Method for treatment of high pH silica brines
一种硅石、盐水的技术,应用在采矿废水处理、水/污水处理、化学仪器和方法等方向,能够解决处置成本上升等问题,达到节省成本的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
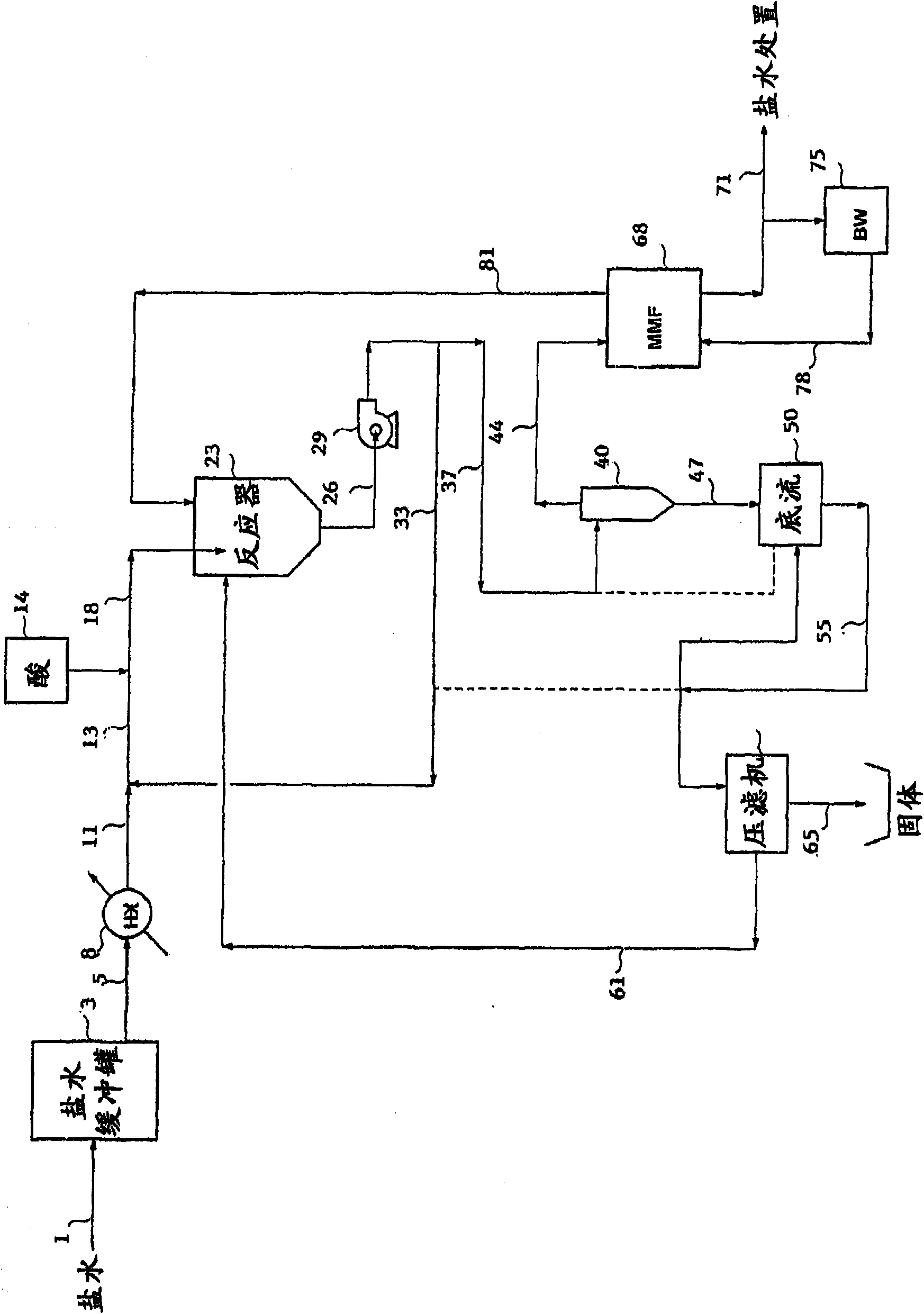
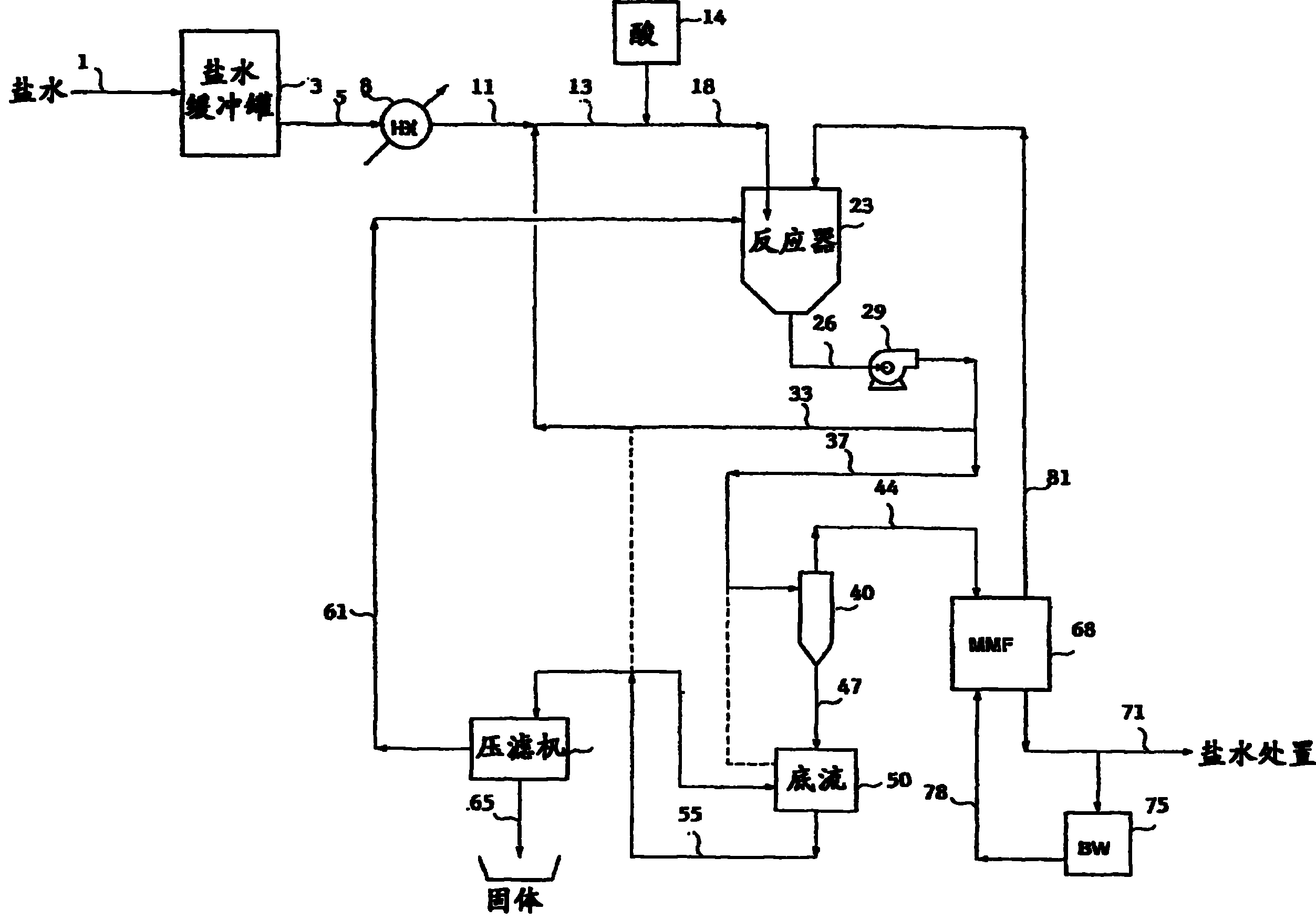
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] At 2% by weight, pH 9, with CaSO 4 2H 2 O (gypsum) conducted the first set of tests. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0046] Table 2
[0047] 70-75℉ and pH 9
[0048]
[0049] These results clearly show that adding a strong acid after the inert matrix has been mixed with the water leads to a significant reduction in dissolved silica content. The centrate sample was clean water, indicating that centrifugation was sufficient to remove even small particles. The supernatant sample showed a moderate amount of turbidity from free colloidal silica particles.
[0050] Another set of experiments was carried out under similar conditions as in Table 2, except that the pH was lowered to 7. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0051] table 3
[0052] 70-75℉ and pH 7
[0053]
[0054] Compared to Table 2, these results show that pH has minimal effect when the process is carried out at 70-75°F. The foregoing results also show that the choice of acid to be used has no...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Another series of experiments was performed to determine the effect of inert seed particles on silica reduction results by neutralizing the brine in the absence of inert seeds. The results are given in Table 6.
[0068] Table 6
[0069] Silica Precipitation Without Inert Substrate
[0070]
[0071] These results are very similar to those obtained with inert seeds at the temperature and pH employed previously, demonstrating the efficacy of the pH neutralization process. However, during this set of experiments, the amount of suspended silica particles in the different supernatants was significantly greater than that observed in the previous experiments. This set of experiments is also representative of current attempts at various sites to lower brine pH and utilize highly agitated reactors to remove silica from brine streams. The superimposed silica is broken up by agitation to produce fine discrete particles that require coagulants and flocculants to increase parti...
