Vertical iii-nitride light emitting diodes on patterned substrates with embedded bottom electrodes
A technology of light-emitting diodes and nucleation layers, applied in electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as complex and expensive methods, increased cost of insulating substrates, and affecting LED performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
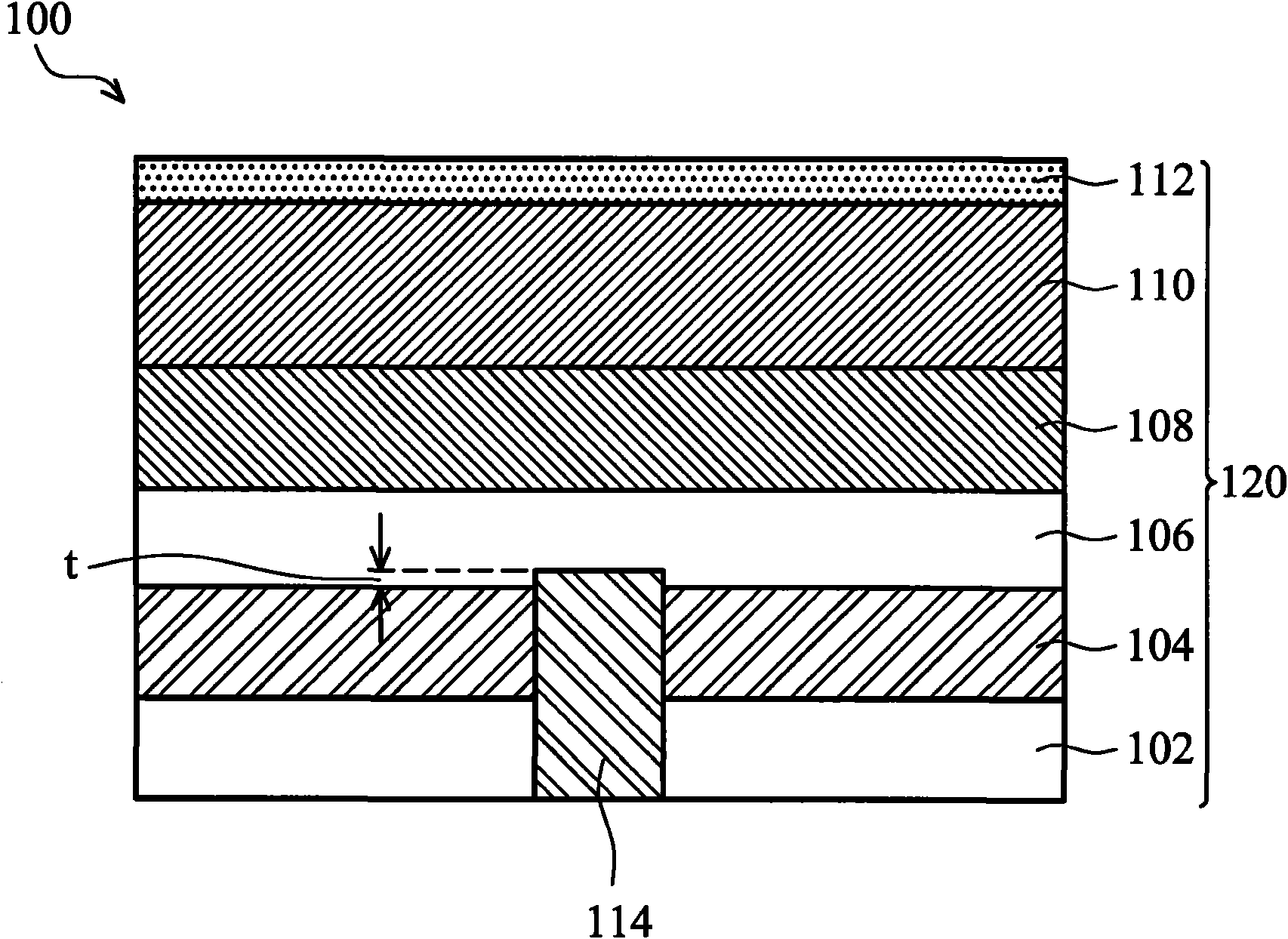
[0016] figure 1 A first embodiment of an LED of the present invention is shown, comprising a patterned substrate containing a mosaic bottom electrode. The LED 100 includes a substrate 102 and an LED structure 120 formed on the substrate 102 . The substrate 102 may include a conductive substrate or a non-conductive substrate. Non-conductive substrates can be sapphire, MgAl 2 o 4 , single crystal oxide or the like. The semiconductor substrate may be GaN, Si, Ge, SiC, SiGe, ZnO, ZnS, ZnSe, GaP, GaAs or the like. The substrate 102 may have a thickness of about 200 μm to about 600 μm. Epitaxial film formed LED structure 120 grown on substrate 102, which includes buffer / nucleation layer 104, first contact III-nitride layer 106, active layer 108, second contact III-nitride layer 110, and top contact layer 112 .
[0017] The buffer / nucleation layer 104 can be a low temperature or high temperature grown III-nitride layer, III-nitride superlattice layer, metal carbon-nitrogen lay...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com