference and expression vectors, applied in the direction of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, viruses, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem of incomplete treatment and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0121] Example 1: Design and Construction of shRNA Expression Cassette, T7 Transcription Reaction and Reporter Gene Test
[0122] Chemically synthesized oligonucleotides were obtained from IDT (Coralville, IA), resuspended in RNase- and pyrogen-free water (Biowhittaker), and annealed as described below. The following oligonucleotide pairs used to prepare shRNAs contain the T7 promoter element (double underlined), sense and antisense HCVIRES sequences, and the miR-23 small RNA loop structure (reported to favor cytoplasmic localization [21,22] ).
[0123] T7-HCVa-wt fw:
[0124] 5'- agcacgaatcctaaa c ctca
[0125] aagaCTTCCTGTCAtctttgaggtttaggatt c gtgctcTT-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1);
[0126] T7-HCVa-wt rev:
[0127] 5’-AAgagcacgaatcctaaa c ctcaaagaTGACAGGAA
[0128] Gtctttgaggtttaggatt c gtgct -3'
[0129] (SEQ ID NO: 2)
[0130] (T7 promoter sequence is double underlined). T7 transcripts of HCVa-mut shRNA were identical except for the nucleotide changes (G→C vs. C→G)...
Embodiment 2
[0146] Example 2: shRNA Inhibition of HCV IRES-mediated Gene Expression in Human Tissue Culture Cells system
[0147] In this study, the ability of short interfering RNA (shRNA and siRNA) targeting the conserved region of hepatitis C IRES designed and constructed according to Example 1 to inhibit HCVIRES-mediated reporter gene expression in human tissue culture cells was tested.
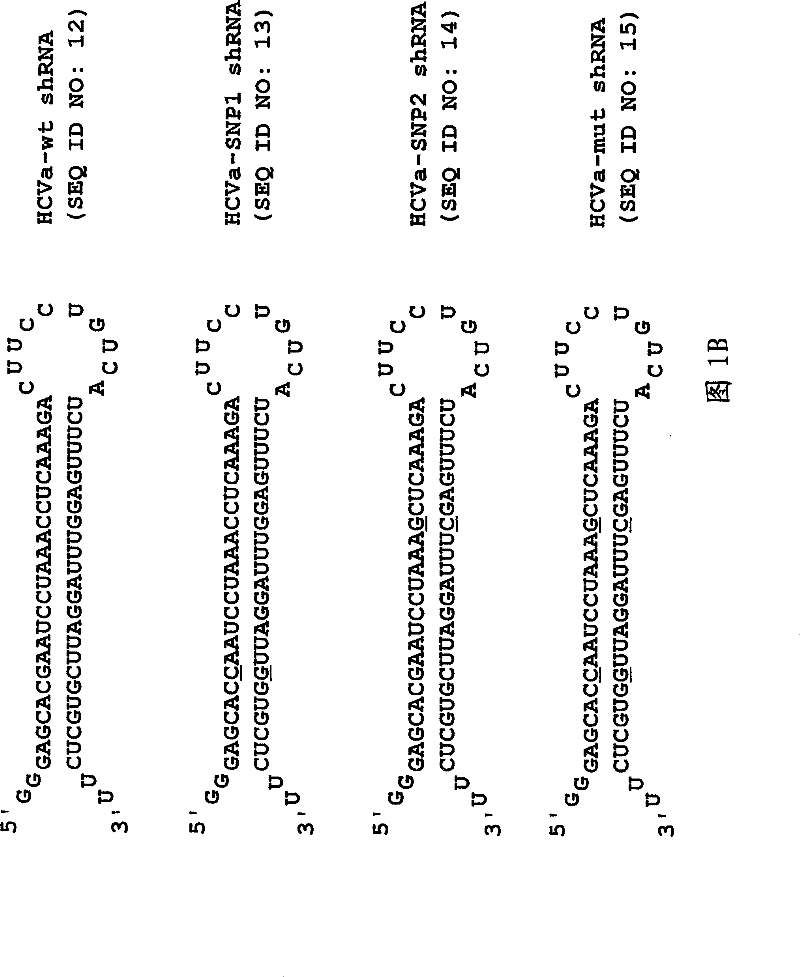
[0148] Figure 1A Shows the HCV IRES target site (Panel A) and the HCV shRNA transcribed via T7 from a template prepared from a hybrid oligonucleotide containing the T7 promoter sequence and the HCV IRES target ( Figure 1B ). The underlined residues are those that were changed to generate the mutant HCV shRNA. This shRNA contains the miR-23 small RNA loop structure previously suggested to facilitate cytoplasmic localization [21,22] and 25 base pairs of RNA stem and 2 nucleotides at the 5' (2 guanines) and 3' (2 uridines) ends (which can also be base-paired by non-Watson-Crick G:U to hybridiz...
Embodiment 3
[0159] Example 3: shRNA Inhibition of HCV IRES-Mediated Gene Expression in a Mouse Model System
[0160] The ability of HCV shRNA and HCV shRNA expression plasmids to repress target gene expression was extended to a mouse model system by using hydrodynamic injection to deliver these nucleic acids to the mouse liver. Figure 5 shows the injection of a large volume of PBS (1.8 ml) containing pHCV dual Luc, pSEAP2, and shRNA (based on the mass of shRNA or pol III expression vector expressing shRNA, 10-fold excess to target) into the mouse tail vein (n = 4-5 mice). in such as Figure 5B At the indicated time points, luciferin was injected intraperitoneally and mice were photographed with a high-sensitivity, cooled CCD camera. ( Figure 5A Representative mice selected from each group (4-5 mice per group) at the 84 hour time point are shown). HCV shRNA strongly suppressed luciferase expression at all time points tested, from 98% (84-hour time point) to 94% (48-hour time point)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com