Method and equipment for recovering cadmium and nickel from waste and old nickel-cadmium battery and preparing metal cadmium ingot and superfine nickel powder
A nickel-cadmium battery and metal cadmium technology, applied in the field of metal cadmium ingots and ultra-fine nickel powder, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, low added value of nickel-containing products, and high cadmium recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
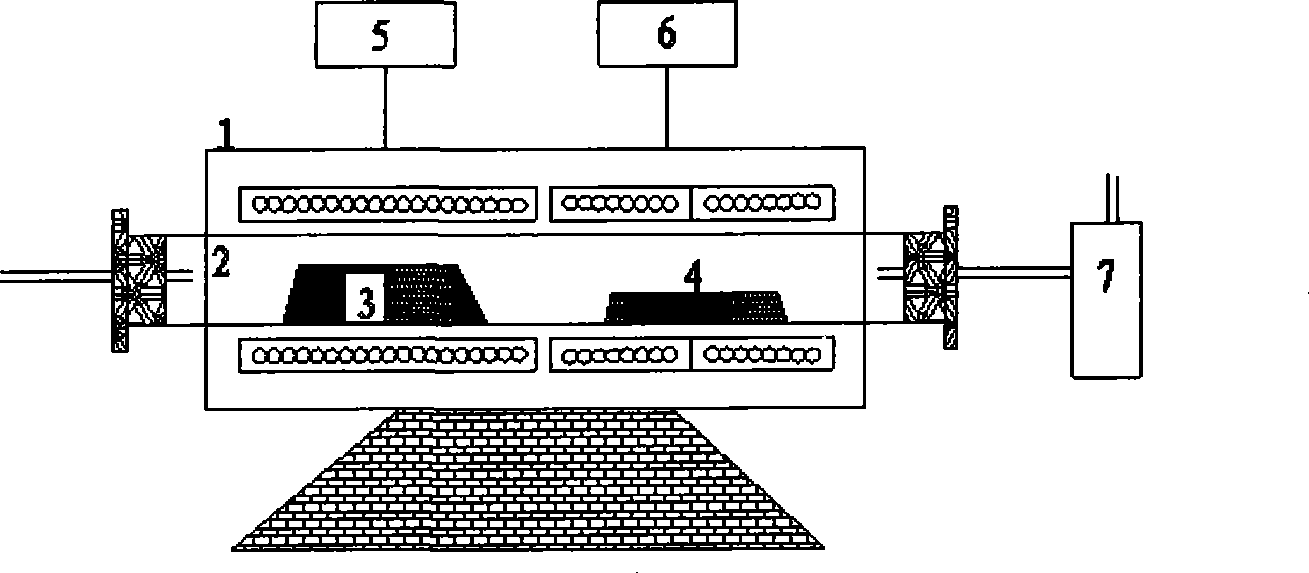
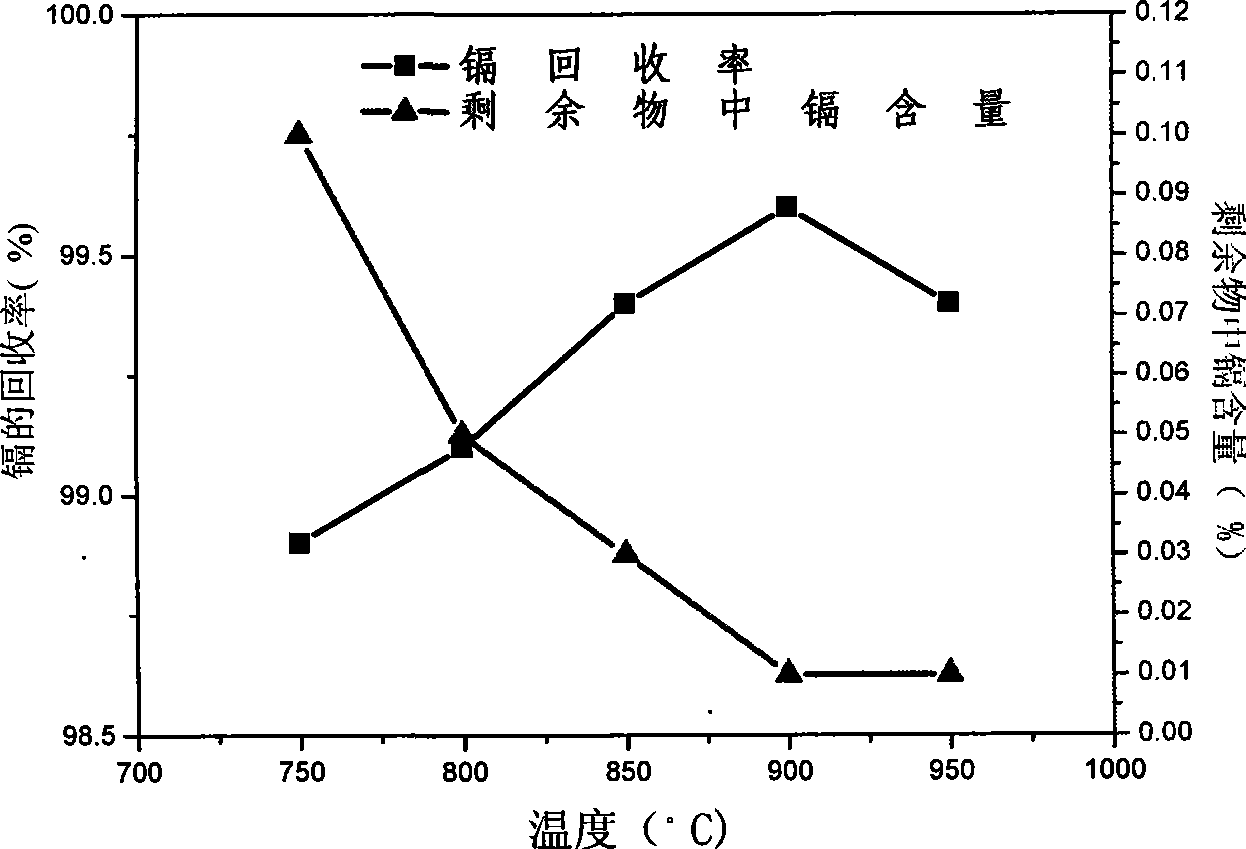
[0035] Use a professional dismantling machine to cut along the top of the AA nickel-cadmium battery without positive and negative active materials, so that the tabs are disconnected, and the tops of the positive and negative active materials are exposed. Take 179.2g of the battery and put it into a high-temperature furnace, keep nitrogen purging, and raise the temperature to 900°C for about 2 hours; keep the temperature of the low-temperature section at 150°C, and after the cadmium vapor is blown into this section by the nitrogen flow, it is