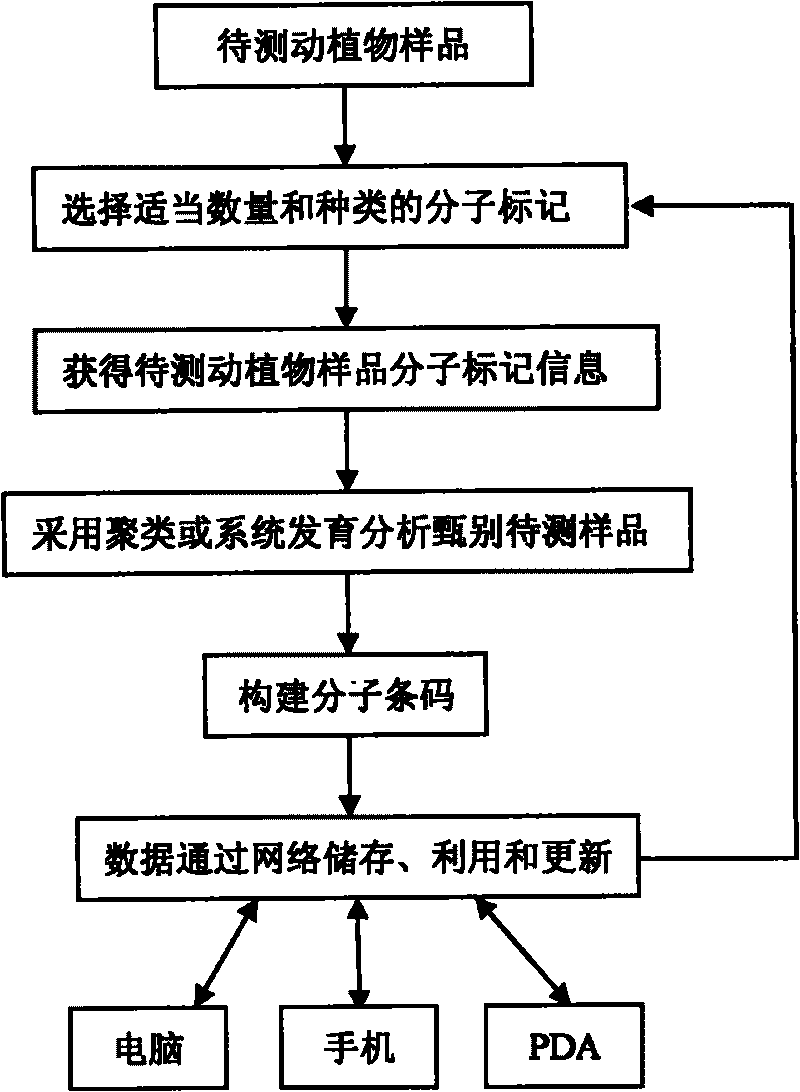
Method for preparing molecular bar code system for describing and discriminating animals and plants and application thereof
A molecular bar code, animal and plant technology, applied in the field of molecular bar code system preparation, can solve the problem of single molecular marker types, no set of standards for marker types and numbers, no new species, close relatives or recently differentiated varieties classification or screening. Issues such as direct availability and sharing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
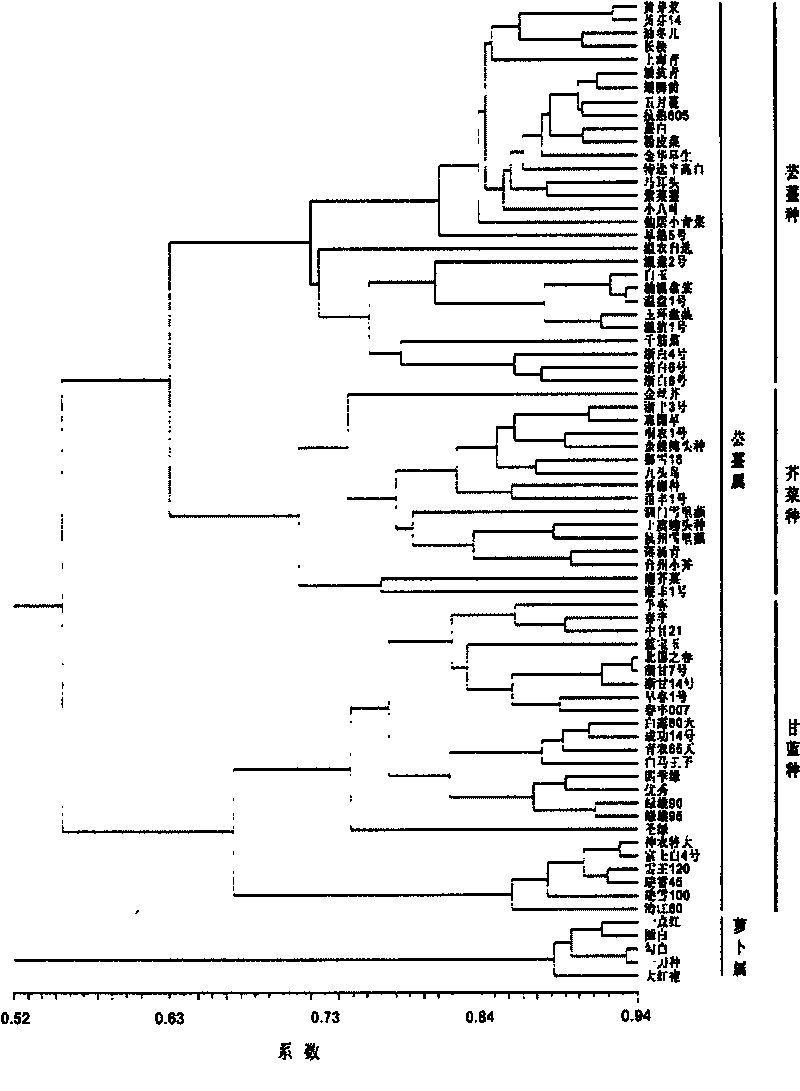
[0042] Example 1, Screening of Cruciferous Crops and Construction of Molecular Barcodes
[0043] 74 cultivar materials (Table 1) of Brassica rapa, cabbage (B.oleracea), mustard (B.juncea) and radish (Raphanus sativus) crops were selected for molecular barcode construction and variety screening.
