Production of iron using environmentally-benign renewable or recycled reducing agent
A reducing agent, iron ore technology, applied in the field of iron ore smelting, can solve environmental problems, disadvantages and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
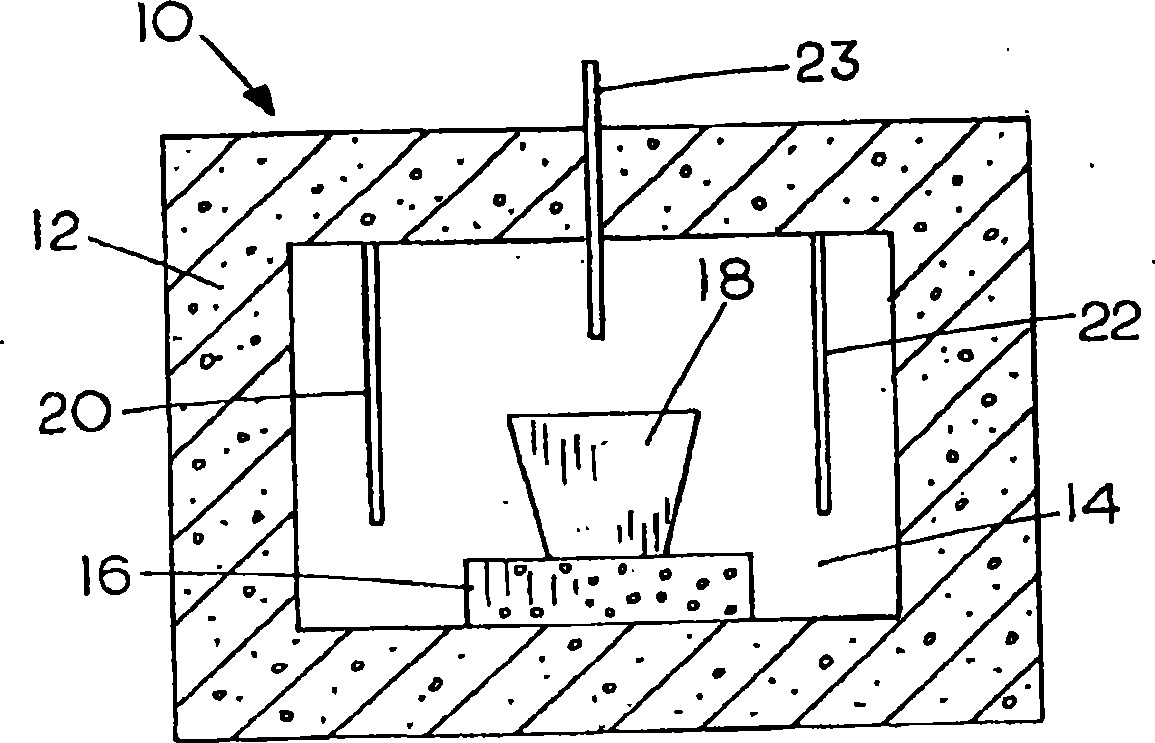
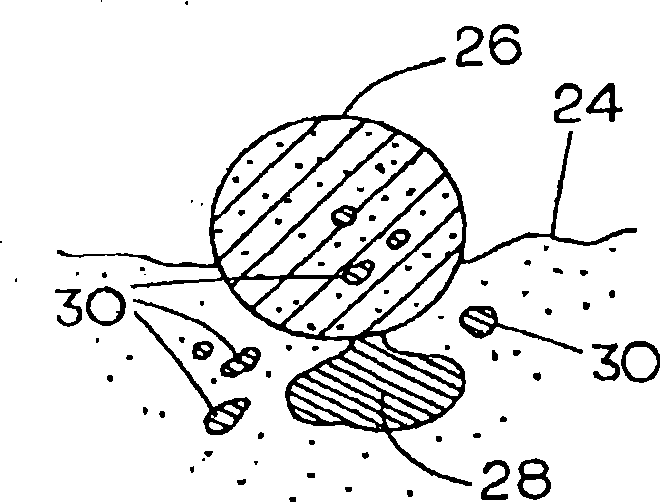
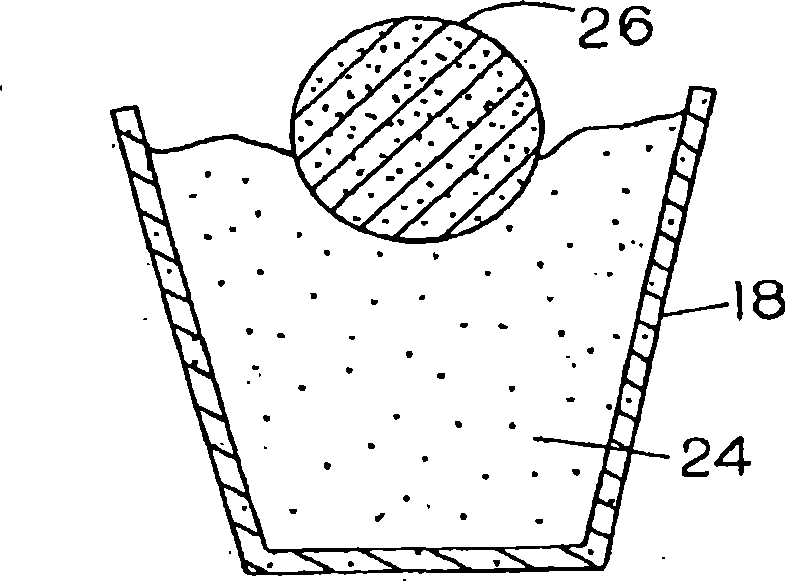
[0053] Iron ore concentrate is mixed with ground wood, wherein the ore concentrate comprises magnetite (Fe 3 o 4 ), consisting of 90% particles passing through a 25 μm sieve, and containing 5% silica, the wood includes Wood chips, averaging about 1 inch in length, about 1 / 8 inch thick, and about 5% moisture, were supplied by Carbontec, Energy Corporation of Bismarck ND. The wood chips were dry ground in a rod mill and passed through a 4.75mm sieve. Because ground wood does not have enough cohesive force to form a cohesive mass, a small amount of wheat flour is added as a binder. The magnetite, ground wood, and wheat flour are weighed separately and blended together in a high-speed blender humidified to create a thin layer of moisture until the mixture begins to form clumps. The mixture was then formed into pellets containing about 25 g of fine iron ore and about 7.5 g of ground wood chips and wheat flour, resulting in a reducing agent weight of about 30% by weight of the m...