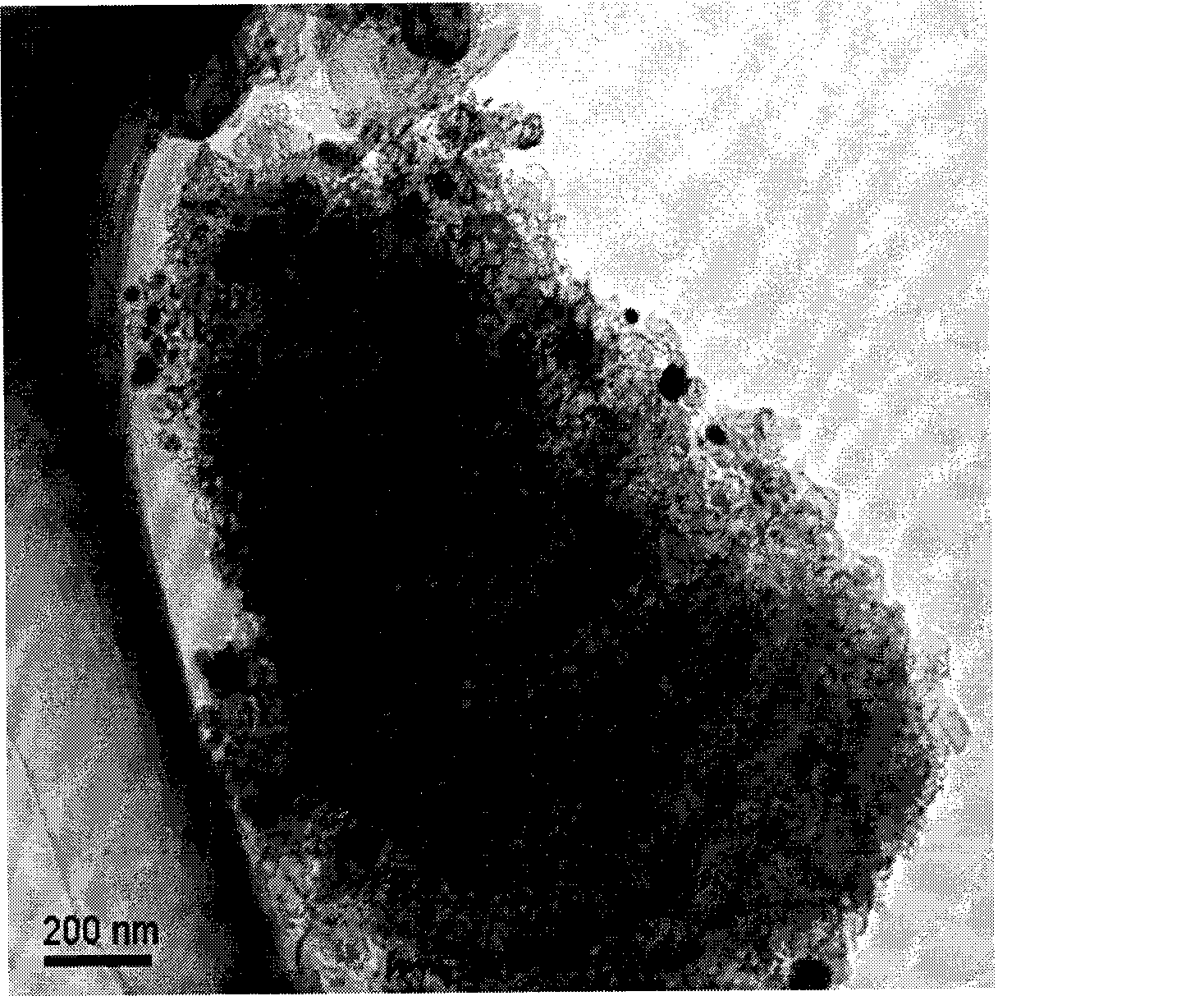Method for preparing graphitization nano carbon
A nano-carbon and graphitization technology, which is applied in the field of nano-carbon preparation, can solve the problems of low purity, uncontrollable shape, and low yield of graphitized nano-carbon, and achieve the effect of easy operation and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
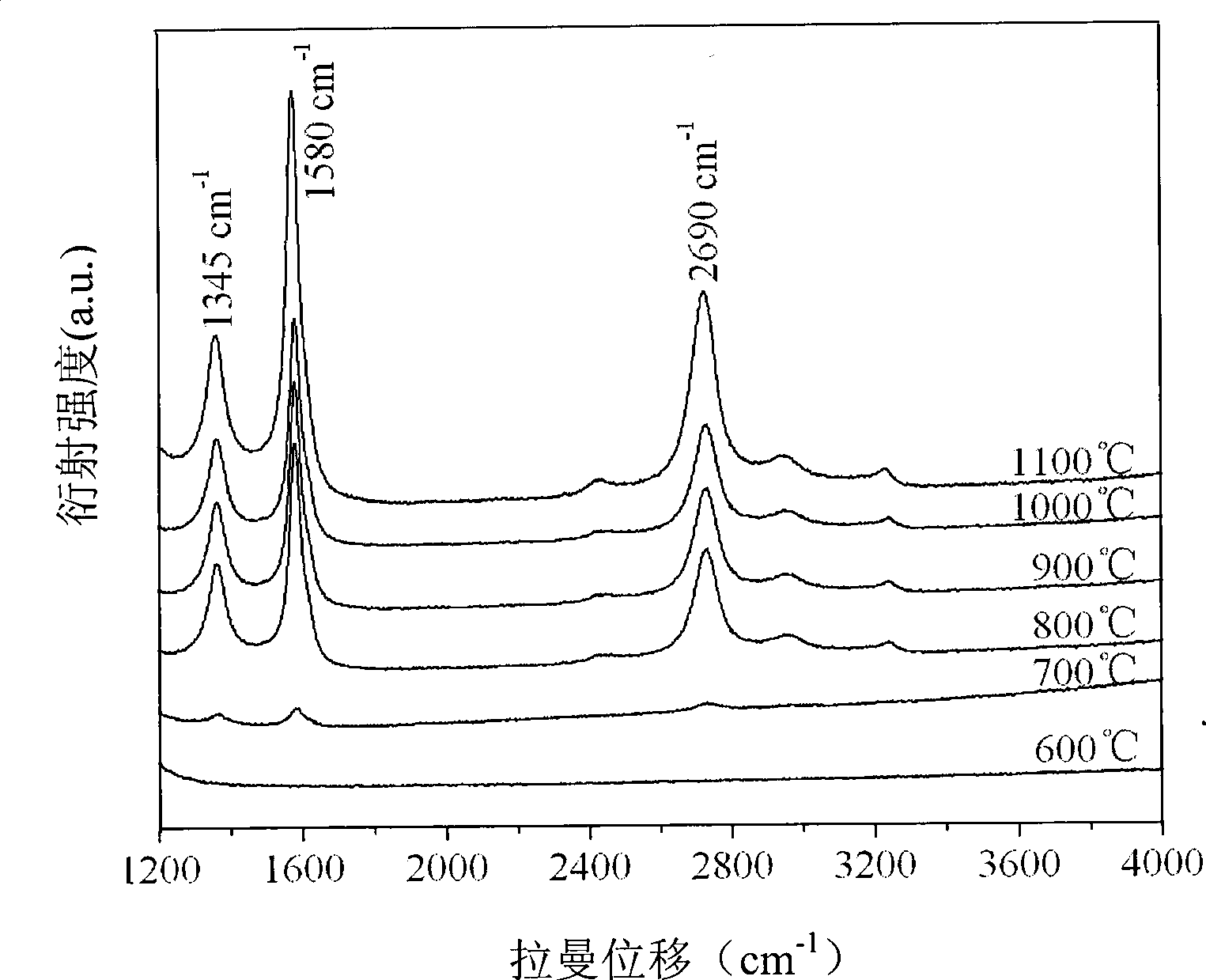
[0008] Specific embodiment 1: The graphitized nanocarbon of this embodiment is prepared according to the following steps: 1. Coordination of carbon source and metal ions: mix the carbon source with the metal catalyst solution, stir for 12-24h, and then ultrasonically treat the mixture for 30-120min. Add the surfactant solution to it, and continue to stir for 1~3h; 2. Solidification of the complex: The mixed solution prepared in step 1 is vacuum dried at 20~100℃ for 2~24h, and then cooled to room temperature; 3. Heat treatment: 5 The temperature is increased to 400~1100℃ at a rate of ~20℃ / min, and the product of step 2 is heat-treated for 0.5~6h under the conditions of air flow rate of 60~250ml / min and temperature of 600~1100℃; 4. Activation treatment: Yes The product of step 3 is physically activated or chemically activated to obtain graphitized nanocarbon; wherein the weight ratio of the solute in the metal catalyst solution to the carbon source in step 1 is 0.025~0.05:2.5, and t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0015] Specific embodiment 2: The graphitized nanocarbon of this embodiment is prepared according to the following steps: 1. The carbon source is coordinated with the metal ion: the carbon source is mixed with the metal catalyst solution, stirred for 12 to 24 