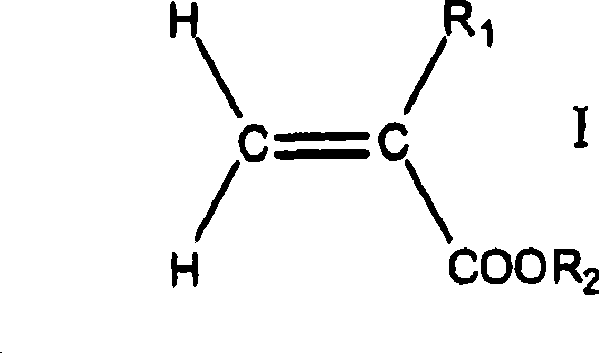
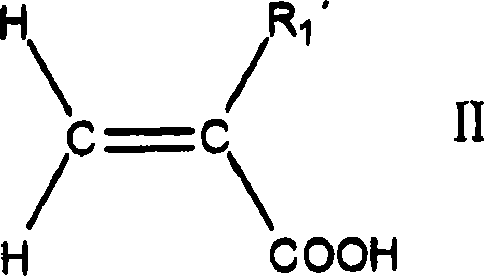
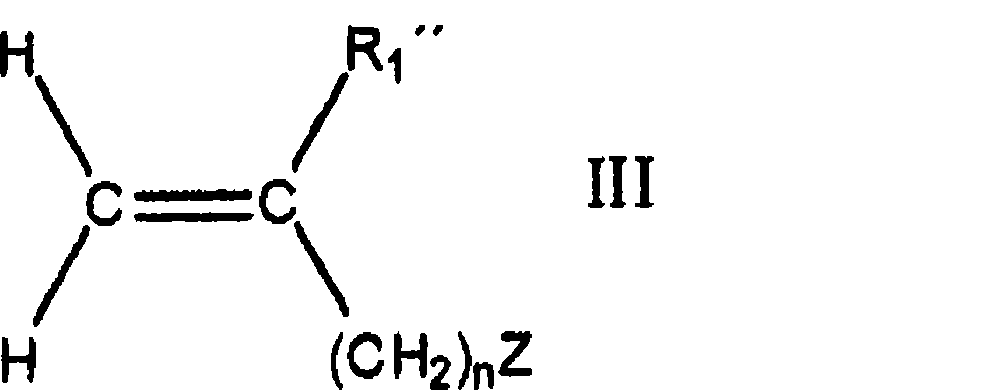Adhesives based on polyester graft poly(meth)acrylate copolymers
A graft copolymer, acrylate technology, used in ester copolymer adhesives, graft polymer adhesives, polyurea/polyurethane adhesives, etc., can solve the problem of expensive alkyl acrylate polymerization and processing, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102]Isophthalic acid (453g, 2.73mol); terephthalic acid (216g, 1.30mol), monoethylene glycol (130g, 2.1mol), neopentyl glycol (190g, 1.83mol) and 1,6-hexane Diol (154 g, 1.31 mol) was melted in a 21-flask with distillation column and distillation head under nitrogen flow. Water started to distill off when the temperature of 180°C was reached. The temperature was continuously increased to 240°C over a period of two hours. After about another four hours at this temperature the water slowly separates. The temperature dropped to 215°C. Then itaconic acid (40 g, 0.31 mol) and 100 mg MEHQ were stirred in for one hour. Then 300 mg of Tegokat 129 were stirred in and the workup was continued under vacuum, which was adjusted during the course of the reaction so that a distillate continued to form. The reaction is terminated after reaching the desired hydroxyl number and acid number ranges. The properties of Polyester 1 are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0104] Adipic acid (577 g, 3.95 mol); itaconic acid (39 g, 0.30 mol), 1,6-hexanediol (546 g, 4.63 mol) and 100 mg MEHQ were placed in a 21-flask with distillation column and distillation head Melt in a stream of nitrogen. Water started to distill off when a temperature of 160°C was reached. The temperature was continuously raised to 215°C over two hours. After about another three hours at this temperature the water slowly separates. Then 300 mg of Tegokat 129 were stirred in and the workup was continued under vacuum, which was adjusted during the course of the reaction so that a distillate continued to form. The reaction is terminated after reaching the desired hydroxyl number and acid number ranges. The properties of Polyester 2 are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0106] Isophthalic acid (464g, 2.80mol); terephthalic acid (221g, 1.33mol), monoethylene glycol (127g, 2.05mol), neopentyl glycol (186g, 1.78mol) and 1,6-hexane Diol (150 g, 1.27 mol) was melted in a 2 1 -flask with distillation column and distillation head under nitrogen flow. Water started to distill off when 185°C was reached. The temperature was continuously raised to 245°C over two hours. After about another four hours at this temperature the water slowly separates. The temperature dropped to 215°C. Then itaconic acid (41 g, 0.31 mol) and 500 mg MEHQ were stirred in for one hour. Then 300 mg of Tegokat 129 were stirred in and the workup was continued under vacuum, which was adjusted during the course of the reaction so that a distillate continued to form. The reaction is terminated after reaching the desired hydroxyl number and acid number ranges. The properties of Polyester 3 are listed in Table 1.
[0107] Table 1: Properties of Polymer Type A
[0108] E...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com