Process to reduce the amount of cr (vi) in a cement-containing composition and a composition comprising cement and coated metallic sulphate particles
一种金属硫酸盐、水泥组合物的技术,应用在金属硫酸盐领域,能够解决硫酸亚铁不稳定等问题,达到经济有利、成本低、高溶解性的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Example 1. Reduction of the amount of soluble chromium(VI) in cement using 2% gelatin coated particles
[0092] 2% gelatin coated ferrous sulphate particles were obtained using the method described above with the following measured particle sizes.
[0093] The coated particles had the following measured particle sizes:
[0094] Particle size:
Mass% undersize
500 microns
98
200 microns
90
[0095] 100 microns
73
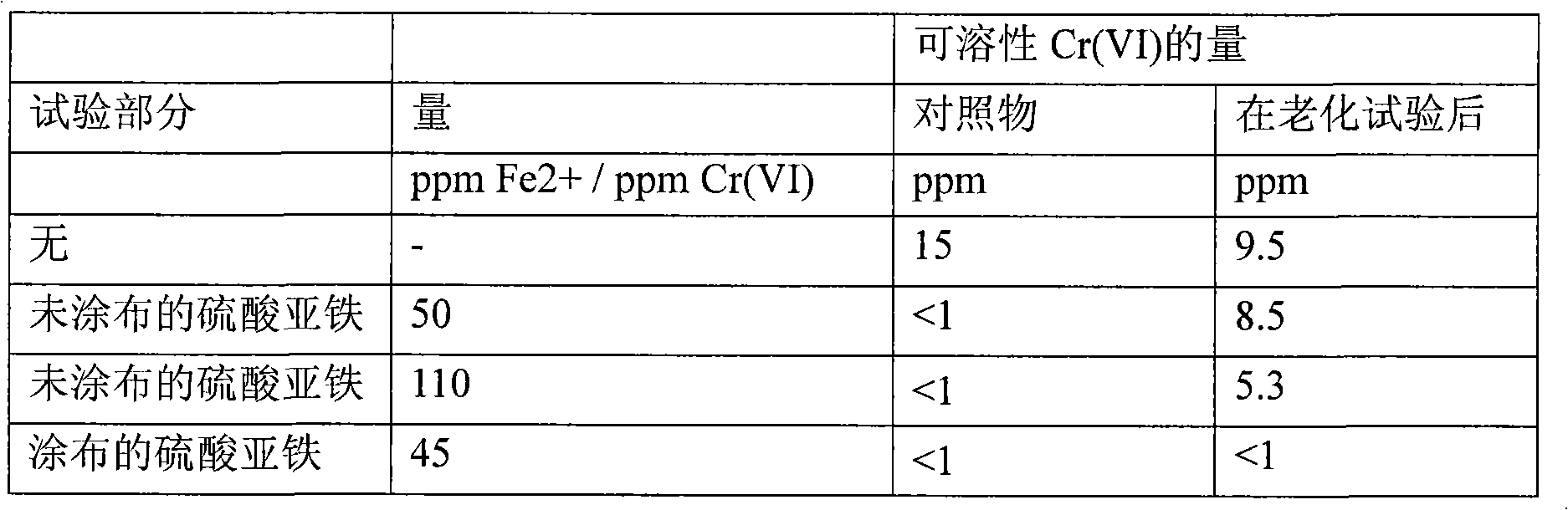
[0096] The reduction of chromium (VI) in each cement was measured by mixing the various cements with virgin ferrous sulfate powder, or with the coated particles. The particular cement used in the examples was identified by reference to the well known standards BS EN 197-1:2000 and BS 4027:1996. Thus, "CEM I" refers to Standard Portland Cement, and code 52.5N refers to the strength classification.
[0097] Experimental results
[0098] The expression "control" as used hereinafter refers...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Example 2. Reduction of Soluble Chromium(VI) Amount in Cement Using 1% Gelatin Coated Particles
[0110] 1% gelatin-coated ferrous sulfate particles were obtained using the method described above.
[0111] In this example, the amount of ferrous sulfate introduced into the cement in order to reduce soluble chromium (VI) was varied.
[0112] Different amounts of coated particles of the invention were added to cement and the retention of potency in the portion of the coated particles in terms of reduction of soluble chromium (VI) was measured after accelerated aging.
