Novel Kit for fluorescence quantitative PCR detection of influenza A H1N1 viruses and detecting method therefor
A detection method and fluorescence quantitative technology are applied in the detection field of a new type A H1N1 virus by fluorescence quantitative PCR, and can solve the problems of high detection cost, detection specificity, limited sensitivity and low sensitivity detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Detection of Primer Sensitivity
[0037] 1) Select the full length of the known sample HA gene as a standard, and increase its viral RNA concentration from 10 -1 sequentially diluted to 10 -10 ;
[0038] 2) Negative control: nuclease-free water;
[0039] 3) The reaction system was prepared according to Table 3.
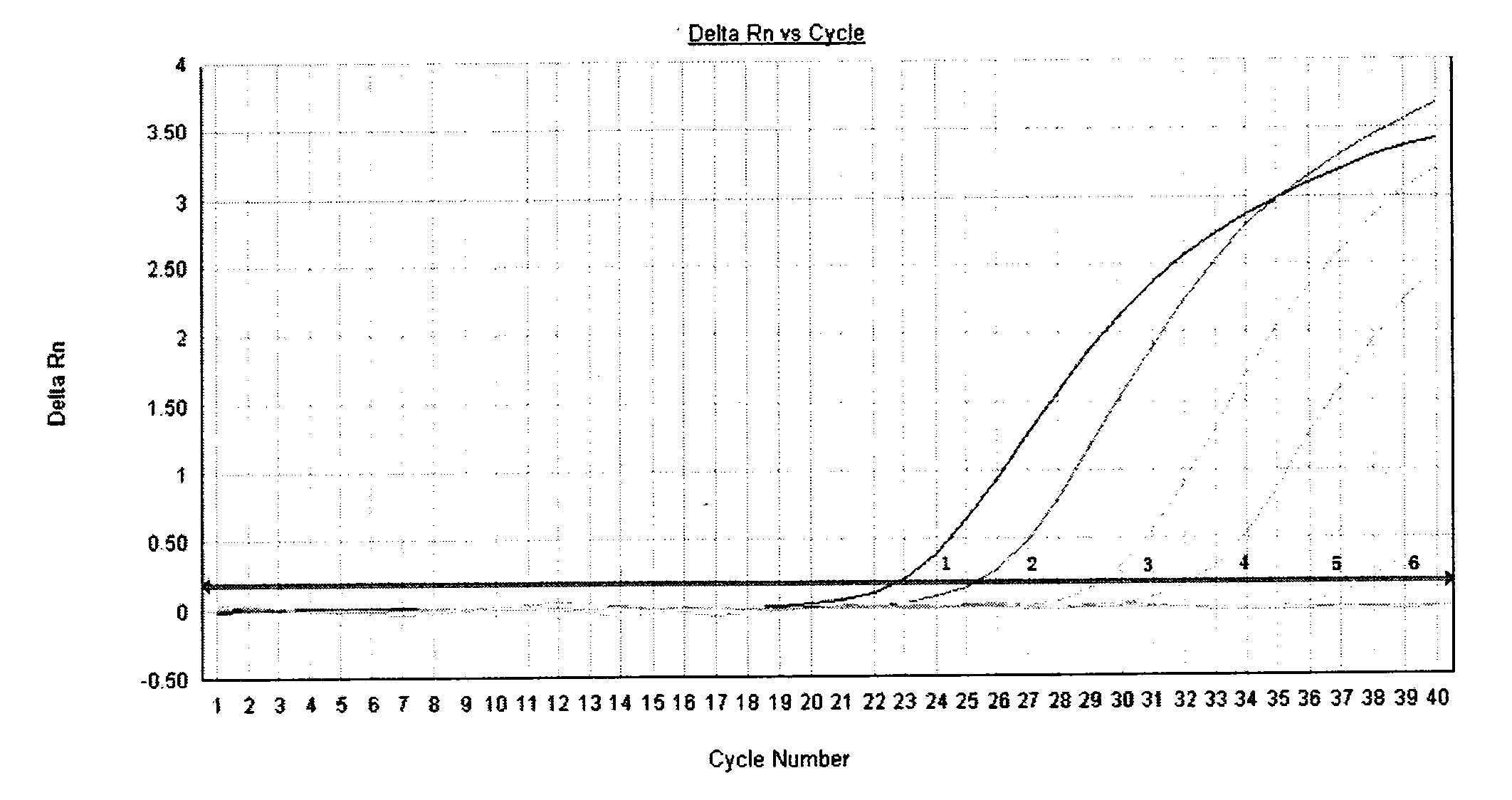
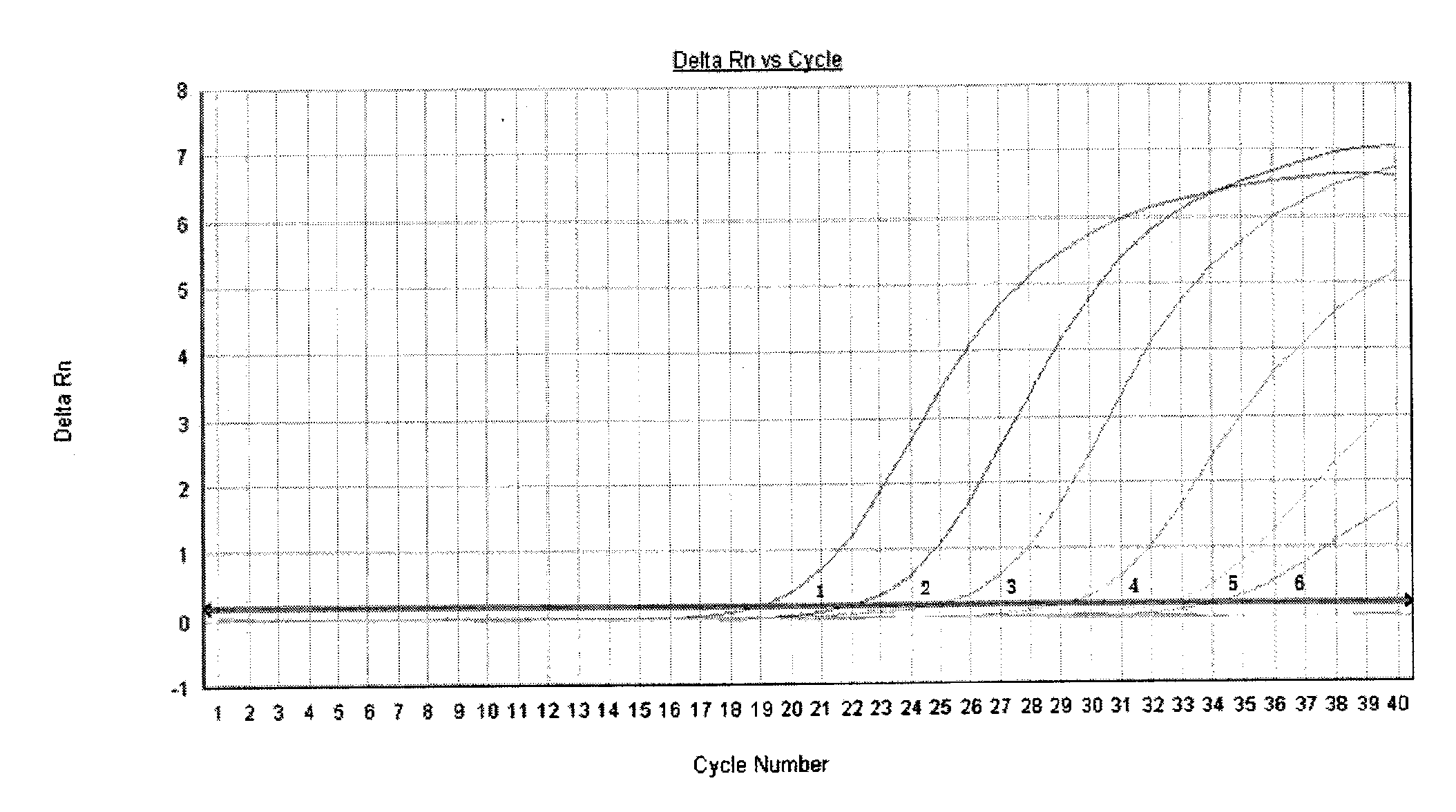
[0040] Test results such as figure 2 , 3 shown.
[0041] figure 2 The curves 1-6 in the middle are respectively the concentration dilution of the standard substance is 10 -4 -10 -10 Amplified curve with primer WHO-SWH1. image 3 The curves 1-6 in the middle are the concentration dilution of the standard substance in order of 10 -4 -10 -10 Curve amplified with primer YHANEW. we start from figure 2 and image 3 It can be seen from the figure that the curve of the amplification result of the YHANEW primer is earlier than the curve of the amplification result of the WHO-SWH1 primer.
[0042] Table 4SWH1, YHANEW primer sensitivity detect...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2: Primer non-characteristic detection
[0046] 1) Non-specific detection of common seasonal influenza H1N1, swine influenza H1N1, avian influenza H5N1, H9N2;
[0047] 2) Positive control: viral HA fragment RNA;