Embodiment 3
[0073] As a cross-check, another set of experiments was performed utilizing a chemical analysis scheme based on input chemical kinetics and ion speciation using an ion association model. The outputs of the temperature and pH based programs are given in Table 7.
[0074] Table 7
[0075] Silica precipitation using ionic species formation
[0076]
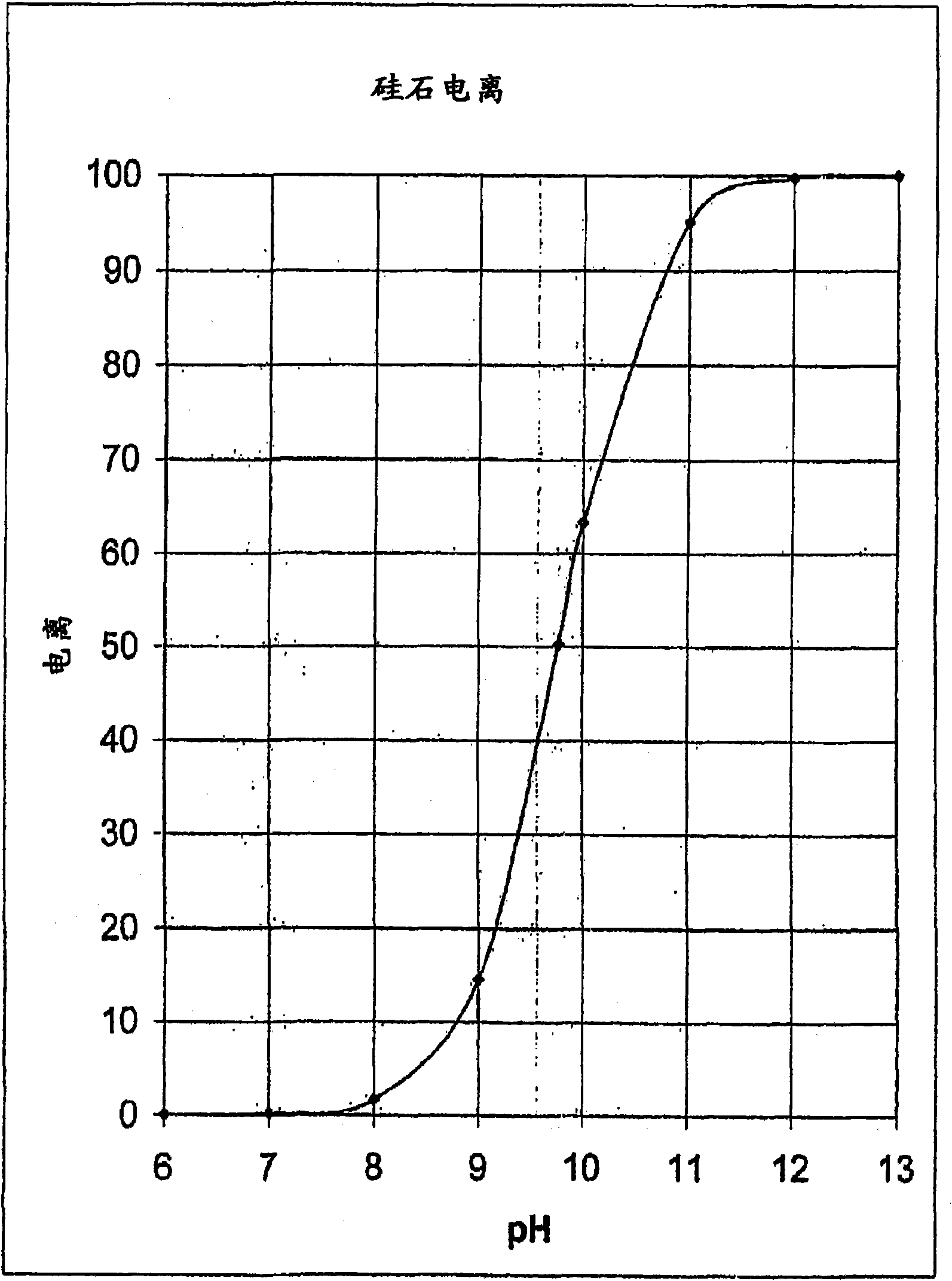
[0077] The results of the analytical analysis indicated the reduction in soluble silica that can be expected given the pH and temperature of the process. It can be seen that the endpoint pH becomes the driving force for the silica reduction and that although a temperature effect participates in the process, this temperature effect is not to the extent observed when deposition is performed using an inert substrate. This is not an unexpected result, since mathematical models cannot account for superposition effects on water flow.
[0078] The experiments performed were static in that they simulated batch operation. Clear results...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com