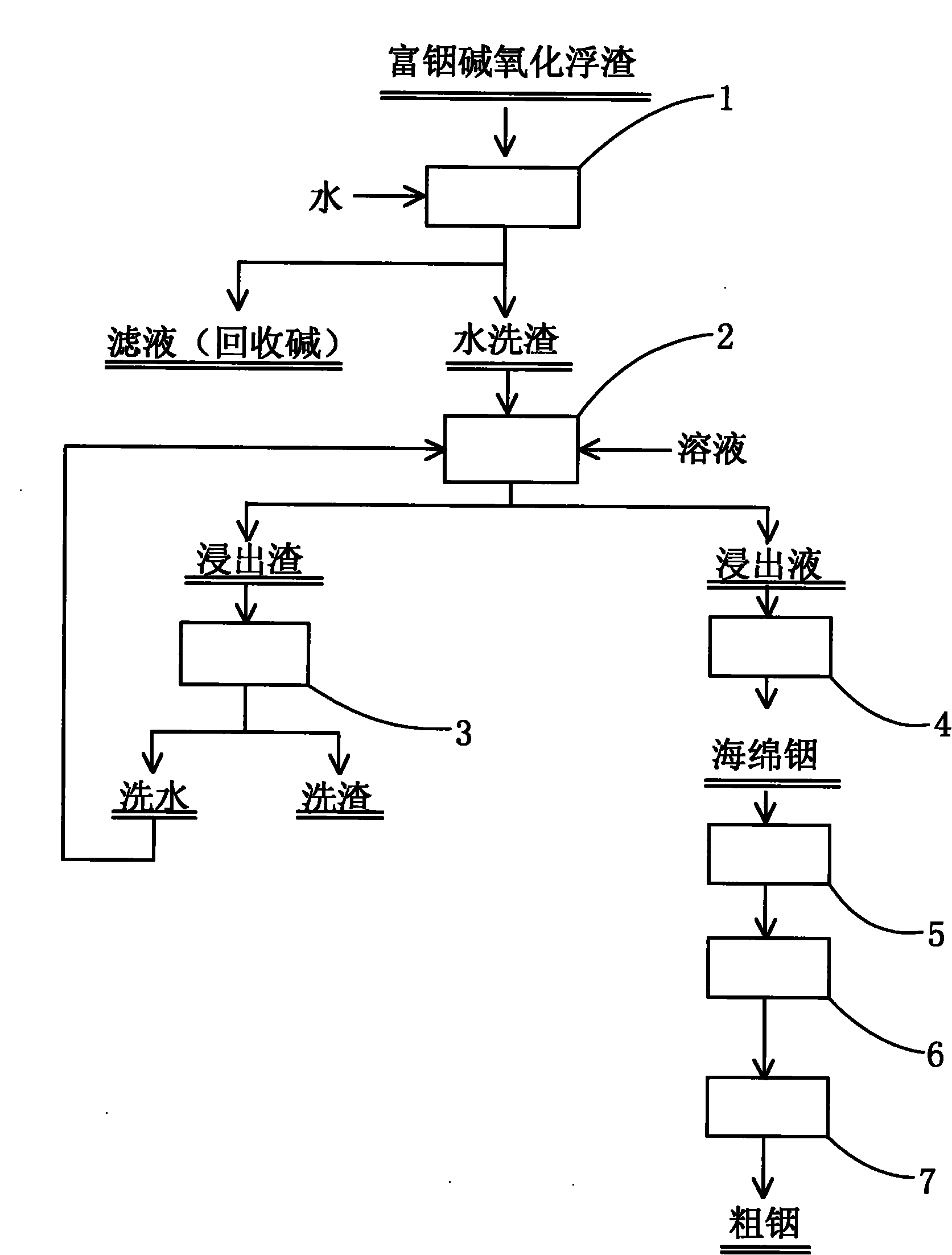
Method for extracting indium from alkali oxidation scum rich in indium
A technology of indium-rich alkali and scum, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of low indium efficiency, and achieve the effects of fast leaching speed, short process flow and high leaching rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Get 500 grams of indium-rich alkali oxidation scum, the mass percent of its composition is: In4.86%, Zn 5.33%, Pb 60.21%, Cu 0.12%, Bi 0.59%, Sb 0.57%, Fe0.20%, Sn 0.12%, the balance is alkalized. The mass ratio of water washing residue and solvent during leaching is 1:5. The concentration of sulfuric acid in the solvent is 6mol / L, and the concentration of chloride (ion) is 0.5mol / L. The leaching temperature is 60-70°C, and the leaching time is 5 hours. Separation by filtration, washing, drying and weighing. It is measured that the mass percentage of indium in the leaching slag is 0.018%, and the leaching rate of indium in the leaching process is 99.70%.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Get 500 grams of indium-rich alkali oxidation scum, the mass percent of its composition is: In5.19%, Zn 2.76%, Pb 62.28%, Cu 0.10%, Bi 0.50%, Sb 0.26%, Fe0.18%, Sn 0.08%, the balance is alkalized. During leaching, the mass ratio of washing residue and solvent is 1:5, the concentration of sulfuric acid in the solvent is 4mol / L, and the concentration of chloride is 1.5mol / L. The leaching temperature is 70-80°C, and the leaching time is 5 hours. Separation by filtration, washing, drying and weighing. It is measured that the mass percentage of indium in the leaching slag is 0.02%, and the leaching rate of indium in the leaching process is 99.69%.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Get 500 grams of indium-rich alkali oxidation scum, the mass percent of its composition is: In8.53%, Zn 1.20%, Pb 58.26%, Cu 0.11%, Bi 0.60%, Sb 0.65%, Fe0.22%, Sn 0.08%, the balance is alkalized. During leaching, the mass ratio of washing residue and solvent is 1:5, the concentration of sulfuric acid in the solvent is 3mol / L, and the concentration of chloride is 2mol / L. The leaching temperature is 80-90°C, and the leaching time is 5 hours. Separation by filtration, washing, drying and weighing. It is measured that the mass percentage of indium in the leaching slag is 0.03%, and the leaching rate of indium in the leaching process is 99.71%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com