rapidly cooled into liquid cadmium beads Into the curing mold, and finally condensed into cadmium block. Weigh after cooling: the weight of the cadmium block is 37.6g, and the weight of the nickel-iron slag is 89.5g. The cadmium content in the cadmium block detected by EDTA complexometric titration is 99.9%, and the cadmium content in the remaining ferronickel slag detected by atomic absorption spectrometer is 0.01%, and the calculated rec...
Embodiment 2
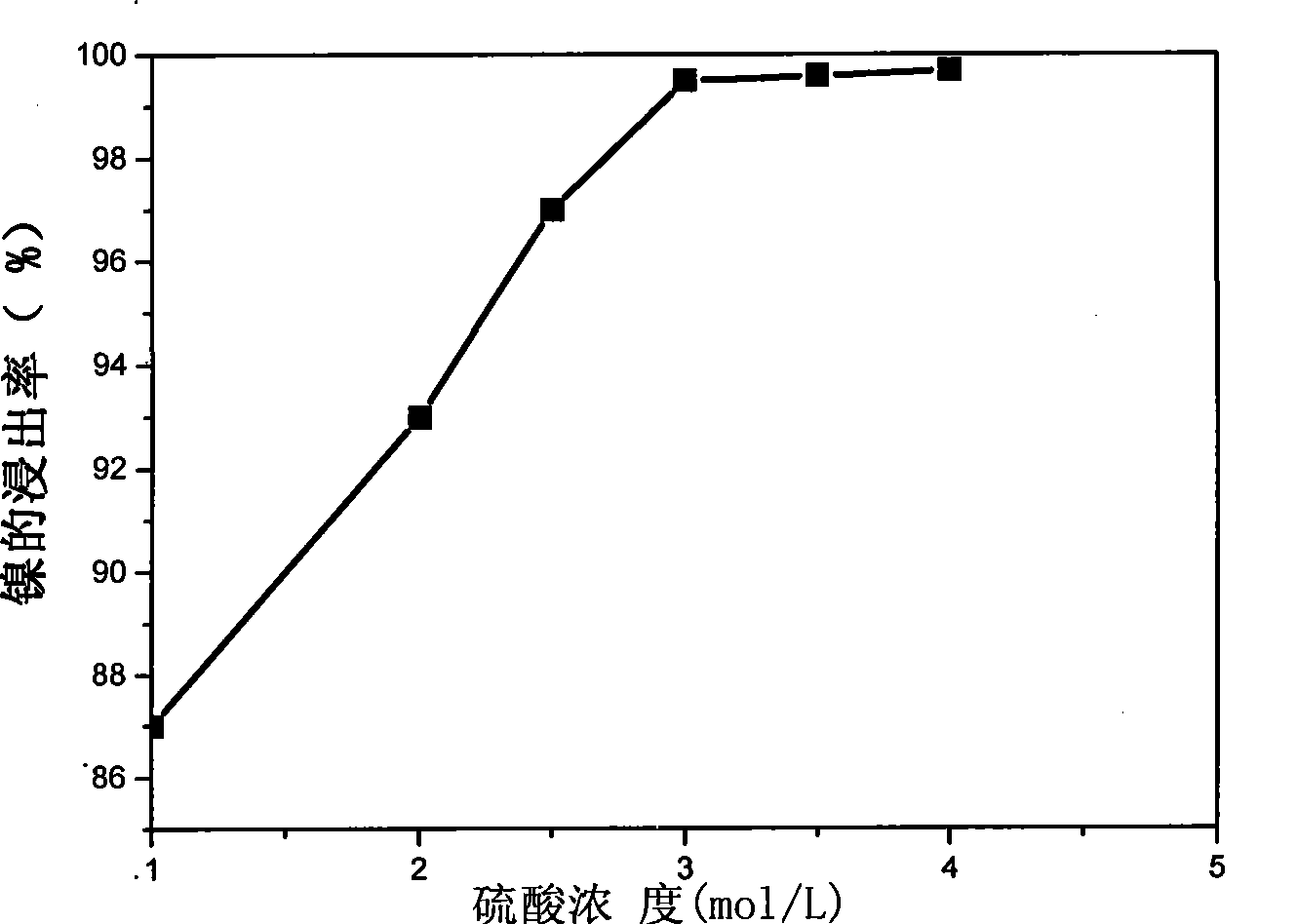
[0037] Get the ferronickel slag 50.0g among the embodiment 1 and put into the beaker, add the sulfuric acid 150ml and the 10ml hydrogen peroxide solution (H 2 o 2 content is 30%), put the beaker into a constant temperature water bath, adjust the temperature to 90°C, keep stirring with a magnetic stirrer, after 40min of reaction, filter to remove the filter residue, and set the filtrate to a constant volume of 500ml. EDTA complexometric titration, flame atomic absorption spectrometry and plasma emission spectrometry (ICP) are used to detect the metal element content in the leachate as follows:
[0038] element Fe Ni K co mn Zn Mg Cd Leaching solution (g / L) 46.3 39.4 5.92 2.21 0.76 0.45 0.24 0.02
[0039] After calculation, the leaching rate of nickel is 99.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Get leaching solution 150ml in embodiment 2 and pour into beaker, add 15ml hydrogen peroxide solution (H 2 o 2 content is 30%), put the beaker in a constant temperature water bath, adjust the temperature to 90°C, keep the magnetic stirrer stirring, after reacting for 30min, add an appropriate amount of potassium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to 3.5, filter and remove the filter residue after standing, Dilute the filtrate to 250ml. Adopt EDTA complexometric titration, flame atomic absorption spectrometry and plasma emission spectrometry (ICP) to detect metal element content in the filtrate as follows:
[0042] element Ni K co mn Zn Mg Fe Cd Filtrate (g / L) 23.5 4.55 1.30 0.44 0.23 0.12 0.03 0.01
[0043] At this time, the iron removal rate was 99.86%, and the nickel loss rate was 0.32%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com