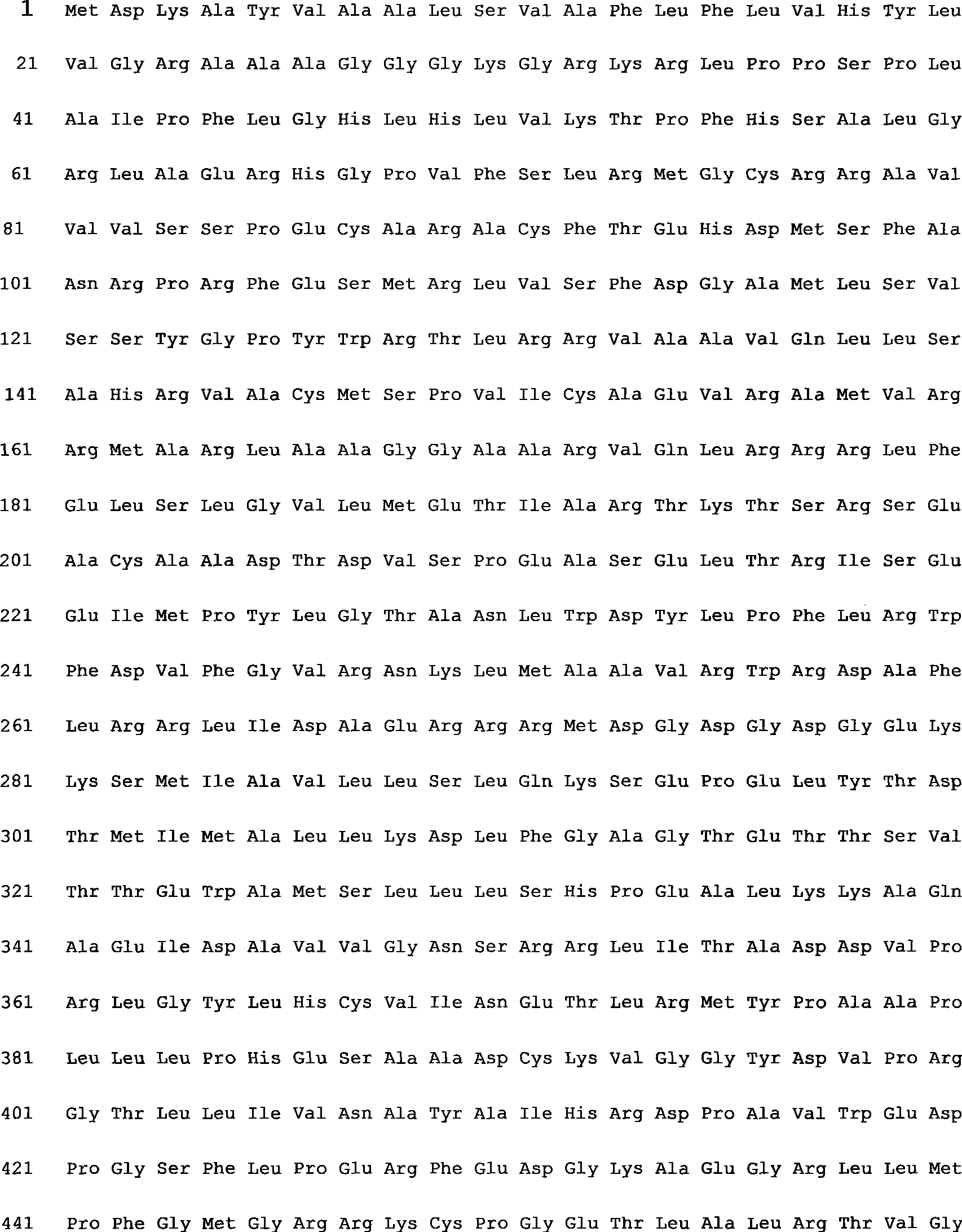Anti-herbicide gene and use thereof
A herbicide-resistant gene and herbicide technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of unstable gene expression products and low expression abundance of a single gene, reduce food and ecological risks, simplify weed control methods, and expand application. range effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1, the selection of the corn product system sensitive to nisulfuron corn
[0038] Collect 10 different corn varieties and spray nisulfuron (g active ingredient / mu) at the 5-6 leaf stage. One of the varieties, N-SS, is sensitive to nisulfuron, and it can kill 100% by spraying 5g / mu of active ingredient once. The offspring of N-SS crossed with two resistant varieties D001 and D002 were still resistant. N-SS, D001 and D002 are all provided by Zhejiang University College of Agriculture and Biotechnology (can be obtained by purchasing).
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Cloning and comparison of P450 genes in niasulfuron-sensitive maize and nisulfuron-resistant maize
[0040] According to the sequence of the maize genome database, 5 pairs of PCR primers were designed to amplify 5 P450 genes that may be involved in resistance to nibasulfuron from the resistant line D001 and the sensitive line N-SS, respectively.
[0041] The primers for PCR are:
[0042] Gene 1:
[0043] Azm-1-F: GGATCCACCATGGATAAGGCCTACATCGCCGCCC;
[0044] Azm-1-R: TCTAGATTCAGAGCCTCTTAAGAACACCACGC;
[0045] Gene 2:
[0046] Azm-2-F: GGATCCACCATGGATAAGGCCTACGTGGCCGTG;
[0047] Azm2-6R: TCTAGATTCAGAGCTCCAGAAGAAGATGGCGC;
[0048] Gene 3:
[0049] Azm-3-F: AGATCTACCATGGATCTGGCGGCCTACATCGCCA;
[0050] AZM-3-R: TCTAGATCATATCTTCTGAAGAACGTCATAC;
[0051] Gene 4:
[0052] Azm-4-F: GGATCCACCATGGACGACAAGTCCTGCTACGTGG;
[0053] Azm-4-R: TCTAGATCAGAGCTGCTGAAGAACATGACGC;
[0054] Gene 5:
[0055] Azm-5-F: GGATCCAACAATGGATAAGGCCTATGTCGCCG;
[0056] Azm-5-R: GGT...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3, the construction of the transformation vector of corn P450 gene transfection rice
[0060] In order to further prove the functions of the maize P450 genes obtained from the resistant variety D001 in Example 2, the expression cassettes of these genes were constructed in plant transformation vectors, and then transformed into rice for expression to study their functions. The promoter controlling the expression of the maize P450 gene in the expression frame is the maize ubiquitin (Ubiqutin-1) promoter. It was amplified from the maize genome by PCR, and the primer used was ZmUbiF (GCG AAGCTT GCATGCCTACAGTGCAGCGTGACCCGGTCGTGC, (the underline is the HindIII site) and ZmUbiR (GTG GGATCC TCTAGAGTCGACCTGCAGAAGTAACACCAAACAACAG, (the underline is the BmHI site). Maize P450 genes and their terminators were obtained directly from the genome by PCR (Example 2).
[0061] Five transformed T-DNA vectors pCAMB1300Rice-G6-zm1 / 2 / 3 / 4 / 5 were constructed using the vector pCA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com