Methods for characterizing molecular interactions
A qualitative analysis and specific technology, applied in analytical materials, chemical method analysis, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as slow apparent dissociation rate constants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0042] Example 1: Overview of methods for qualitative analysis of antibody-antigen responses.
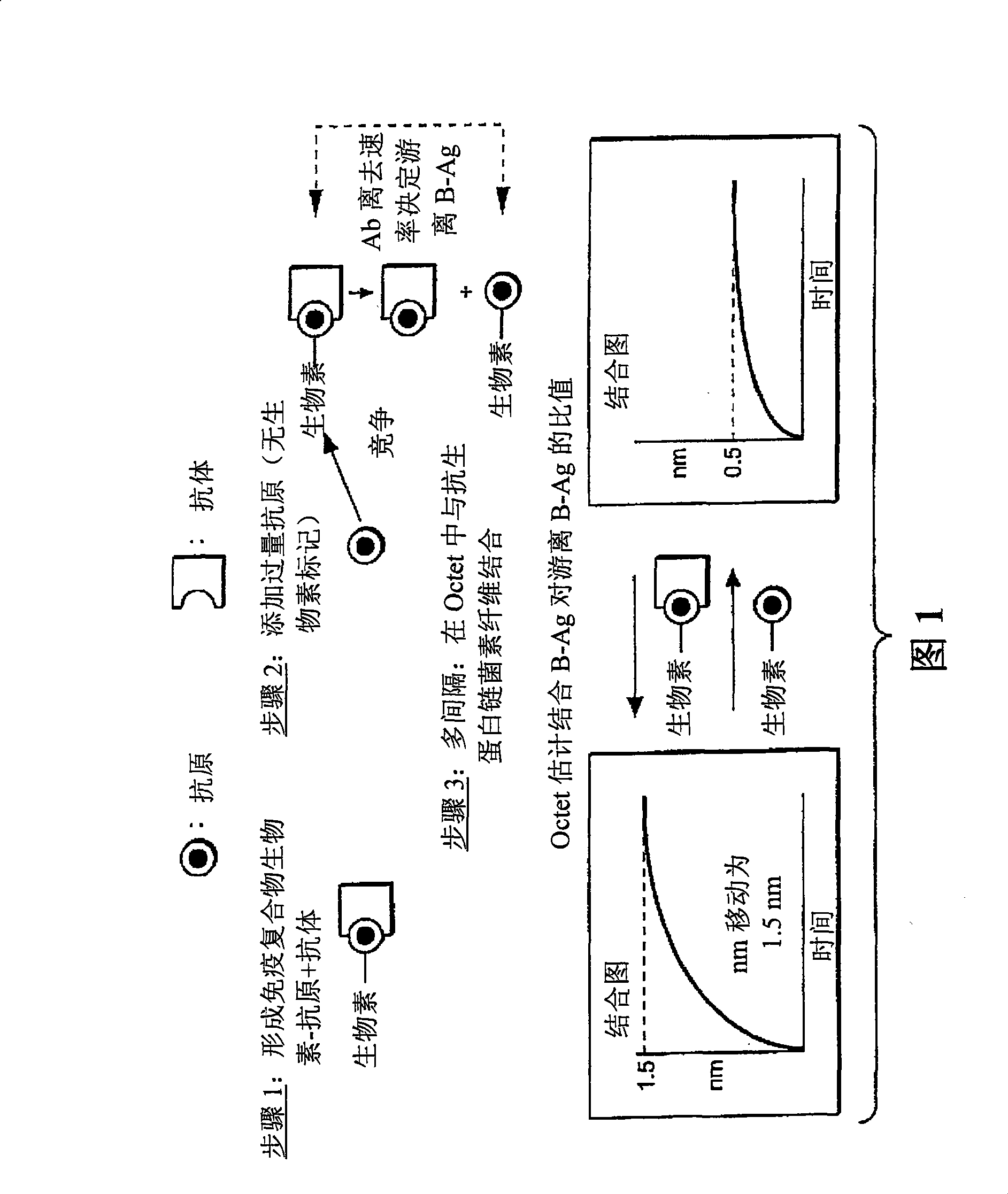
[0043] A scheme for practicing the method of the present invention to qualitatively analyze antigen-antibody responses is disclosed in FIG. 1 . In Step 1, samples are prepared as follows: affinity-tagged (e.g., biotinylated) antigen ( L * ) forms an immune complex with the antibody (R) whose dissociation rate constant is to be estimated. The labeled antigen and antibody concentrations are preferably selected such that at equilibrium substantially all of the labeled antigen is bound by the antibody. In step 2, a large excess of unlabeled antigen (L) is added to elicit a reaction that competes with the biotin-antigen for the antibody binding site. In this format, since the biotin-antigen has been previously bound by the antibody, the immune complex must dissociate in order to bind the unlabeled antigen. After dissociation, a molar excess of unlabeled antigen preferentially binds...
example 2
[0044] Example 2: Qualitative analysis of anti-FITC / FITC responses using glass fiber biolayer interferometry sensors.
