Solar energy linkage tracking method
A solar energy and solar energy conversion technology, which is applied in the field of solar energy tracking and utilization, can solve the problems of affecting the use efficiency, high utilization cost and high cost, and achieve the effects of increasing wind resistance, reducing investment cost and improving use efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
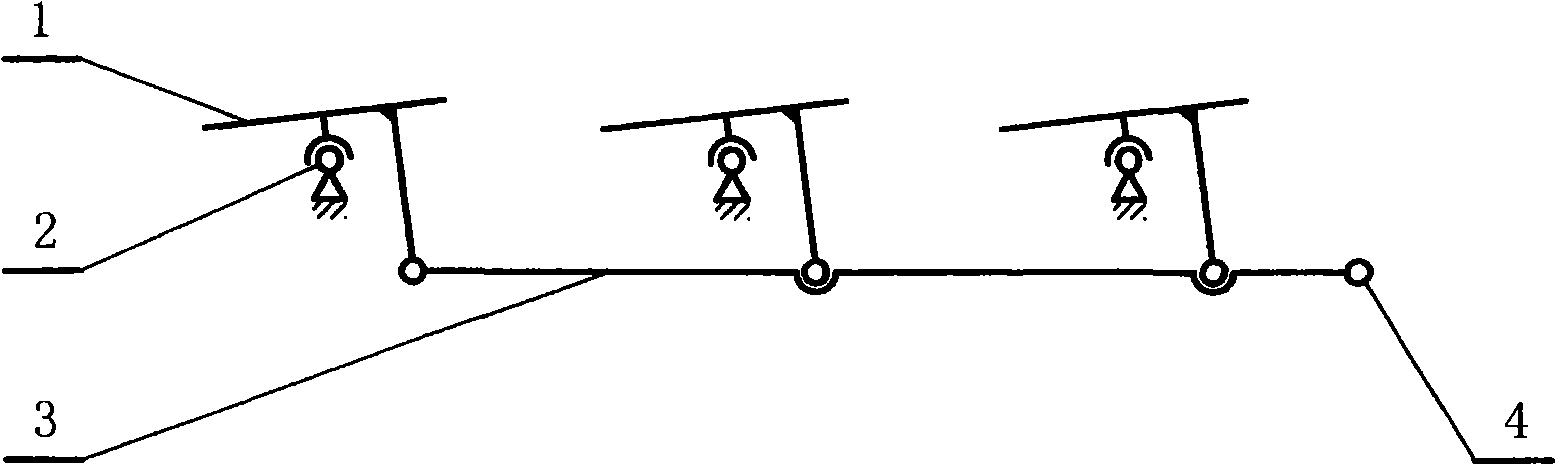
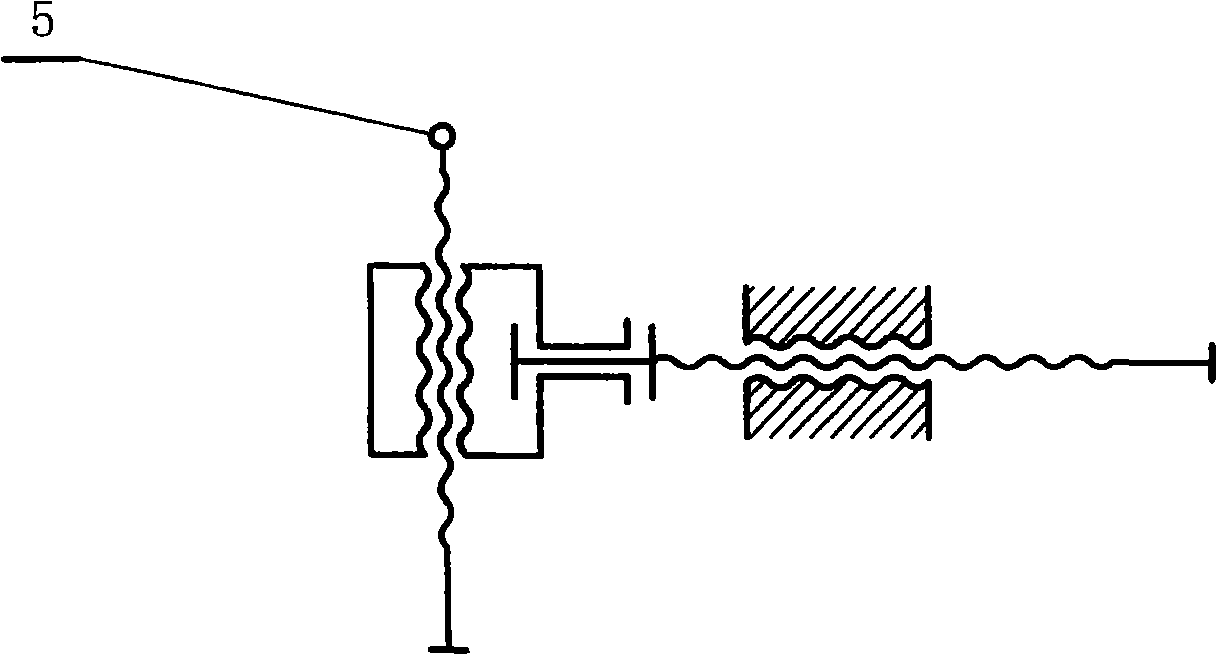
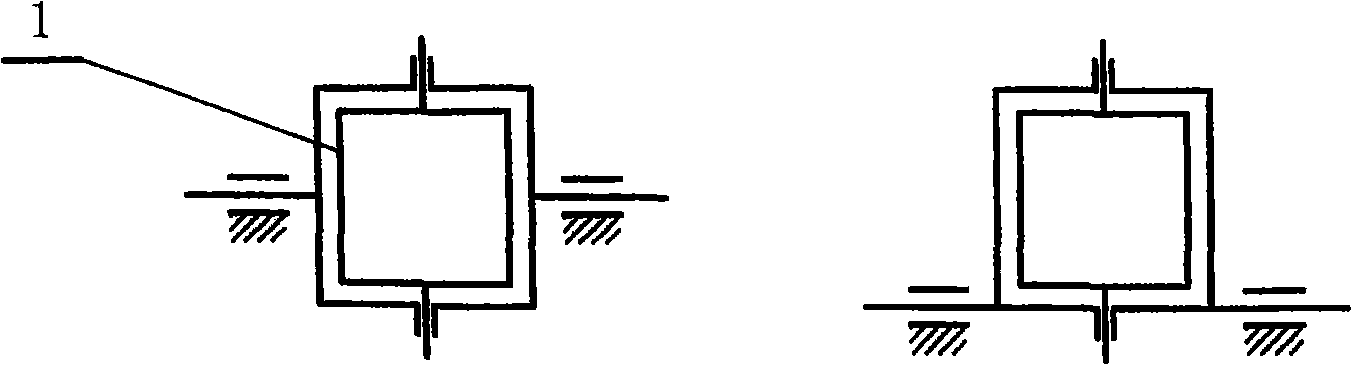
[0034] Embodiment 1: as attached figure 1 The solar conversion device 1 shown is a synchronous deflection mode supported by a single universal hinge (which can be deflected forward, backward, left, and right) and is connected by a connecting rod 3 to form a synchronous linkage mechanism of parallel connecting rods. The automatically controlled driving system is connected, and as the driving end 4 moves, all solar conversion devices will deflect synchronously. Because the tracking movement of the sun is divided into the daily tracking in the east-west direction and the annual tracking in the north-south direction, it is two-dimensional. figure 2 It means that the twin-screw mechanism can meet the two-dimensional movement of the displacement output end 5, and the two-dimensional movement of the output end 5 can meet the requirements of the design law by controlling the speeds of the two screws respectively by the control system. figure 1 When the driving input terminal 4 in th...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2: as attached Figure 8 Shown is a synchronous and interlocking plane concentrating schematic diagram of reflectors. The concentrating point is set in the concentrating plane formed by the sun rays passing through the deflection axis of the support frame. The support frame tracks the sun rays and deflects synchronously. Install with different deflection angles and phase differences in the deflection direction in the light-gathering plane to meet the need for a suitable deflection speed in the process of synchronous deflection tracking the sun so that the reflected light always faces the light-gathering point (receiver) in the light-gathering plane 11. In order to calculate the relationship between the "appropriate deflection speed" of the mirror surface and the deflection speed of the sun's rays in the light-gathering plane, the line a in the figure represents the sun's rays, b is the normal line of the mirror, c is the reflected light, d is the horizon, and...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3: as attached Figure 11 It is a schematic diagram of a synchronous interlocking plane concentrating system with downward secondary reflection. The high-position reflector 12 is added to first reflect the light to the plane mirror and then downward secondary reflection to the receiver 11, making solar high-temperature heating more convenient. The position of the focal point of the secondary reflection can be determined by the principle of mirror imaging (it is always mirror-symmetrical to the primary focal point), but the distance of the downward reflection should not be too large or the high-position reflector needs a large area. In order to adapt to concentrating heating in more areas, a convex reflector can be used to extend the reflection distance downward, which requires reducing the single mirror area of the ground reflector. For example, when the diameter of the light spot produced after condensing light is 1 meter, if the area of the single mirro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com