hours, and then ultrasonically treated for 30 to 120 minutes. Add the surfactant solution to it and continue to stir for 1~3h; 2. Solidification of the complex: dry the mixed solution prepared in step 1 at 20~80℃ for 2~24h in vacuum, and then cool to room temperature; 3. Heat treatment: Raise the temperature to 600~1100℃ at a rate of ~20℃ / min, and then heat the product of step 2 for 0.5~6h under the conditions of air flow of 60~250ml / min and temperature of 400~1100℃; 4. Activation treatment: Yes The product of step 3 is subjected to physical activation or chemical activation treatment; 5. Add 50ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 12mol / L to the product prepared in step 4, and react at 90-100°C for 5-1...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0017] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is different from specific embodiment one or two in that the carbon source in step one is a polymer with polar groups, agricultural and forestry crop extracts or agricultural and forestry wastes; those with polar groups The polymer is one of polymethacrylic acid, polystyrene, polyfurfuryl alcohol, polyacrylamide, polyimine, polyurethane, polyglucosamine, polyethylene glycol, anion and cation exchange resin, polyvinyl alcohol, polyaniline or A mixture of several, the extracts of agricultural and forestry crops are glucose, sucrose, fructose or starch, and the agricultural and forestry wastes are beet residue, bagasse, corn stalks, reeds, cattail or wormwood. Others are the same as the first or second embodiment.
[0018] When there are two or more polymers with polar groups in this embodiment, the components are mixed in any ratio.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com