[0113] Experimental results
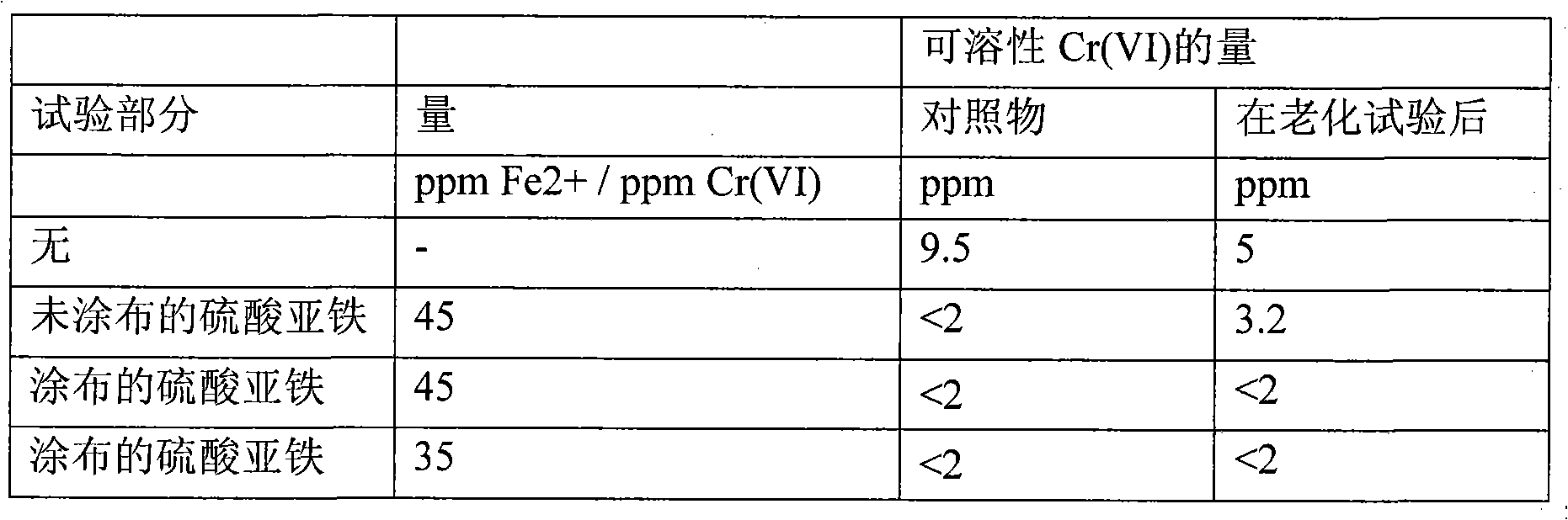
[0114] Table 4
[0115] CEM I 52.5N cement containing 13.3 ppm soluble chromium (VI) treated with coated particles with 1% gelatin was used.
[0116]
[0117] Observed at 40ppm Fe 2+ Particles coated with 1% gelatin added at a ratio of Cr(VI) / ppm remained effective in terms of reduction of soluble chromium(VI) after the aging test, while uncoated ferrous sulfate powde...
Embodiment 3
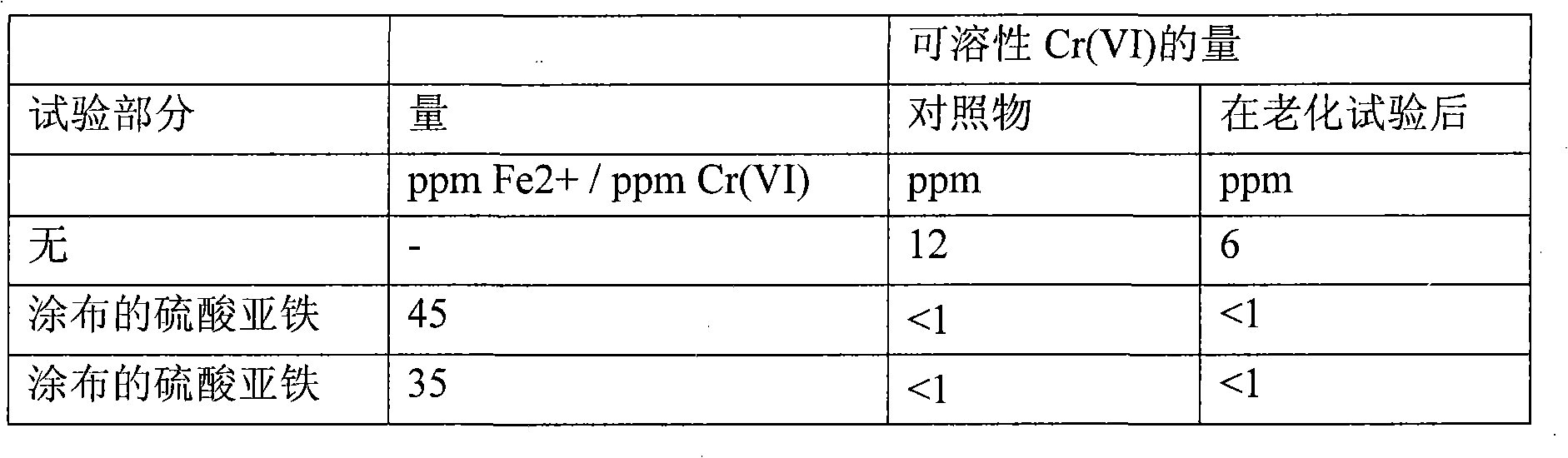
[0118] Example 3. Use of different types of coatings around ferrous sulfate on standardized sand Influence of the amount of soluble Cr(VI) in slurry
[0119] Cement 1 was CEM I 52.5N with 12 ppm soluble Cr(VI).
[0120] Prepare standardized mortars according to standard NF EN 196-1.
[0121] The measurement of entrained air is carried out according to standard NF EN 413-2.
[0122] A coating protocol using a different gelatin (oleate, oleic acid, styrene-acrylic, and alginate) involves the following steps:
[0123] - dehydration of ferrous sulfate as described in step 1 above;
[0124] - preparation of the coating solution by dissolving 1% by weight or 2% by weight of the coating material of dehydrated ferrous sulphate in an amount of water sufficient to rehydrate the dehydrated ferrous sulphate and obtain ferrous sulphate heptahydrate;
[0125] - rapid introduction of about 200 g of dehydrated ferrous sulfate in the coating solution at 90°C;
[0126] - mixing in a Ray...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com