Method for ultrasonic acid extraction of sulfated polysaccharide from gracilaria tenuistipitata
A technology of polysaccharide sulfate and ultrasonic acid, applied in the field of chemical food, can solve the problems of less extraction and preparation of polysaccharide sulfate, increase the extraction rate of polysaccharide sulfate, etc., and achieve the effects of quick effect, simple and practical process, and low investment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Raw material handling:
[0020] Dried gracilaria is rinsed with water to remove impurities and air-dried. Crush 85-95% ethanol and degrease with an equal volume of petroleum ether for 2 hours, recover ethanol from the supernatant, and dry the residue for polysaccharide extraction.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Polysaccharide extraction process:
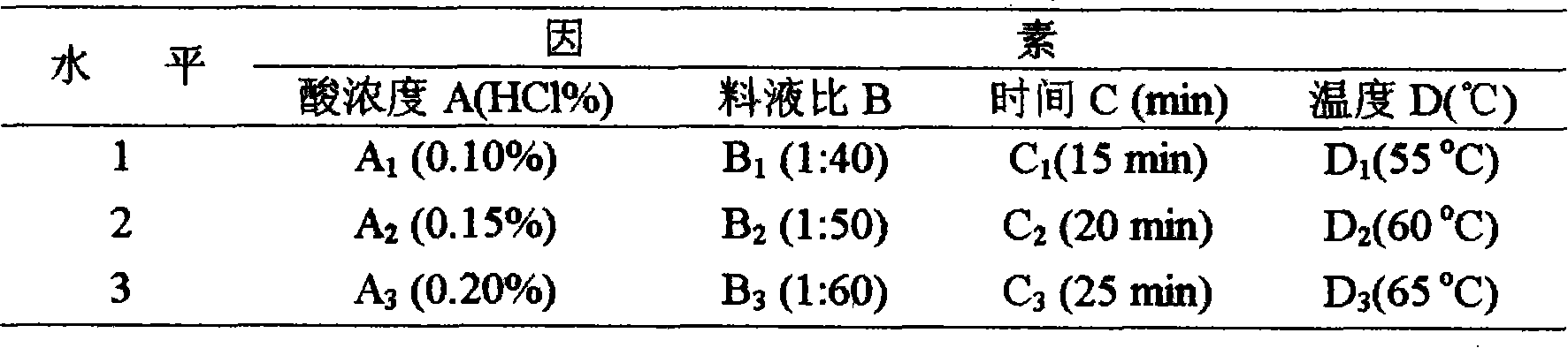
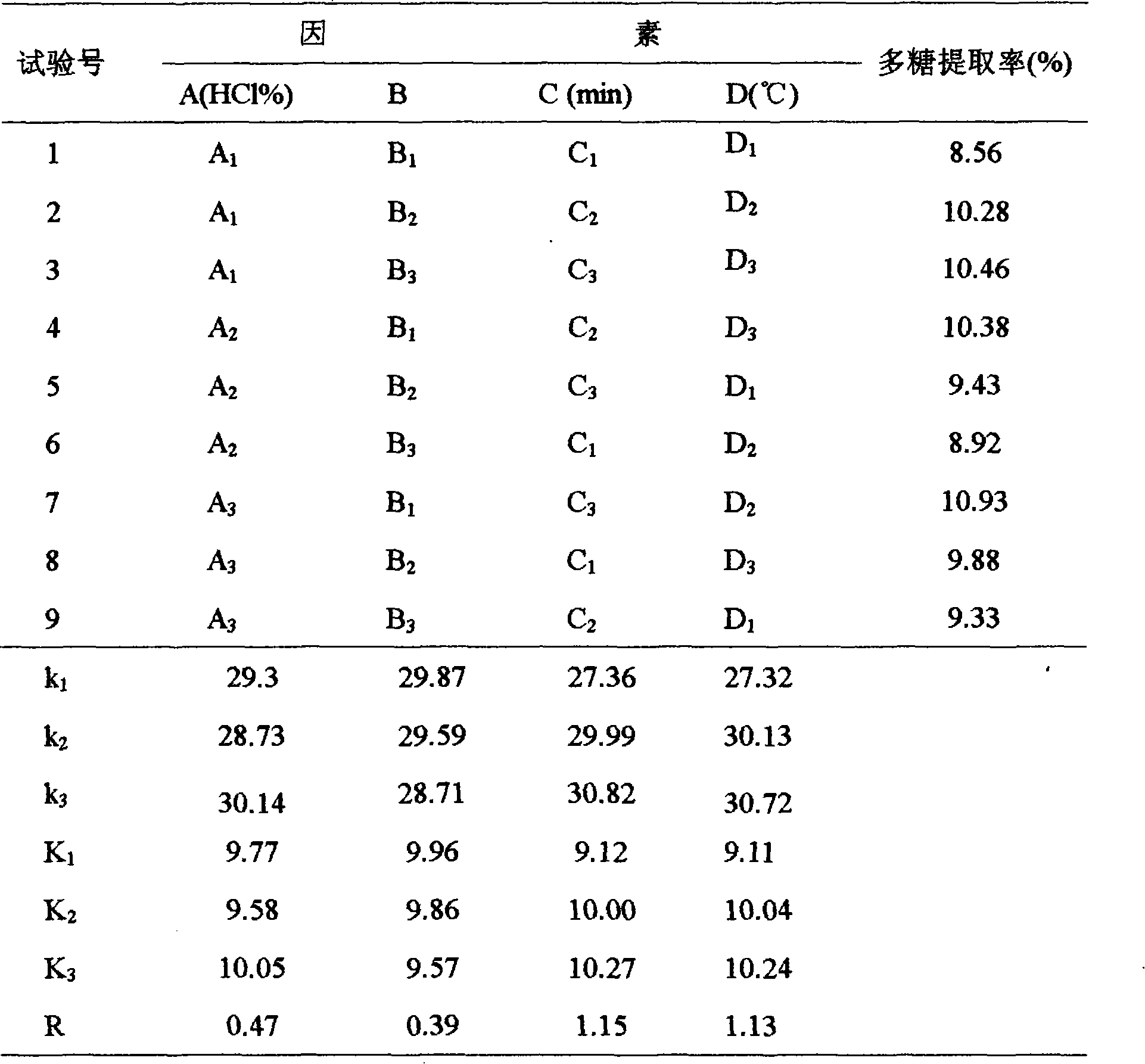
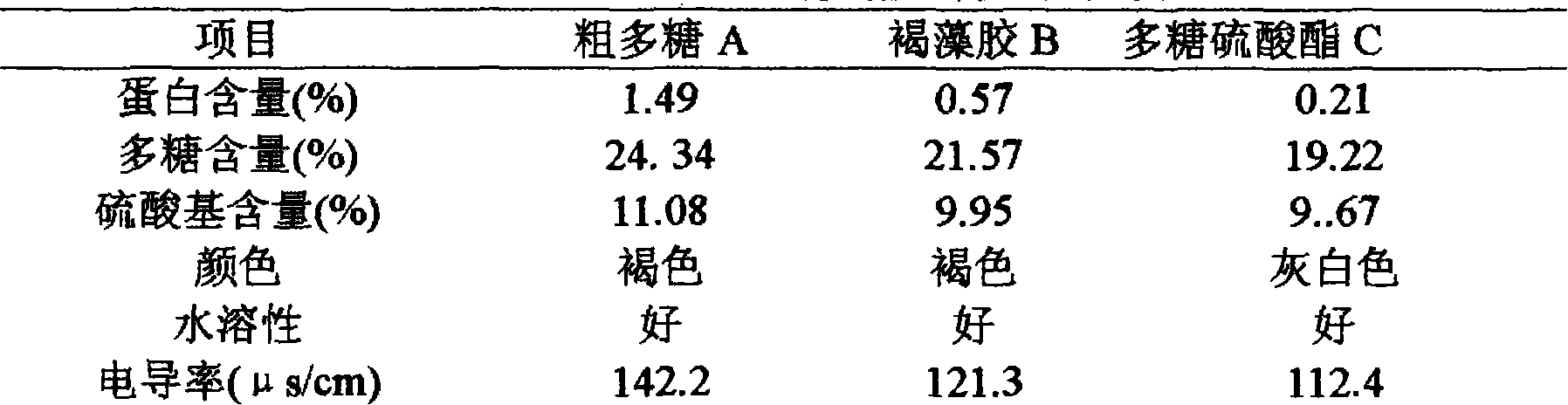
[0023] Dried Gracilaria is rinsed to remove impurities, air-dried, crushed, degreased with 85-95% ethanol for 2-3 hours, the material ratio is 1:40-1:60, leached with HCI 0.10-0.20% solution at 60°C, and ultrasonically extracted with a power of 500W , centrifuged to obtain the filtrate, the filtrate was neutralized with NaOH to pH = 7, centrifuged to concentrate the supernatant, added ethanol to 60-65%, let stand, centrifuged to precipitate, washed the precipitate with ethanol, and dried the crude polysaccharide sulfate ester under reduced pressure a.
[0024] Prepare crude polysaccharide A into an aqueous solution, add ethanol to 20-25%, precipitate alginate B, centrifuge, add ethanol to the supernatant to 60-65%, then centrifuge, precipitate with ethanol and acetone, and dry at 40-45°C Polysaccharide sulfate C.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Determination of conductivity:
[0027] The concentration of the polysaccharide solution is 1 (mg / ml), and distilled water is used as a blank, and measured at 20°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com