Method for auxiliary heating with pulse laser and machining with supersonic vibration
A technology of ultrasonic vibration cutting and auxiliary heating, used in metal processing, metal processing equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of fast tool wear, high laser power, difficult to hard and brittle materials processing, etc., and achieve the effect of solving difficult processing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
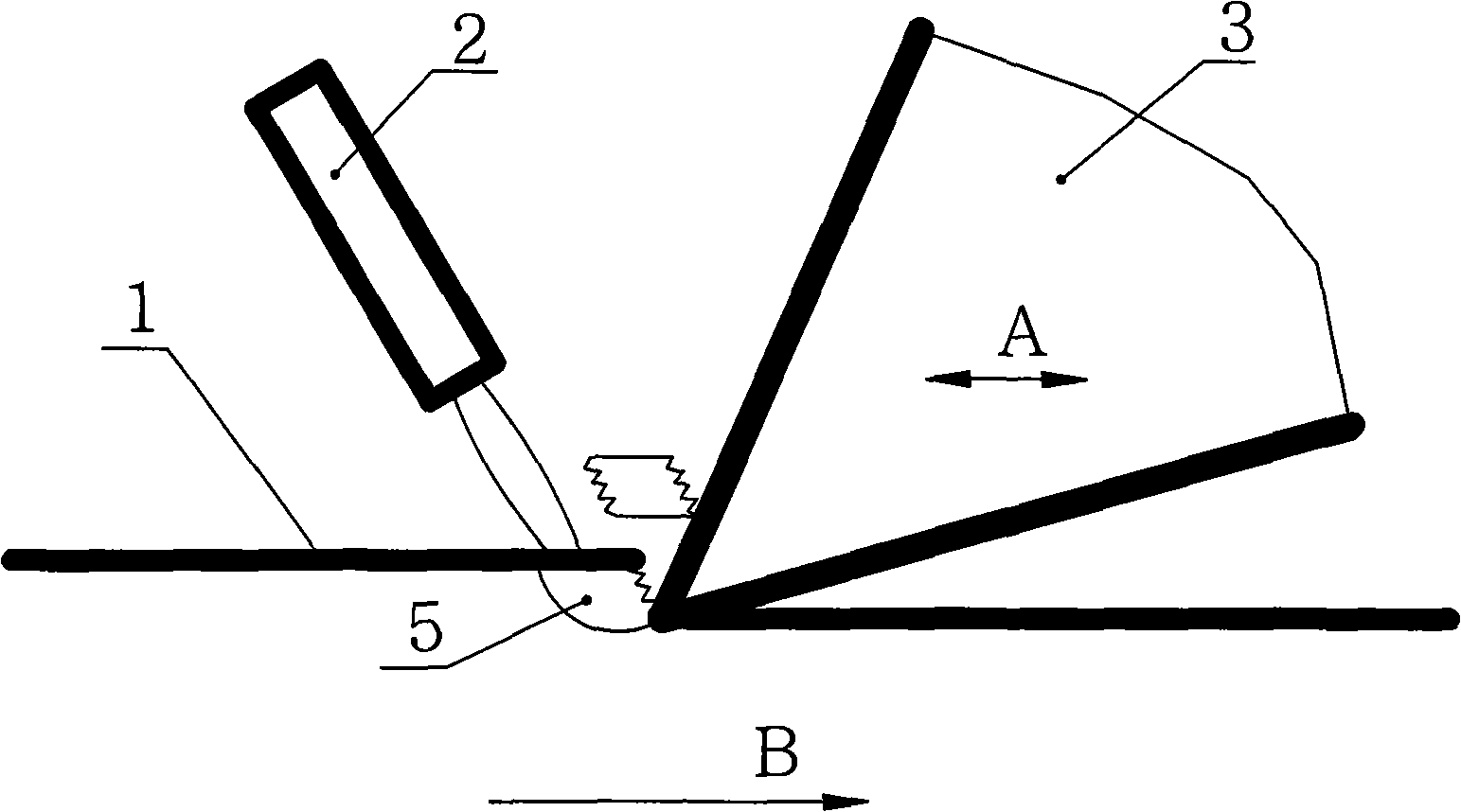
[0014] Such as figure 1 As shown, the device of the present invention is composed of a workpiece to be processed 1, a processing machine tool, an ultrasonic generator, an energy converter, a cutter 3 and a pulse laser 2. The ultrasonic generator and the energy converter are connected with the tool 3 or the workpiece 1 to be processed. A is the cutting direction, B is the vibration direction, and 5 is the laser heating zone. The specific processing steps are: ① install the workpiece 1 to be processed, select the appropriate tool 3, and install the tool 3; ② according to different process parameters. Adjust the laser pulse frequency to an integer multiple of the ultrasonic vibration frequency. ③Adjust the irradiation position of the pulse laser 2, start the machine tool, and set the tool. ④ The pulse laser 2 emits 1~n laser pulses to irradiate the tool 3 to the next part to be processed to heat the material. ⑤ The ultrasonic generator vibrates, and the work piece (or tool) vibrates ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com