[0044] Table 1. Information on 74 varieties of cruciferous crops
[0045] Species / varieties (Latin name)
Variety
Species / varieties (Latin name)
Variety
Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis var.
pekinensis
yellow sprouts
Brassica rapa ssp.
rapifera
Yuhuan Dish
Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis var.
pekinensis
Yellow Bud 14
Brassica rapa ssp.
rapifera
Nanxi dish
Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis var.
pekinensis
Zhebai No.4
Brassica rapa ssp.
rapifera
Wenkang No.1
Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis var.
pekinensis
Zhebai No. 6
Brassica rapa ssp.
rapifera
...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2, the screening of the genus Suis and the construction of molecular barcodes
[0068] Seventeen Chinese local pig breeds and one wild boar breed were selected to construct molecular barcodes (Table 2).
[0069] Table 2. Information on 17 Chinese local pig breeds and 1 wild boar breed
[0070]
[0071] For each variety material in Table 2, the following steps are carried out respectively:
[0072] (1) Acquisition of Genomic DNA Sequence
[0073] 5 mL of blood was collected from the anterior vena cava of pigs, and frozen with EDTA anticoagulant. Genomic DNA was extracted by traditional phenol / chloroform extraction method, and the purity of the product was about 80% to 97%. After TE was dissolved, it was diluted to a final concentration of 50ng / μL.
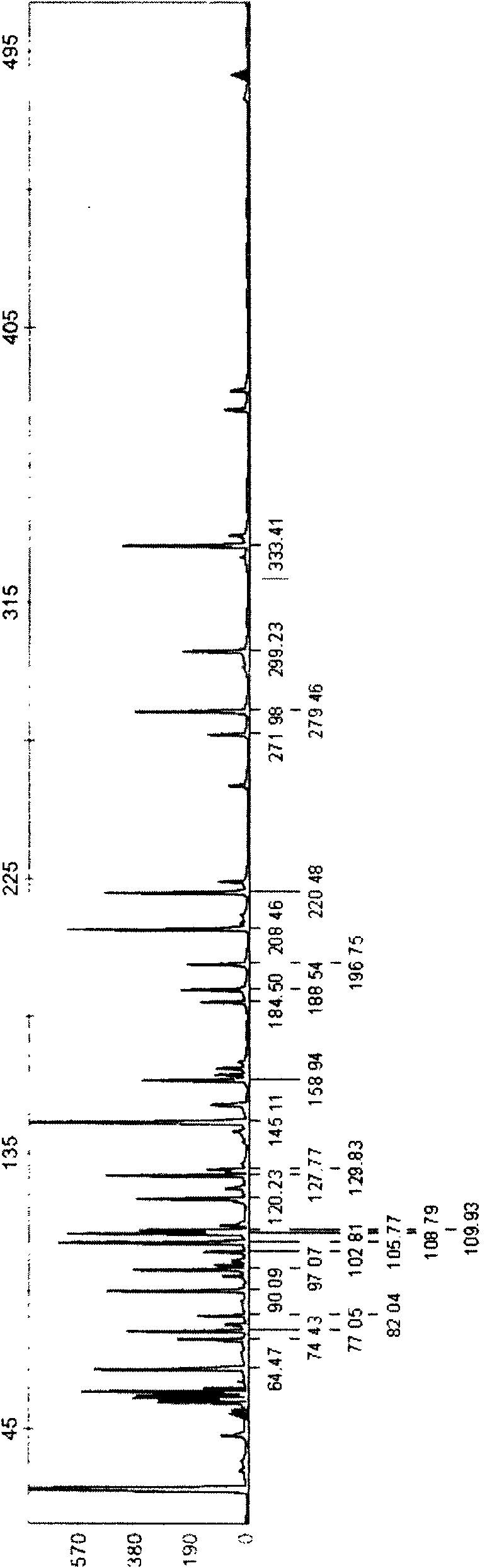
[0074] (2) Using fluorescent AFLP molecular markers to obtain genome information of each material
[0075] Enzyme digestion of genomic DNA: Take 250ng of genomic DNA and perform double digestion with EcoR I and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com