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Produce metallic iron with magnetite ore in 4 experiments, its process is basically the same as embodiment 1, but heating temperature drops to 1425 ℃ and 1400 ℃. The feed mixture consisted of approximately 100 g magnetite, 30 g ground wood and 2 g wheat flour. The combined mixture was divided into 4 portions to form aggregates each containing 25g of magnetite, 7.5g of ground wood and 0.5g of wheat flour. When the heating time is at least 20 minutes, a good metallic iron product can be obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0058] In the third run, the feed mixture consisted of approximately 100 g magnetite, 20 g ground wood and 2 g wheat flour. The combined mixture was divided into 4 portions to form aggregates each containing 25g of magnetite, 5g of ground wood and 0.5g of wheat flour. Each pellet was then heated at a temperature ranging from 1375°C to 1425°C. After heating in the furnace, a fine metallic iron nugget product is obtained.
[0059] The results obtained for Examples 2 and 3 are listed in Table 1 below.
[0060] Table 1
[0061]
[0062] The column of "initial pellet weight" is the total weight of each pellet including magnetite reducing agent and binder. The estimated percent iron recovery is based on the weight of primary metallic iron produced and does not include the weight of the small metal beads contained in the slag. It was concluded that, under the furnace conditions employed, a minimum of 20 minutes was required to complete the reduction process and successfully se...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com