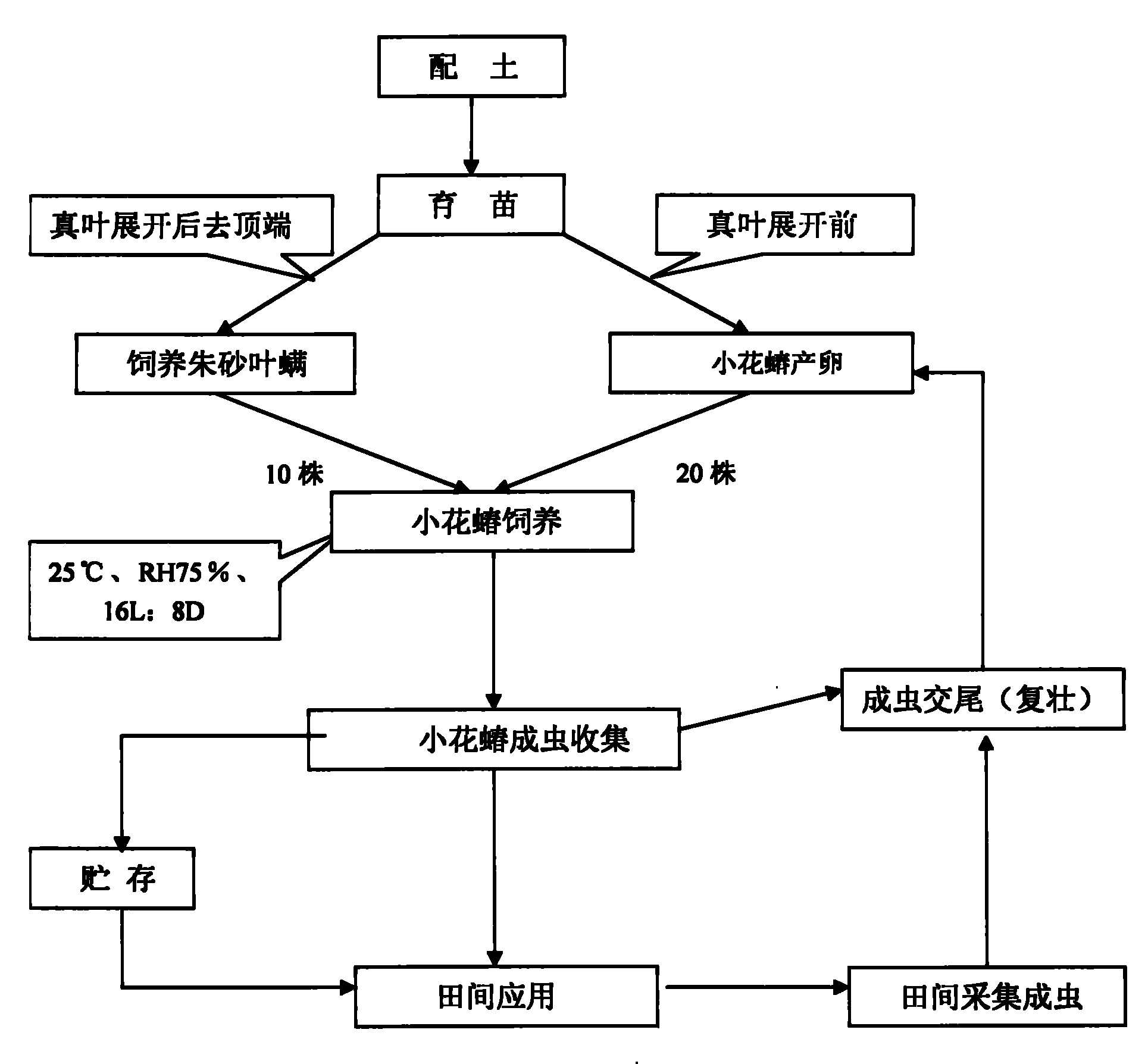
Artificial propagation method of minute pirate bugs
A technology of artificial breeding and small flower bugs, which is applied in the field of artificial breeding of flower bugs and small flower bugs. It can solve the problems of less research, difficulty in mastering breeding technology, and lack of large-scale breeding of small flower bugs, so as to achieve the breeding density. Reasonable, improve the survival rate and development speed, increase the adult acquisition rate and the effect of egg production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] 1. Production tools
[0053] 1) Fluke tube:
[0054]Large fluke tube: inhale multiple adults or nymphs at one time. Take a plexiglass tube with an inner diameter of 2.5 cm and a height of 10 cm and two rubber stoppers whose size matches the mouth of the tube, punch an 8 mm hole in the center of each rubber stopper, and then insert a 2ml pipette into the two tubes respectively. One of the insertion methods is to insert the tip of the pipette from the end of the small diameter of the rubber stopper, and the other is to insert the tip of the pipette from the end of the large diameter of the rubber stopper, inserting the tip of the former pipette Cut off at a diameter of 4mm (to facilitate the fluke), insert a plexiglass tube as one end of the fluke; the latter is to cut off the tip of the pipette with a knife against the rubber stopper, and wrap the rubber stopper with a small diameter of 120 mesh gauze. Insert one end into the plexiglass tube (to prevent the insects fro...