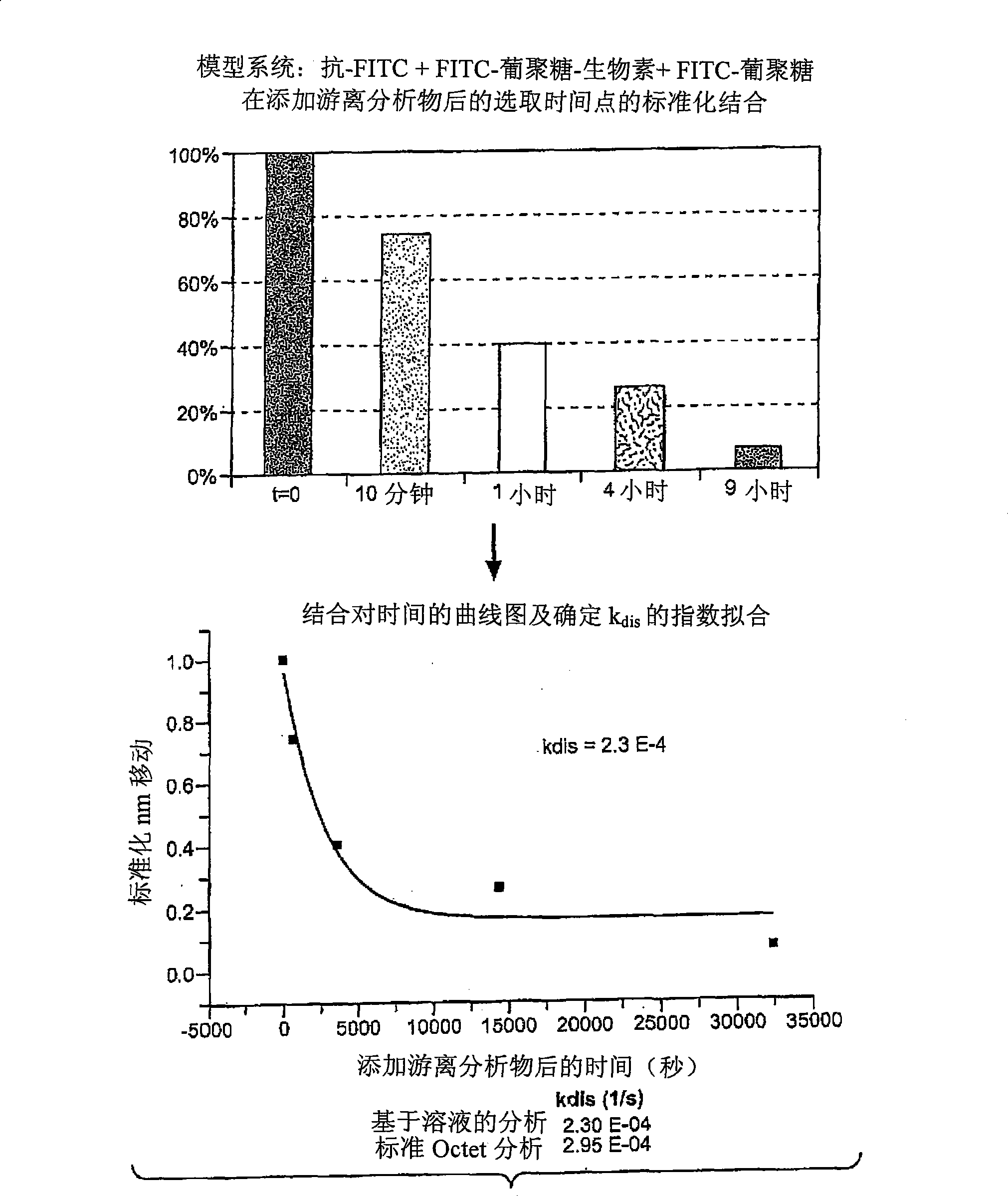
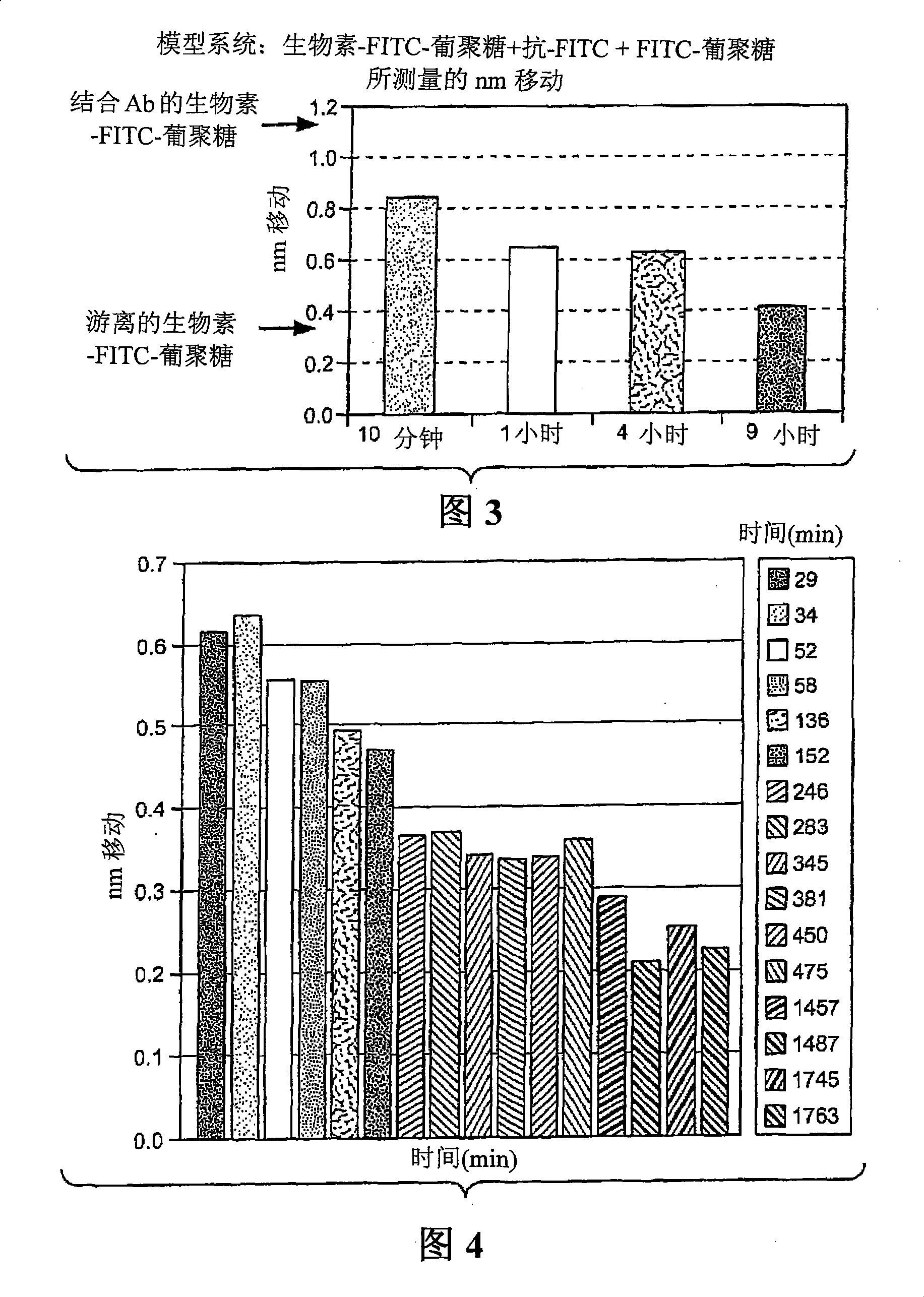
[0045] figure 2 The step 3 dissociation results for the anti-fluorescein / fluorescein-dextran binding pair are shown (schematically in Figure 1). In this example, a glass fiber biolayer interferometer sensor was used to perform a solid phase binding assay. Sensors and methods of making and using them are described in detail in commonly owned US Patent Application Publication No. 20050254062, the entirety of which is hereby incorporated by reference for all purposes. In this example, the fibers were derivatized with streptavidin conjugated to a biotin label present on the FITC-dextran ligand. The use of this type of sensor in the practice of the method may provide unexpected advantages. In the early stages of developing a therapeutic antibody, the amount of antibody available may be limited. The accuracy of off-rate estimates is improved by performing rep...
example 3
[0091] Example 3: Implementation of the inventive method on a biomolecular interaction analyzer device
[0092] 1. Sample preparation was performed in a manner similar to that described in Example 2, except that samples were prepared in larger batches (eg, 10-20 mL). Each analysis consumes an aliquot (eg, approximately 1-2 mL). Additionally, use a solution control to correct for any refractive index changes due to protein concentration. For this working example, the ideal solution control consisted of analyte plus antibody that was not biotinylated to give a similar total protein concentration to the sample.
[0093] 2. Using a streptavidin Bacow chip (Sensor Chip SA, Bacow Registry No. BR-1000-32). Alternatively, streptavidin can be immobilized by standard protocols using an amine-reactive CM5 chip (Bacow Accession No. BR-1006-68).
[0094] 3. For each time point, a new Bacow chip is used. Each chip contained four flow cells that could be used to analyze three samples a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com