[0048] 3) Negative control: nuclease-free water;
[0049] 4) The reaction system was prepared according to Table 2.
[0050] See the test results Figure 4 and Table 5.
[0051] Figure 4 The results showed that only the positive control HA numbered 1 showed an amplification curve. The curves of the remaining samples were all below the baseline, and there was no amplification reaction.
[0052] Table 5 Human, poultry and swine influenza virus detection results
[0053]
[0054] The data in Table 5 shows that the primers have a CT value of "-" for gene amplification of common seasonal influenza H1N1, swine influenza H1N1, avian influenza H5N1 and H9N2. It shows that the primer has no amplification reaction to its viral RNA.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Embodiment 3: detection of patient's throat swab
[0056] 1) Detect the throat swabs collected from suspected cases to screen for the new type A H1N1 influenza virus;
[0057] 2) Positive control: viral HA fragment RNA;
[0058] 3) Negative control: nuclease-free water;
[0059] 4) The reaction system was prepared according to Table 3.
[0060] See the test results Figure 5 and Table 6.
[0061] Figure 5 Only one amplification curve appeared in the positive control, and the rest of the samples had no amplification. The reaction was negative.
[0062] Table 6 Throat swab test results
[0063]
[0064] The results of the data in Table 6 show that the results of the patients' throat swabs were all negative.
[0065] Result analysis:
[0066] After the amplification reaction completed 40 cycles, the primer sensitivity detected that the viral RNA concentration dilution was 10 -8 ; There is no cross-reaction with common seasonal influenza H1N1, swine influenza ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com