Embodiment 2
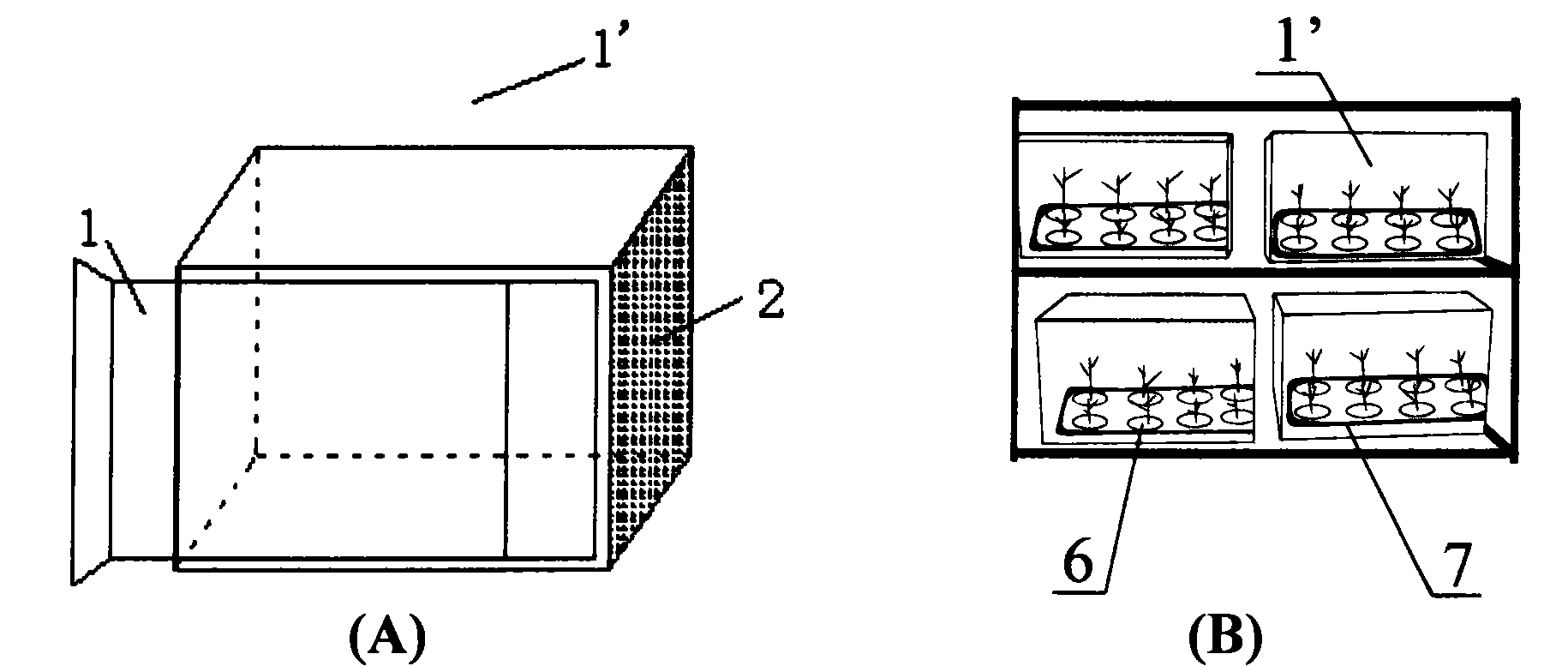
[0090] 1. Production tools: soilless culture insect cage
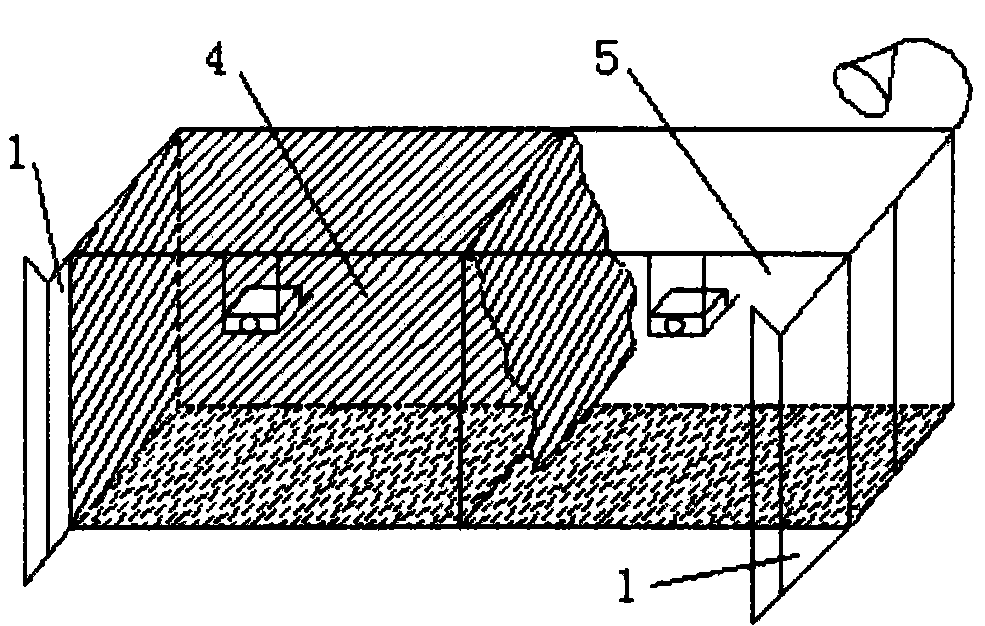
[0091] In the process of using large insect cages to raise small flower bugs, it was found that the amount of watering was difficult to control, and it was inconvenient to operate. Therefore, the inventor designed a new type of soilless culture insect cage 1", the soilless culture in use Bug cage 1" as Figure 4 shown. The main body of the soilless culture insect cage 1” is an aluminum alloy frame. The design of the entire insect cage is mainly divided into two parts. The upper part is the insect room, which is located above the seedling hole. Glass topping (good for light transmission), one side is provided with a sliding door 1, the material of the sliding door 1 is plexiglass, and a handle is provided on the sliding door 1, and two handles and two handles are respectively arranged on the frame. Magnetic buckle, the magnetic buckle on the sliding door 1 corresponds to the magnetic buckle on the frame. In order to p...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Embodiment 3 comparative experiment process
[0097]1. Experimental materials and methods
[0098] Experimental materials: Select four kinds of spawning substrates: kidney bean sprouts, kidney bean leaves, soybean sprouts and broad bean sprouts.
[0099] Special note: Stereo microscope (Motic-SFC-11C-N2GG) is used for experimental equipment: produced by Motic Industrial Group Co., Ltd., which is used to observe and count eggs, other production tools, other feeding materials and experimental methods Same as mass production.
[0100] 2. Results and Analysis
[0101] 1) Selectivity of 4 spawning substrates
[0102] In addition to the average daily egg laying on soybean sprouts and broad bean sprouts, there was no significant level among the other treatments. Among them, the daily average egg production on broad bean sprouts is at least 1.4, the daily average egg production on kidney bean sprouts is at most 12.7 eggs, 7.8 eggs on kidney bean leaves, and 1.7 eggs on broa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com